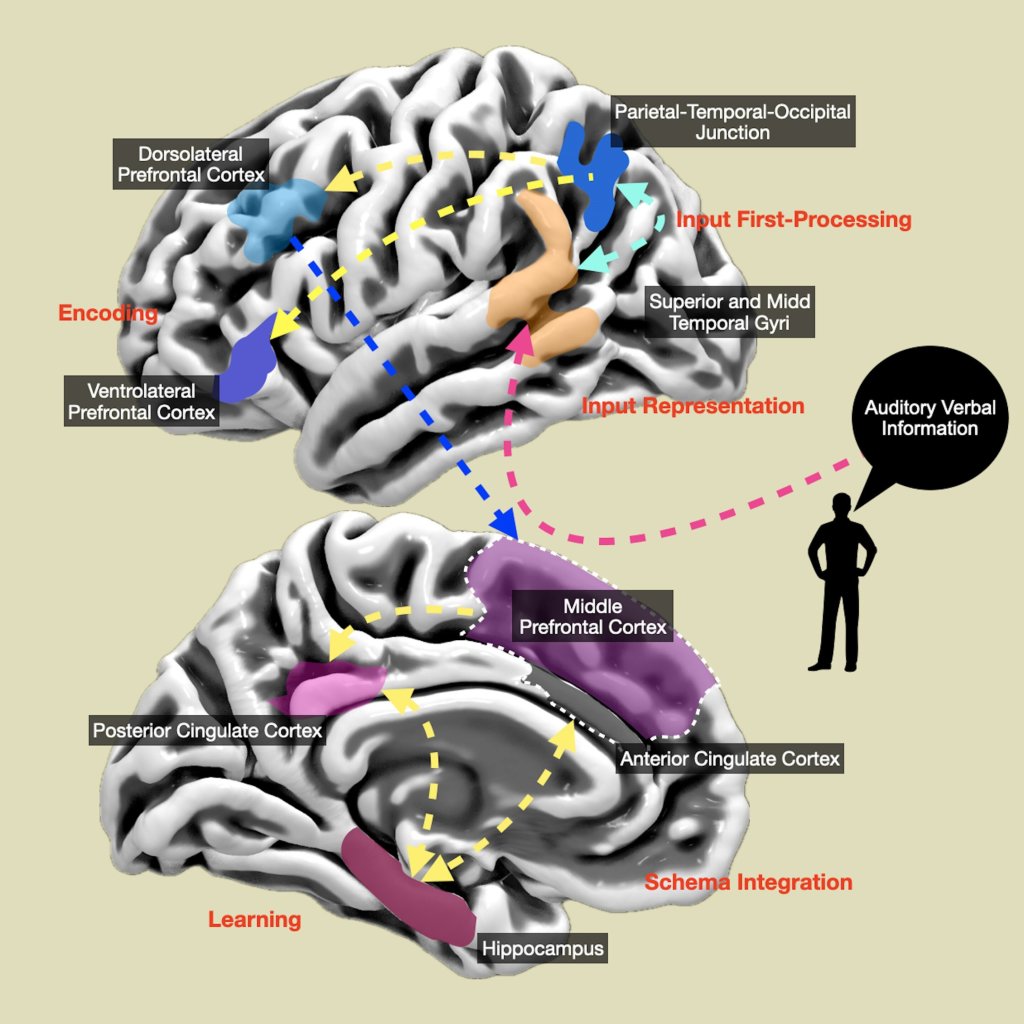
The parts of the brain that are needed to remember words, and how these are affected by a common form of epilepsy, have been identified by a team of neurologists and neurosurgeons.
New research published in PLOS ONE, reveals that witnessing trauma triggers unique brain changes, distinct from those caused by experiencing trauma firsthand. The study is the first to shed light on the molecular differences between directly acquired PTSD and bystander PTSD and could pave the way for changes in how the disorders are treated.
Scientists have discovered that neural changes in teens may predict how decision-making and behavioural control develop.
A new study shows that the rubber hand illusion can reduce the intensity of pain caused by heat. Researchers found that when participants viewed a rubber hand being illuminated while their hidden hand received a heat stimulus, they reported feeling less pain. This suggests that integrating visual and sensory cues can influence pain perception. The findings may one day help develop new treatments for chronic pain conditions such as complex regional pain syndrome.
Verbal fluency, the ability to recall and use vocabulary, is the strongest cognitive predictor of longevity in a 20-year study of elderly adults. This suggests a link between linguistic ability and overall health.
Neuroscientists have discovered a way to control how much zinc is released to specific locations in the brain. The essential mineral plays a major role in the brain’s function, including improving memory and lessening symptoms of some neurological disorders, but getting the right amount to the right place is key.
According to new research, inflammation inside and outside the brain may contribute to neurological complications in COVID-19.
A study published in the British Journal of Psychiatry has found that nearly half of people diagnosed with depression don’t respond to multiple antidepressant medications and are considered “treatment-resistant.” The study found that 48% of patients whose electronic health care records reported a diagnosis of depression had tried at least two antidepressants, and 37% had tried four or more different options.
Scientists have developed a computational framework that maps how the brain processes speech during real-world conversations.
For children with autism who severely injure themselves, a pilot study suggests that deep brain stimulation (DBS) of the brain’s reward centre (nucleus accumbens) is a safe and possible treatment that could be beneficial, especially when behavioural therapies don’t work.
New research suggests that factors present in the placenta during pregnancy might play a role in increasing the risk of a child developing schizophrenia.
Scientists at Peking University have used a new method to discover that dopamine helps protect and control the function of a protein called Tau. This finding helps us better understand how dopamine works normally and in diseases of the brain.
A research team has uncovered the neural mechanisms underlying the processing of pain and itch in the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC).
A new study finds that women in their 80s who develop increasing daytime sleepiness over five years are twice as likely to develop dementia. Researchers tracked 733 women without cognitive impairment, using wrist devices to monitor sleep and circadian rhythms. Those who showed stable sleep patterns had the lowest dementia risk, while those with increasing sleepiness faced the highest risk. Surprisingly, declining nighttime sleep was not significantly linked to dementia risk.
A research team has developed an electrode capable of safely encasing nerves without causing damage.
Finally this week, new research shows that even 12-month-old babies can form memories, as indicated by activity in the hippocampus. This challenges the idea that infants can’t remember and suggests that infantile amnesia (not remembering early childhood) might be because we can’t access those memories later, rather than not forming them in the first place.
