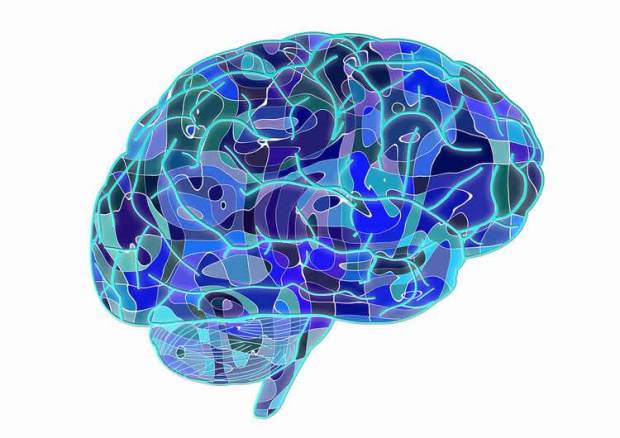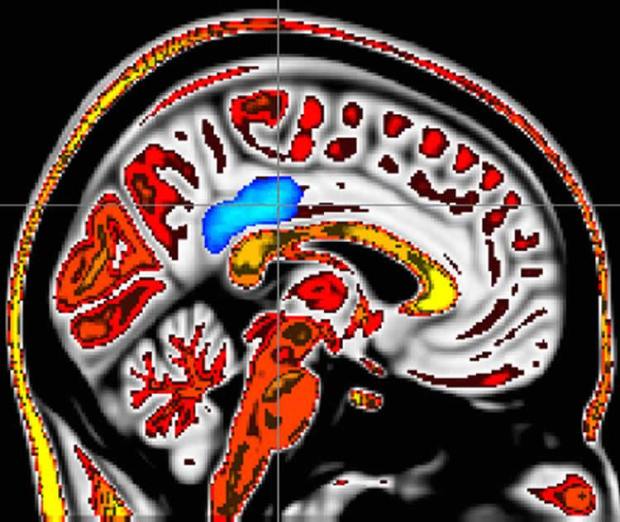
Whole brain analyses revealed that higher dispositional mindfulness during painful heat was associated with greater deactivation of a brain region called the posterior cingulate cortex, a central neural node of the default mode network. Further, in those that reported higher pain, there was greater activation of this critically important brain region. image is credited to Zeidan et al.
Ever wonder why some people seem to feel less pain than others? A new study may have found one of the answers – mindfulness.
Researchers at the Kavli Institute for Systems Neuroscience in Norway in have discovered a network of brain cells that express our sense of time within experiences and memories.
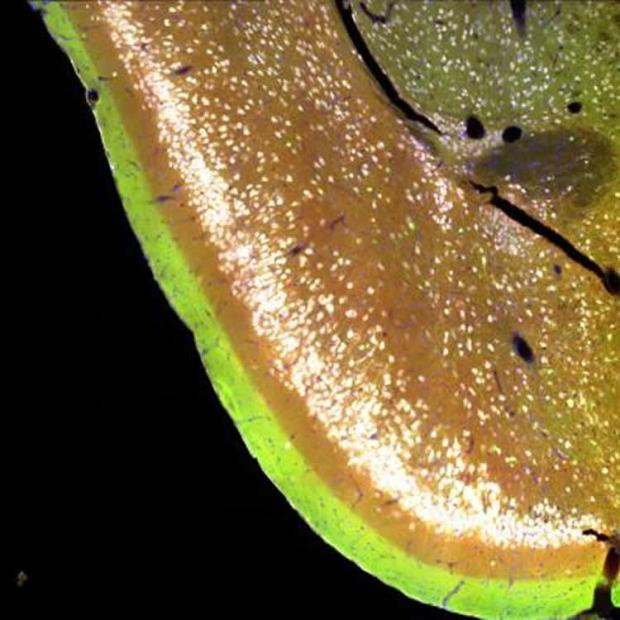
A new study reveals elevated glial activation in the brains of those with fibromyalgia.
Brains of baby boys born prematurely are affected differently and more severely than premature infant girls’ brains. This is according to a study published in the Springer Nature-branded journal Pediatric Research.
According to researchers, the speed at which a person speaks influences the way we hear and understand upcoming words.
A new study reports under conditions of stress, KCNB1 builds up in the brain, before becoming toxic and promoting the production of amyloid beta. In Alzheimer’s patients, the KCNB1 levels are higher than in those without the condition.
Researchers report pyramidal neurons in the basolateral amygdala help us to recognize and categorize foods.
A new study sheds additional light on how the brain consolidates memory during sleep. Researchers report rapid fluctuations in gamma band activity in the hippocampus during nREM sleep helps facilitate memory reactivation.
Finally this week, researchers report on how the brain learns to recognize an individual face, regardless of where it appears in different visual locations.

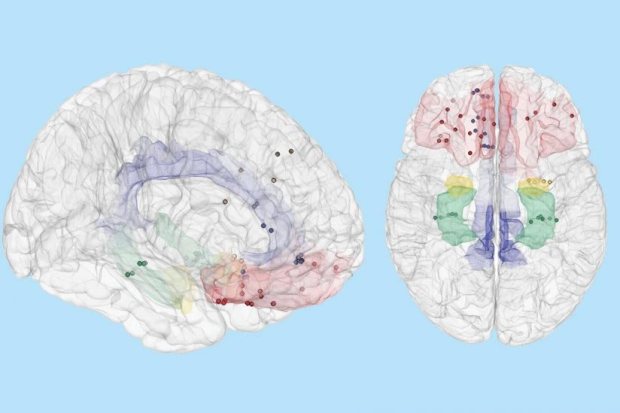


 Researchers have discovered differences in the
Researchers have discovered differences in the 
 Researchers say
Researchers say 