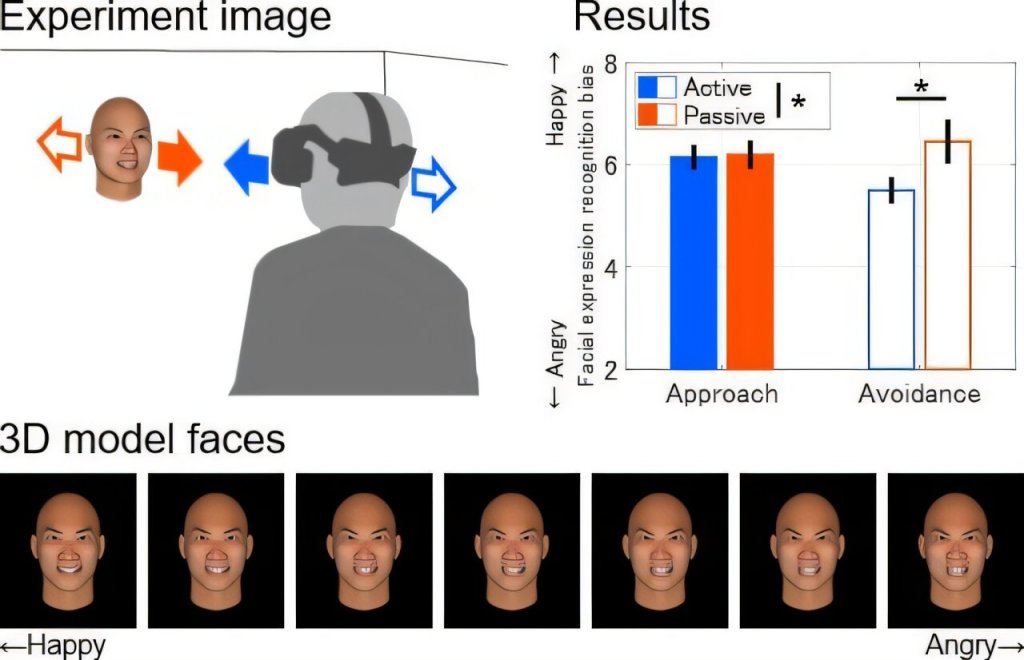
A research team from the Cognitive Neurotechnology Unit and the Visual Perception and Cognition Laboratory at Toyohashi University of Technology has found that approach–avoidance behavior in a virtual reality (VR) environment modulates how individuals recognize facial expressions.
A McGill University-led clinical trial is the first in humans to show online brain training exercises can improve brain networks affecting learning and memory.
A new study reveals that the human brain synchronizes more accurately with rhythm when listening to music than when feeling it through touch. When people tap along to sound, slow rhythmic brain waves align with the perceived beat, helping maintain steady timing.
Psilocybin could be the future of mental health care, with promising findings emerging from Australia’s first research trial using psychedelics to treat depression.
An international research team led by a University of Ottawa Faculty of Medicine investigator has revealed intricate details about how nerve signals activate at the neuromuscular junction. This specialized synapse connects motor neurons to skeletal muscle fibers.
A ‘digital twin’ of your brain could predict mental health issues and slow cognitive decline.
A study published in Environment International concludes that air pollution during pregnancy is associated with slower brain maturation in newborns. It is the first study to analyze brain development within the first month of life.
A new clinical trial is investigating how advanced brain monitoring could improve the diagnosis and management of epilepsy.
University of California San Diego of Medicine researchers, in collaboration with the genetic testing company 23andMe, have identified regions of the human genome associated with cannabis use, uncovering new relationships with psychiatric, cognitive and physical health.
The conditions where you live may influence your brain health and risk for dementia, according to a new study.
Women are affected by severe depression twice as often as men. The reasons for this have not yet been fully clarified. One potential factor is sex-specific differences in the blood-brain barrier. Scientists are conducting research on the project “Leaky blood-brain barrier in major depressive disorder.” A particular focus is on sex-specific differences.
New research reveals how uniquely wired human brains can perceive the world in strikingly similar ways.
A new study published in Scientific Reports indicates that amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and multiple sclerosis (MS) have an extremely high geographic association, even after controlling for race, gender, wealth, latitude, and access to neurological health care.
Finally, this week, a ‘ flight simulator‘ for the brain reveals how we learn—and why minds sometimes go off course.
