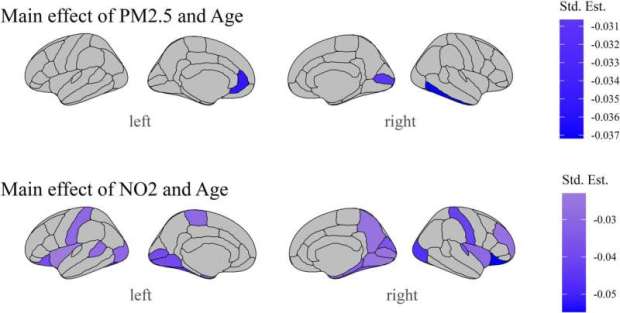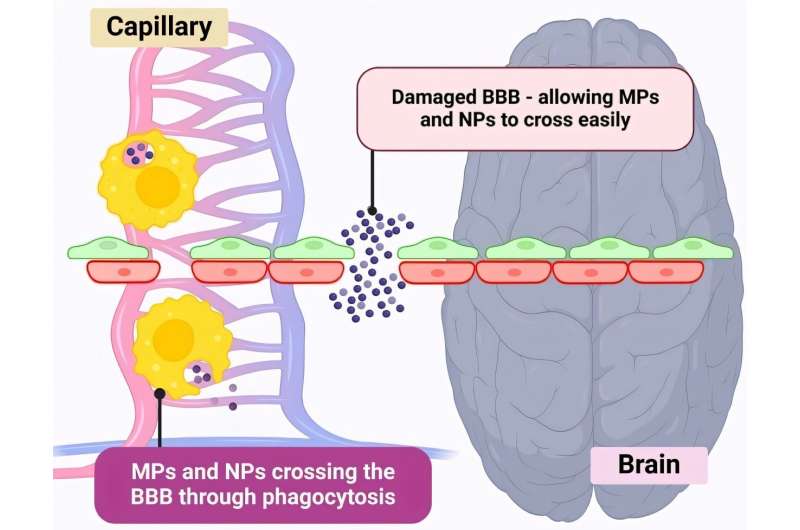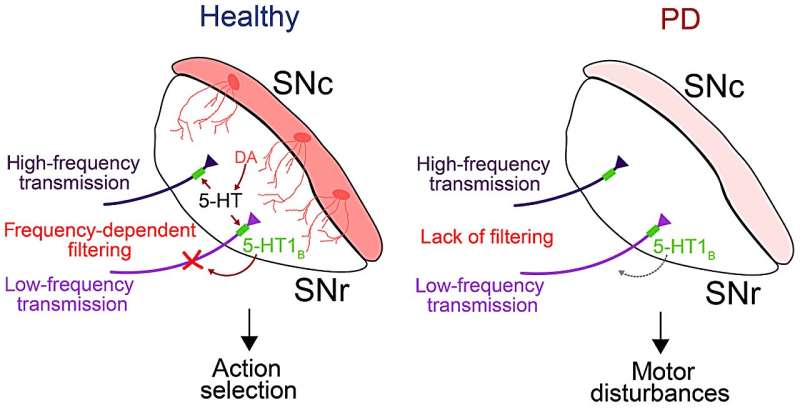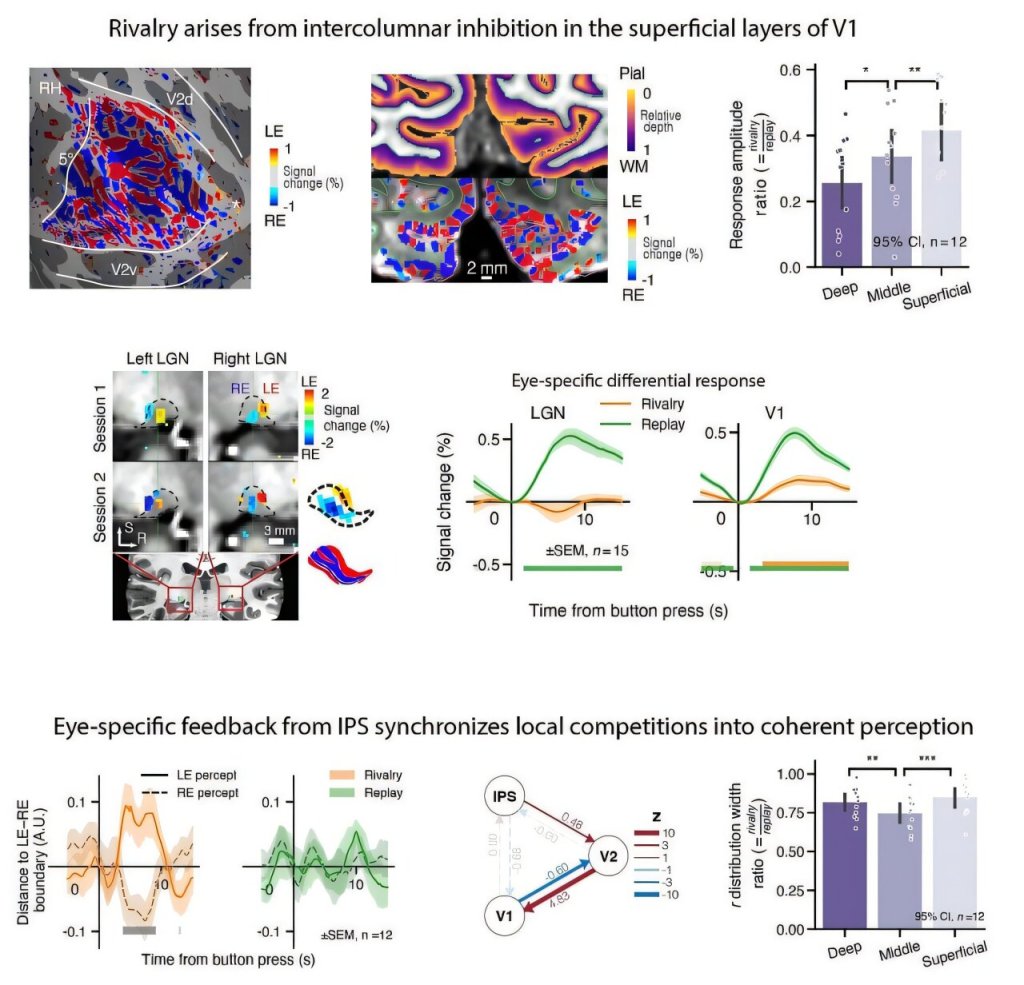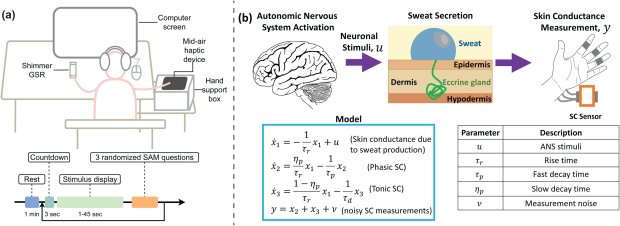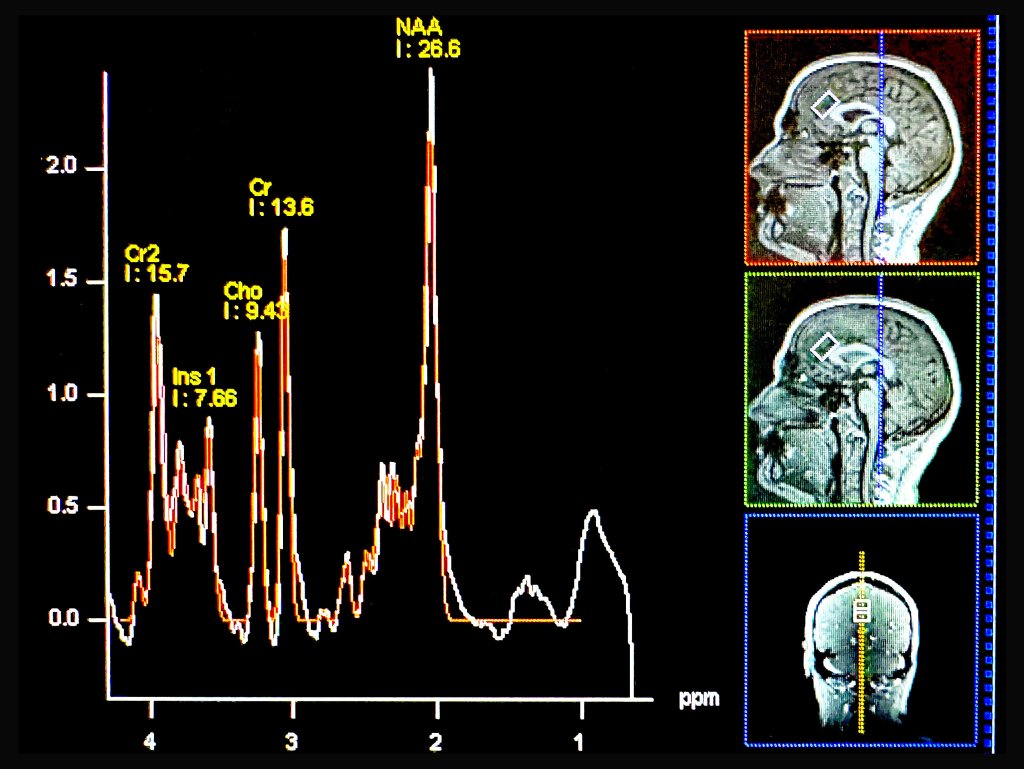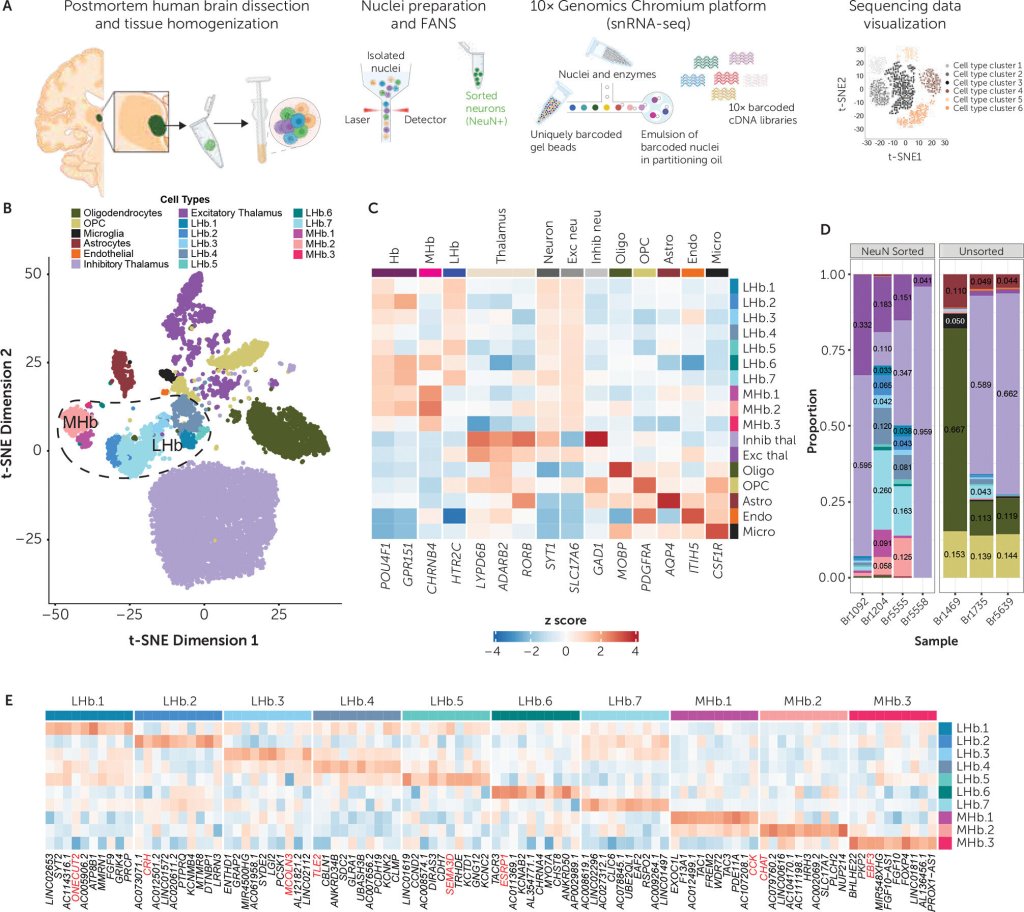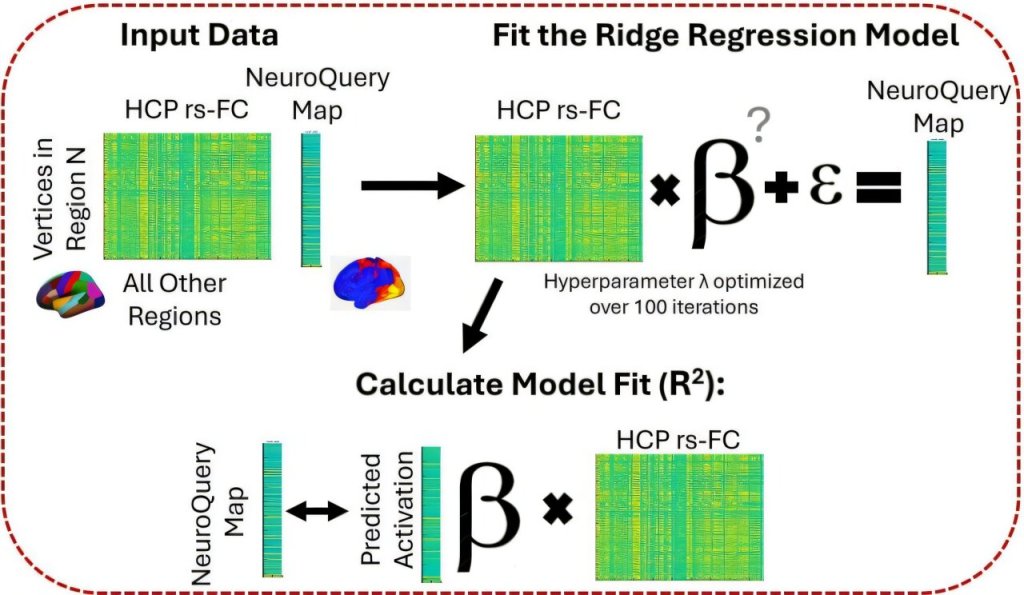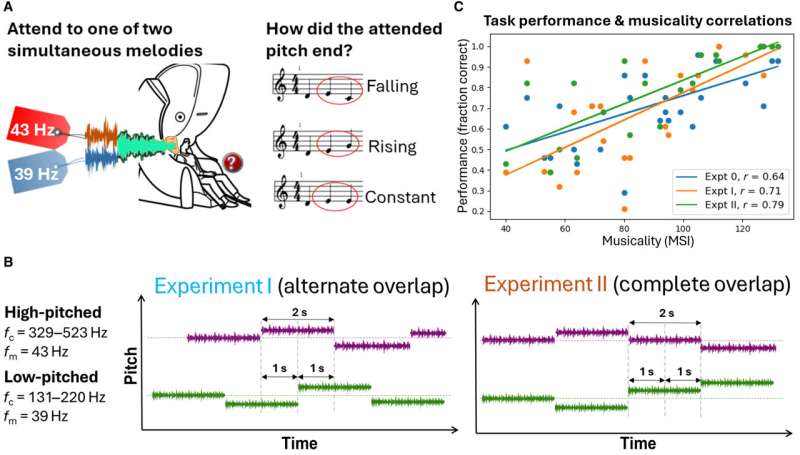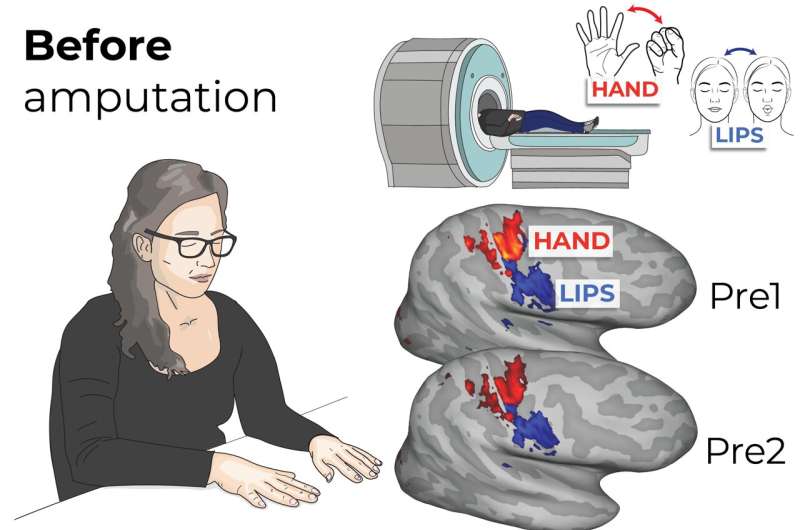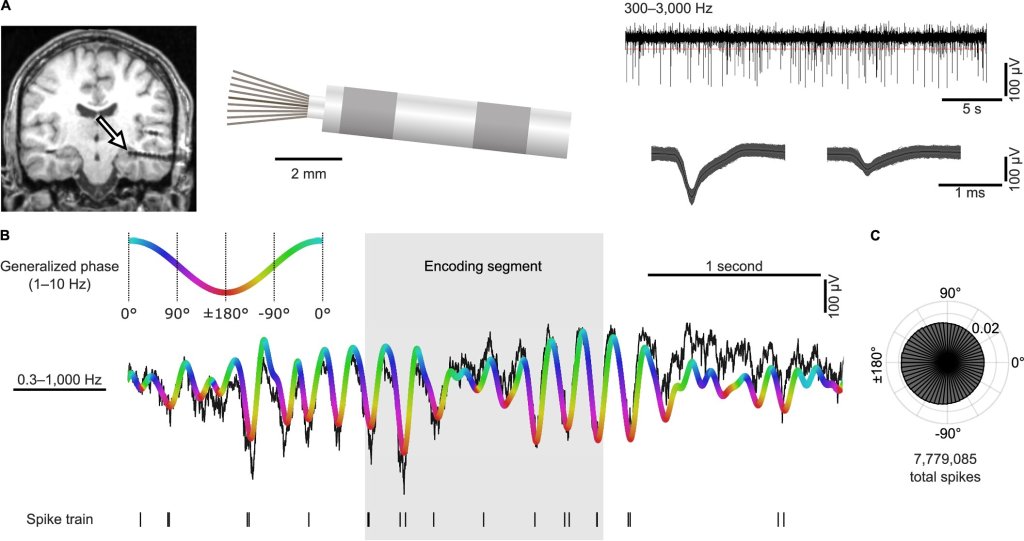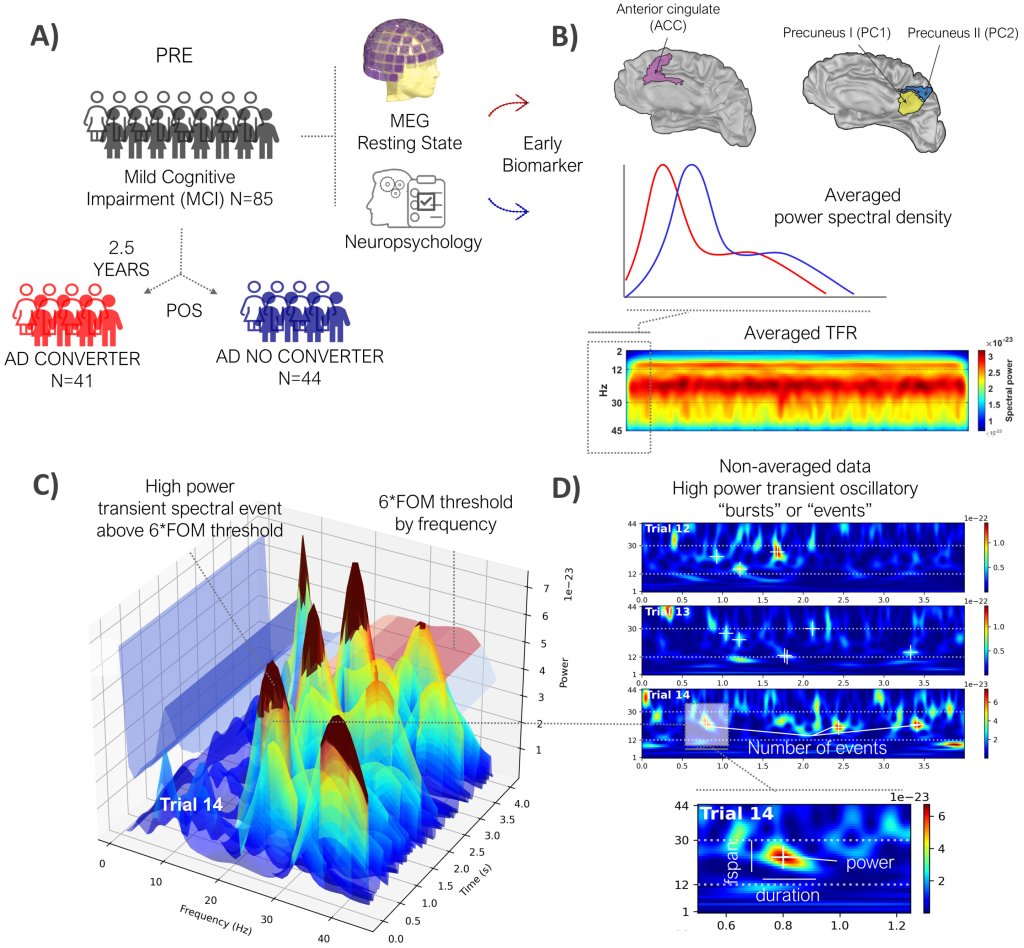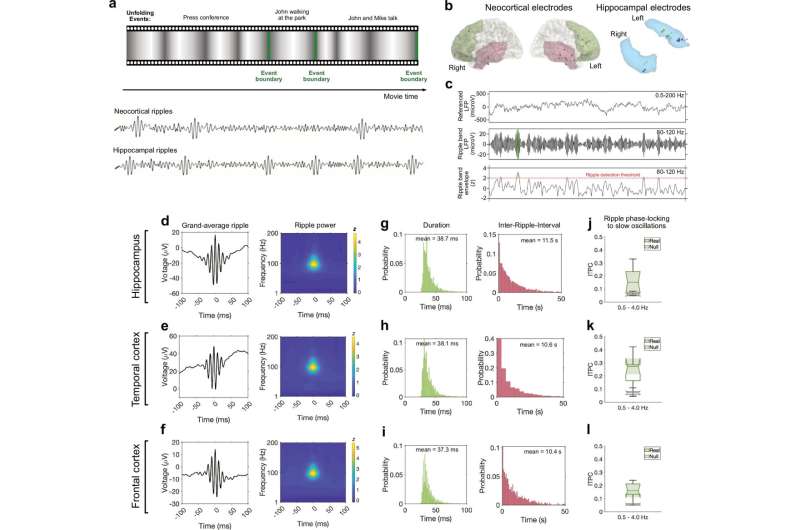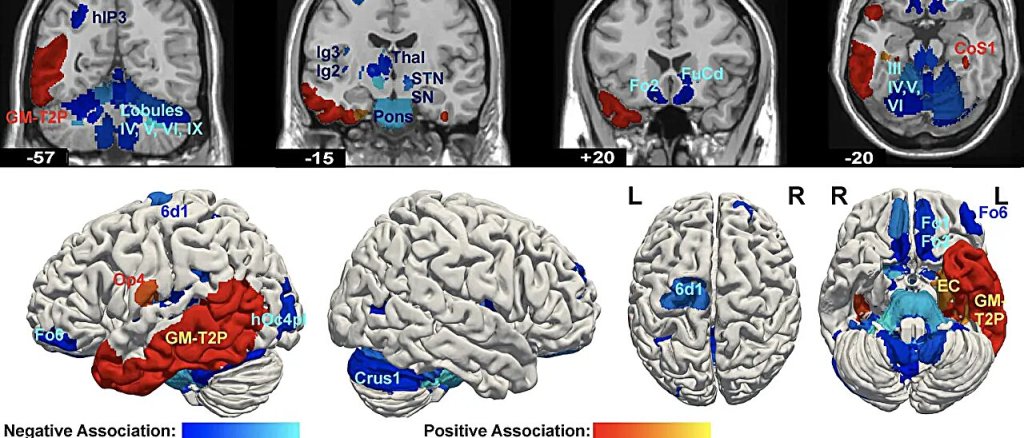