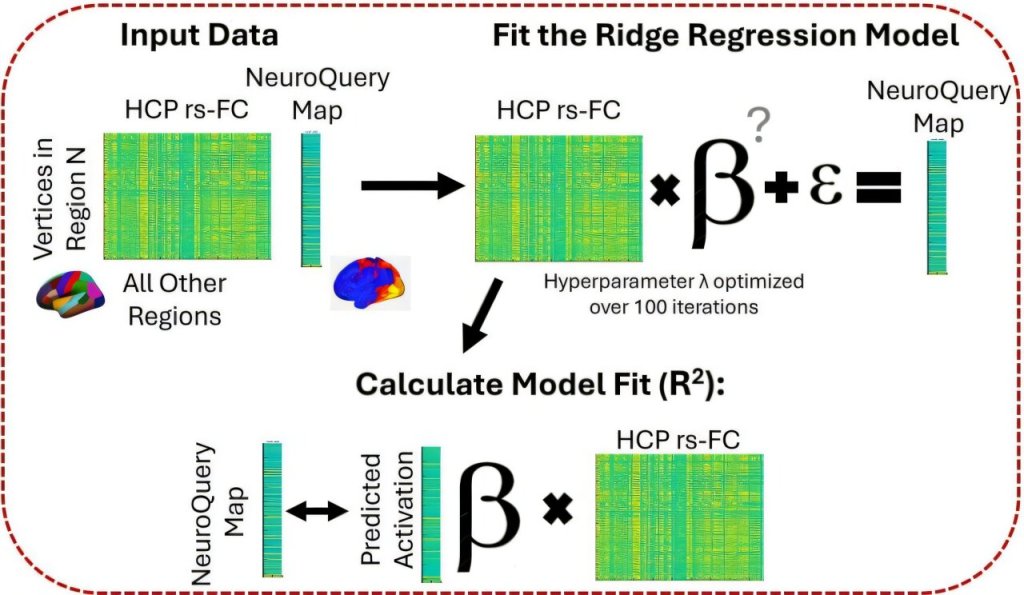
A new study provides the best evidence to date that the connection patterns between various parts of the human brain can tell scientists the specialized functions of each region.
Researchers have discovered that problems with the brain’s waste-clearing system—the glymphatic system—may significantly raise the risk of developing dementia. In one of the most extensive studies to date, MRI data from 40,000 adults revealed that impaired cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flow predicts dementia risk years before symptoms appear.
Statins might help protect the brain function of breast and lymphoma cancer patients for up to 2 years after their cancer treatment, according to a report in JAMA Network Open.
A study published in the journal Music and Medicine demonstrates that intraoperative music therapy significantly reduces the amount of propofol and fentanyl required during laparoscopic cholecystectomy performed under general anaesthesia. Patients exposed to therapeutic music also experienced smoother awakenings and lower physiological stress, as measured by decreased perioperative cortisol levels.
Scientists have used next-generation imaging technology to discover that when the brain is falling asleep, it shows a coordinated shift in activity.
A research team has conducted one of the most comprehensive studies on dopamine and decision-making in humans so far, providing evidence for effects of the former on the latter. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter involved in several functions, including motivation and reward.
Newly decoded brain circuits make memories more stable as part of learning, according to a new study.
Brain scans from American football players reveal subtle differences in the brain’s outer grooves when compared to scans from otherwise healthy men who never played contact or collision sports, a new study shows. Its authors say the findings could potentially predict which people are more at risk of chronic traumatic encephalopathy.
Researchers have uncovered an unexpected molecular partnership that reshapes understanding of how brain inflammation arises in Alzheimer’s disease.
Even when blood pressure is well controlled, older adults whose blood pressure fluctuates widely from one heartbeat to the next may be at greater risk for brain shrinkage and nerve cell injury, according to a recent study.
Finally, this week, new research suggests that a child’s gut microbiome at age 2 may influence their emotional health years later.
