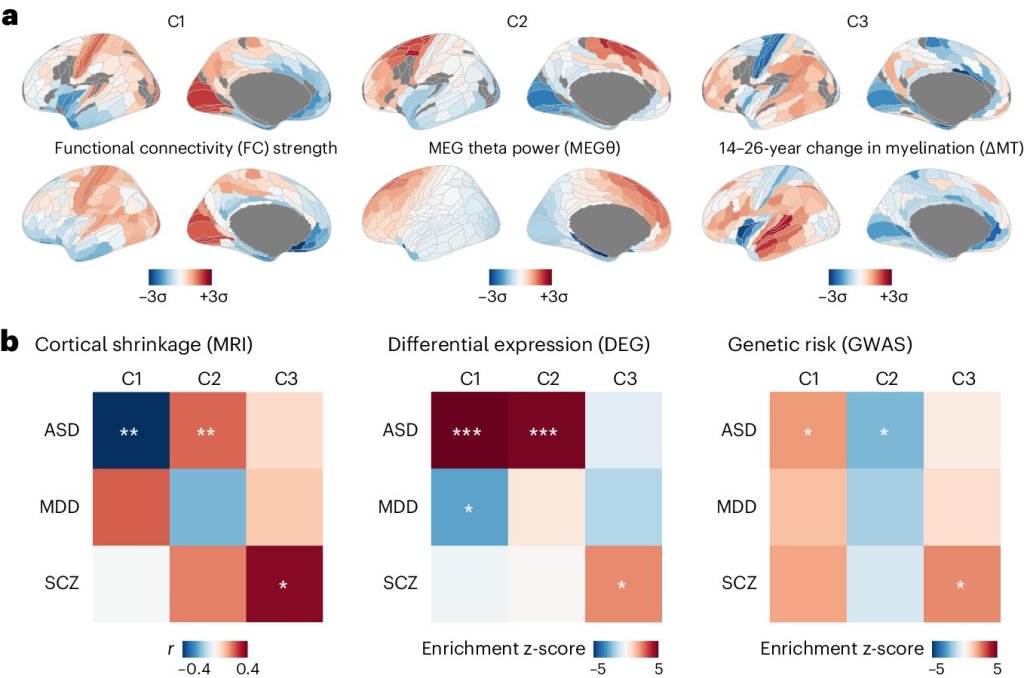
Researchers at University of Cambridge and other institutes worldwide recently carried out a study that linked gene expression in healthy brains to the imaging, transcriptomics and genetics of autism spectrum disorder and schizophrenia. Their paper, published in Nature Neuroscience, unveiled three distinct spatial patterns of cortical gene expression each with specific associations to autism and schizophrenia
A study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology suggests that physical activity may reduce cardiovascular disease risk by lowering stress-related brain activity.
A team of researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and Yale University incorporated generative artificial intelligence (AI) to create a foundational model for brain activity. The Brain Language Model (BrainLM) was developed to model the brain in silico and to determine how brain activities are related to human behavior and brain diseases.
Using MRI, engineers have found a way to detect light deep in the brain.
Stressful life events, such as the death of a loved one or divorce, put a person at greater risk of developing dementia in later life, a recent study has found. But only if the stressful event happened in childhood or midlife.
Our brains process odours differently depending on the names assigned to them, according to new research.
People with neurological disease have a greater chance of death after contracting COVID-19, according to a new study. The research also confirms a higher risk of developing new neurological disorders after COVID infection.
Children who experience chronic lack of sleep from infancy may be at increased risk of developing psychosis in early adulthood, new research shows.
A team of brain specialists at the California Institute of Technology has developed a brain–computer interface approach to decode words “spoken” entirely in the brain by recording signals from individual neurons in real time.
A new study shows that the cerebellum is involved in processing emotions, with implications for ataxia care.
A research team has revealed the link between the frequency of sleep apnea events during the rapid-eye-movement stage and the severity of verbal memory impairment in older adults at risk for Alzheimer’s disease. Verbal memory refers to the cognitive ability to retain and recall information presented through spoken words or written text and is particularly vulnerable to Alzheimer’s.
Results from a recent neuroplasticity study show how singing rehabilitates speech production in post-stroke aphasia.
For the first time, researchers have succeeded in explaining the propagation of traveling waves of activity in the human brain using a computer simulation. Previous studies indicate that these waves are important for various cognitive functions such as memory.
A new publication in Scientific Reports unveils a promising non-opioid pain treatment.
Repeated blows to the heads of football players can damage the small blood vessels of the brain, according to research by scientists who believe this damage may contribute to brain dysfunction in some athletes years after play has ended.
New research has shed light in the complex interplay between cell proteins, and how they impact on neurons in neurodevelopmental disorders and Alzheimer’s disease.
Artificial intelligence (AI) computer programs that process MRI results show differences in how the brains of men and women are organized at a cellular level, a new study shows. These variations were spotted in white matter, tissue primarily located in the human brain’s innermost layer, which fosters communication between regions.
Finally, this week, climate change, and its effects on weather patterns and adverse weather events is likely to negatively affect the health of people with brain conditions.
