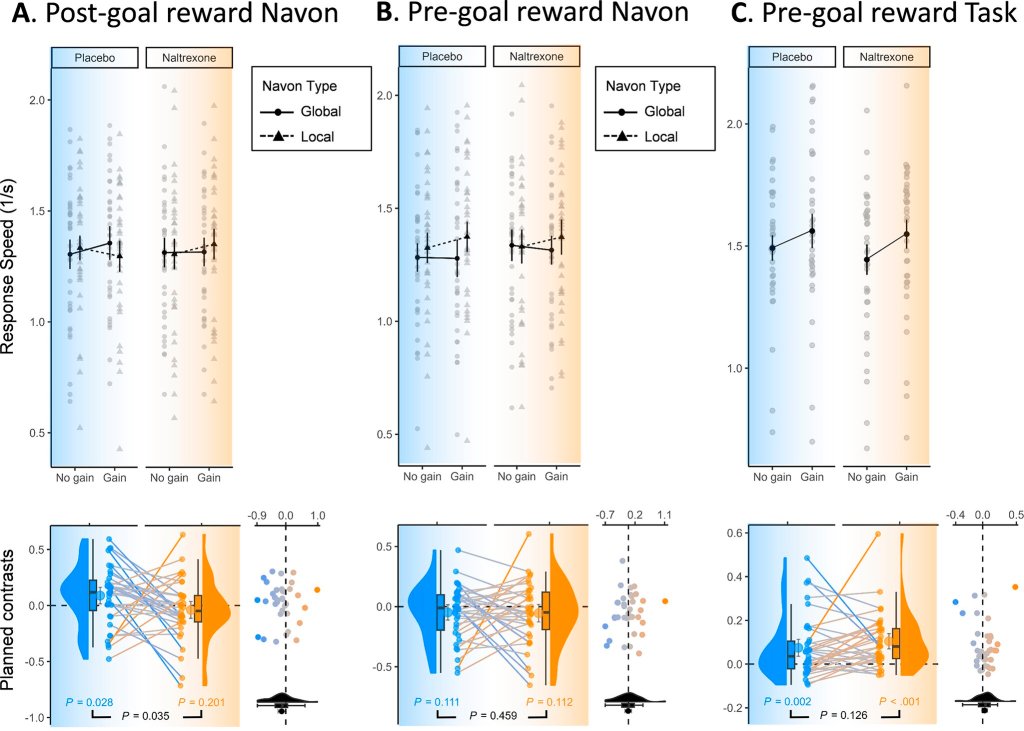
Feeling good doesn’t just lift our mood—it also helps us stay flexible and resilient. A study by an international team of neuroscientists shows that natural brain opioids released after rewards play a key role in broadening attention, offering fresh insights into stress, cognition, and well-being.
A ground-breaking study has shown that ALS may actually be an autoimmune disease.
Engaging in creative experiences, such as music, dance, visual arts, and even specific video games, can slow brain aging and promote healthier brain function, according to a new international study by the Global Brain Health Institute (GBHI), published in Nature Communications.
Can your brain attune itself to a foreign language before you’re born? A team of neuropsychology researchers has found that it can.
A new study reveals that the brain’s social perception pathway—a network that processes faces, gaze, and speech—is already active at birth or shortly thereafter. Using advanced imaging data, researchers showed that newborns exhibit robust connectivity in regions responsible for visual and social processing.
Scientists have discovered why mental maps tend to fade with age.
A new study has identified five distinct “sleep-biopsychosocial” profiles that connect how we sleep with our brain networks, mental health, cognition, and lifestyle. Using data from over 700 participants, researchers found that different sleep patterns—ranging from poor quality to resilience and short duration—each showed unique neural connectivity patterns.
A large-scale international study has revealed that autism diagnosed in early childhood is genetically and developmentally distinct from autism diagnosed later in life.
Scientists have developed a new mathematical model of memory that explores how information is encoded and stored. Their analysis suggests that memory works best in a seven-dimensional conceptual space — equivalent to having seven senses. The finding implies that both humans and AI might benefit from broader sensory inputs to optimize learning and recall.
Researchers have identified a rare type of brain cell that may drive the chronic inflammation and neurodegeneration seen in progressive multiple sclerosis (MS).
A new study shows that bullying activates distress pathways in the brain within seconds. Tweens and adults who viewed first-person bullying videos displayed heightened activity in social and emotional brain networks, alongside strong autonomic threat responses.
New research sheds light on the mechanisms by which humans can isolate and focus on individual sounds in noisy environments.
Scientists have revealed that intentional memory control—deciding what to remember or forget—is more potent than emotional influence when forming long-term memories. Participants were more likely to recall words they were told to remember than those carrying emotional weight, even though emotion sometimes strengthened recall or caused false memories.
Finally, this week, a new study reveals how the brain organizes and directs its slowest activity.