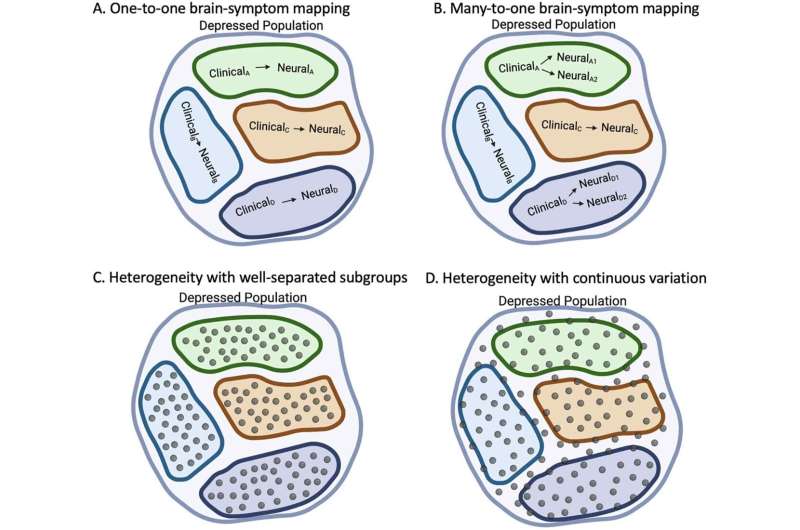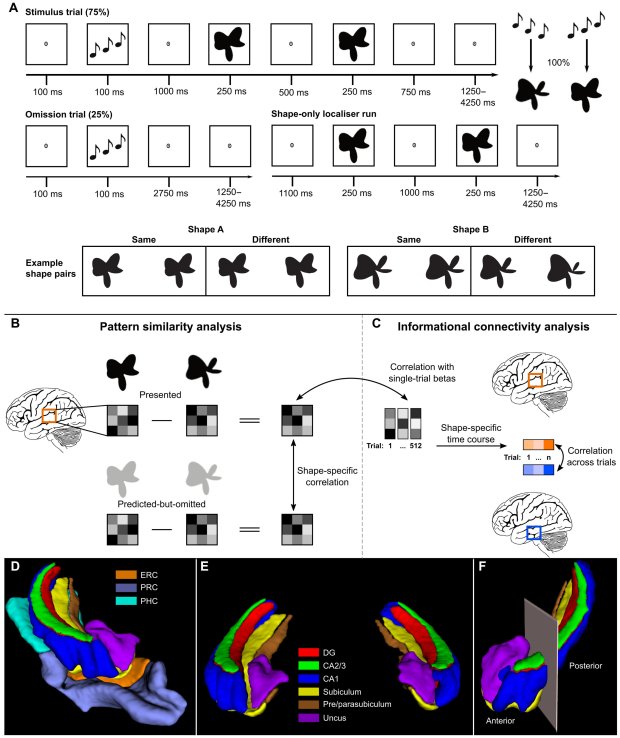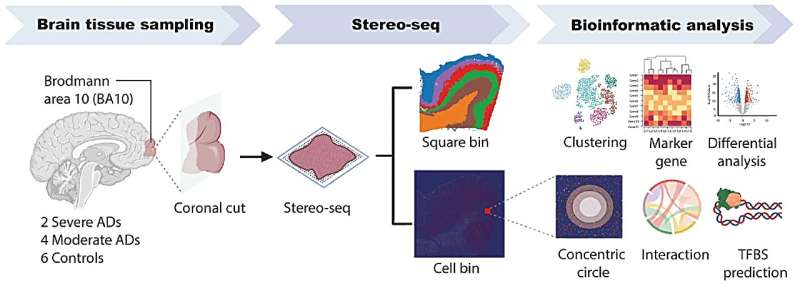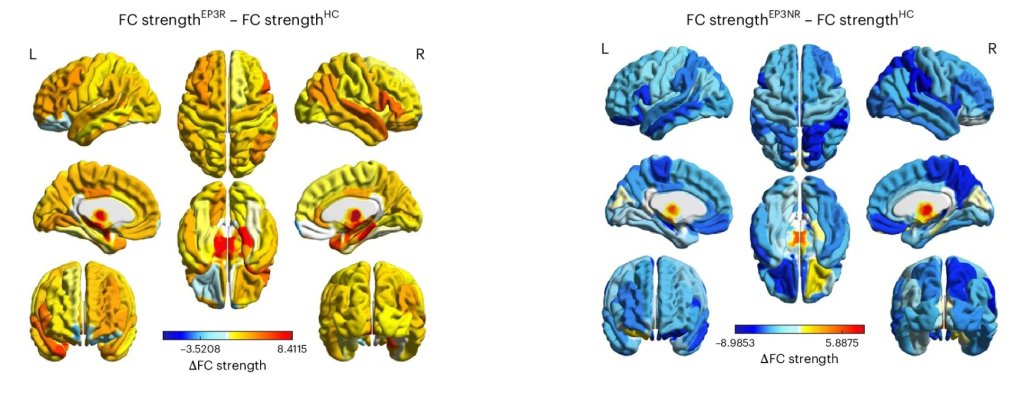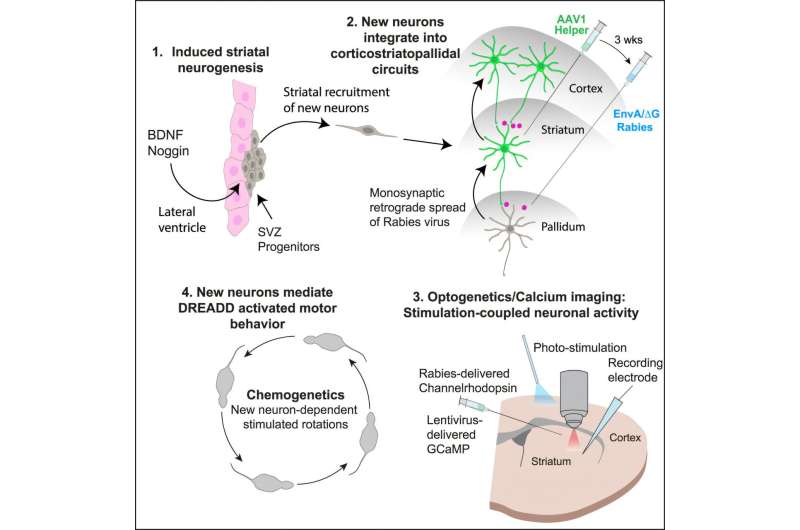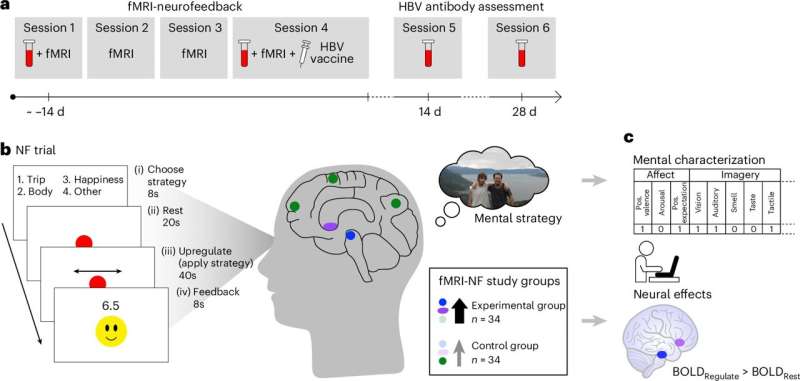
Training people to activate a part of the brain linked to reward and positive expectations may be associated with an increase in the body’s immune response to a vaccine. The findings from a study involving 85 participants, published in Nature Medicine, suggest that positive thinking might help the brain support the immune system in a noninvasive way.
