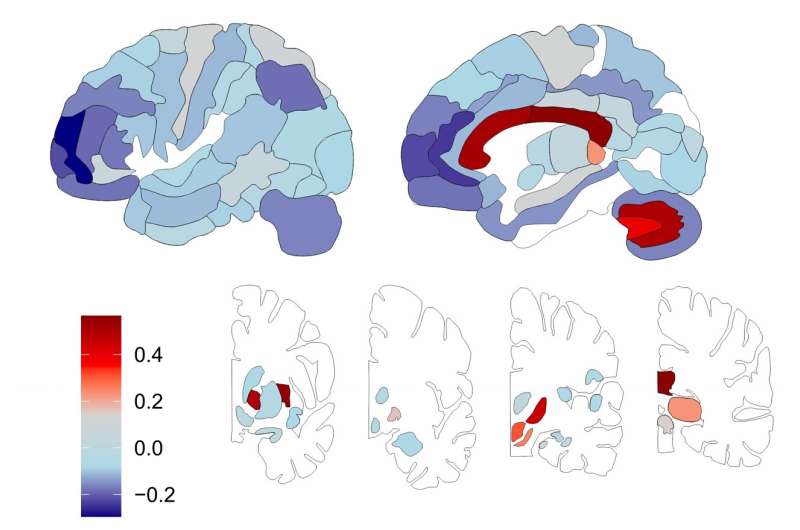
Scientists have found that 93% of the lipids in brain tissue are distributed differently in the white and gray matter, the subcortex, the visual and motor cortices, and the prefrontal cortex, which is responsible for decision-making, social behavior, and other functions.
Researchers have shown how glial cells are reprogrammed into neurons via epigenetic modifications.
Young adults who have higher levels of inflammation, which is associated with obesity, physical inactivity, chronic illness, stress and smoking, may experience reduced cognitive function in midlife, a new study has found.
A paper recently published in Nature Communications advances our understanding of how the brain responds to emotionally charged objects and scenes.
A new study finds that higher inflammation in young adulthood is associated with reduced cognitive function in midlife. Inflammation due to factors like obesity and smoking can impact memory and processing speed. This link, previously noted in older adults, now extends to early adulthood, suggesting long-term brain health effects. Reducing inflammation through lifestyle changes may help prevent cognitive decline.
Researchers have discovered why migraines are often one-sided, revealing that proteins released during aura are carried to pain-signaling nerves via cerebrospinal fluid.
A recent study has pinpointed brain regions associated with mood fluctuations and pleasure responses in bipolar disorder. The findings revealed that people with bipolar disorder show heightened activity in the ventral striatum during rewards, explaining extreme mood shifts.
In groundbreaking research, scientists have determined the structure of molecules within a human brain affected by Alzheimer’s disease.
A global research team has discovered a gene whose variants potentially cause neurodevelopmental disorders (NDDs) in hundreds of thousands of people across the world. The findings published in Nature, are an exciting first step towards the development of future treatments for the disorders which have devastating impacts on learning, behavior, speech, and movement.
A longitudinal study has found that high-intensity interval exercise improves brain function in older adults for up to five years.
A new research collaboration has harnessed a powerful machine learning model to predict concussion status in patients.
A new study shows that human biases in handedness and visual field processing have social and cognitive implications. Researchers found that people with a reversed bias (left hand, right visual) are more likely to have social difficulties and conditions like autism or ADHD.
A recent study sheds light on how the brain adapts hearing in different listening situations.
Finally this week, a study investigating the effect of sleep on brain performance has found a link between an individual’s preference for morning or evening activity and their brain function, suggesting that self-declared “night owls” generally tend to have higher cognitive scores.
