A new study has identified neuroanatomical differences in children associated with early substance use initiation.
Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) shows a positive treatment effect and improved quality of life (QoL) among patients with treatment-resistant depression according to two studies published in Brain Stimulation.
A new analysis of U.S. mortality data reveals the disproportionate impact of traumatic brain injuries on older adults, males and certain racial and ethnic groups.
Gender differences define how the human brain ages and telltale biomarkers in the blood may be strongly suggestive of cognitive impairment and dementia, according to a comprehensive new study involving more than 500 people.
Researchers have identified genetic variations in brain cells, particularly microglia and oligodendrocytes, that influence both aging and Alzheimer’s risk.
New research shows that not all brain cells age equally, with certain cells, such as those in the hypothalamus, experiencing more age-related genetic changes. These changes include reduced activity in neuronal circuitry genes and increased activity in immunity-related genes.
A recent study has found that menopause revs up the progression of multiple sclerosis (MS).
Researchers have discovered that pupil size during non-REM sleep correlates with memory consolidation. When pupils contract, the brain focuses on consolidating new memories; when dilated, it processes older ones. This separation prevents “catastrophic forgetting,” allowing the brain to efficiently manage both new and existing knowledge. These findings could lead to better memory enhancement techniques for humans and inspire more efficient artificial neural networks.
A new study shows head trauma may activate latent viruses, leading to neurodegeneration.
A collaborative effort between Mount Sinai and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center has shed valuable light on how monoamine neurotransmitters such as serotonin, dopamine, and now histamine help regulate brain physiology and behavior through chemical bonding of these monoamines to histone proteins, the core DNA-packaging proteins of our cells.
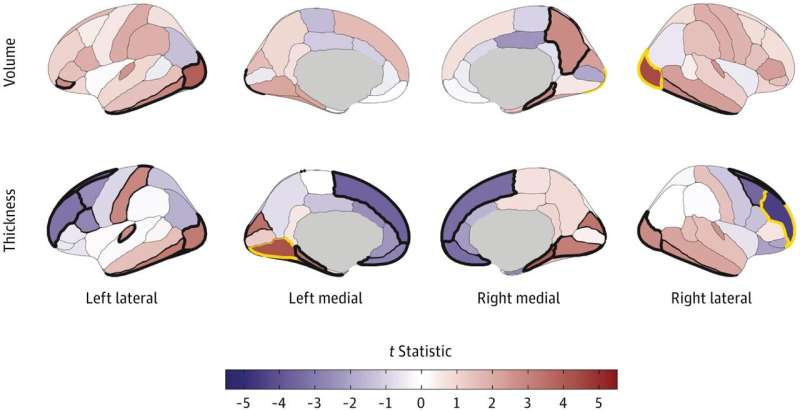
Finally this week, sex differences in brain structure are present from birth, new research shows.