A new study shows that even a short afternoon nap can help the brain recover and improve its ability to learn.
After receiving evidence-based early interventions, roughly two-thirds of non-speaking children with autism speak single words, and approximately half develop more complex language, according to a new study. The findings, published in the Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, offer vital insights into improving success rates for children who remain non-speaking or minimally speaking after therapy.
A newly developed AI computational models that predict the degeneration of neural networks in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
Researchers have determined that a measure of brain complexity, derived from magnetic stimulation and EEG, can effectively evaluate the integrity of conscious processing in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. The findings offer a new potential metric for tracking disease progression.
People with obesity and high blood pressure may face a higher risk of dementia, according to a new study published in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
A new doctoral dissertation shows that gambling disorder is linked to brain networks involved in self-control and brain reward functions. By combining several brain imaging methods, the research provides new biological insight into the disorder and may point to promising directions for treatment development.
Researchers have proposed a neuroscience framework explaining how different types of motivation fundamentally reshape what and how the brain remembers.
Scientists have examined episodic and semantic memory, combining task based and fMRI data and have shown that there is no difference in neural activity between successful semantic and episodic retrieval.
Research by an interdisciplinary team from McGill University and Université Laval provides new insights into the links between social factors and cognitive health among aging adults. While previous research had found positive correlations between specific measures of social connectedness and a variety of health outcomes, this study appears to have been the first to create profiles aggregating multiple social factors and to see how those correlated with cognitive health in older adults, the researchers said.
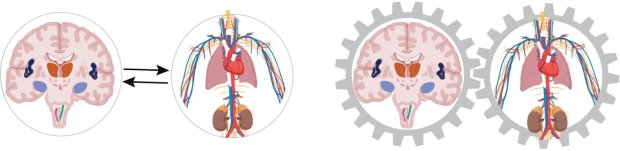
A new study finds that heart attacks involve not just the heart but also the brain and the immune system, revealing a more complex interplay between these critical bodily systems than previously understood.
UCLA Health researchers have created a comprehensive map showing how eight different genetic mutations associated with autism spectrum disorder affect early brain development, providing new insights into the ways diverse genetic causes may lead to shared features and symptoms of the disorder.
The effect of obesity on brain health may depend not only on how much fat is in the body, but also on the areas of the body where fat is stored, according to a study published in Radiology.
A new study published in the journal Brain, Behavior and Immunity has found that people who have had a stroke have fewer of a specific type of immune cell called B cells, which normally produce antibodies to fight off infections. Researchers reviewed 21 clinical trials involving more than 2,100 adults, comparing cannabis-based medicines with placebo over periods of two to 26 weeks.
A research team of has succeeded in identifying biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease in its earliest stages, before extensive brain damage has occurred. The biological processes leave measurable traces in the blood, but only for a limited period.
New research suggests that a person’s overall physical and mental abilities, known as intrinsic capacity, may help predict future cognitive decline.
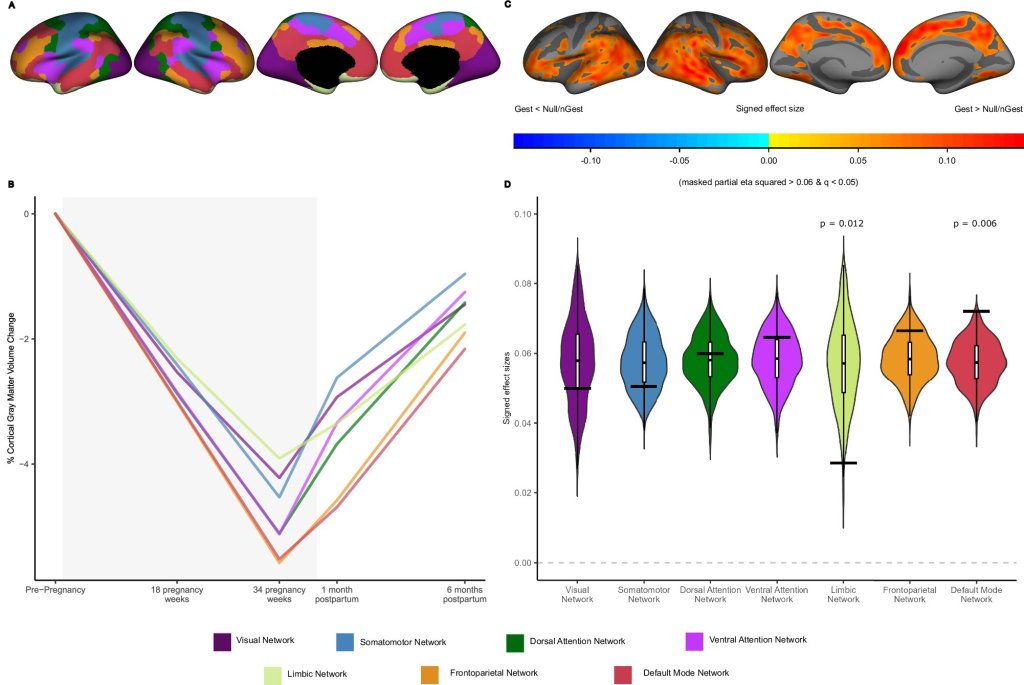
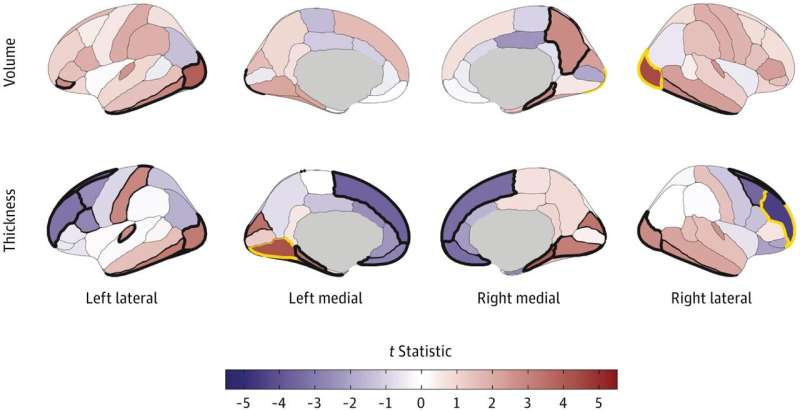
Menopause is linked to reductions in gray matter volume in key brain regions as well as increased levels of anxiety and depression and difficulties with sleep, according to new research from the University of Cambridge. The study, published in Psychological Medicine, found that hormone replacement therapy (HRT) does not appear to mitigate these effects, though it can slow the decline in reaction times.
People exposed to wildfire smoke have a higher risk of suffering a stroke, according to research published in the European Heart Journal.
Researchers have characterized how cellular senescence—where aging cells change their function—is linked to human brain structure in development and late life. This intriguing connection has significant implications, revealing that senescent cells may play a role in the neurodegenerative processes associated with aging, potentially influencing cognitive decline and various age-related diseases.
Finally this week, a new study has found that for people with moderate hearing loss, being prescribed hearing aids had little impact on cognitive test scores.