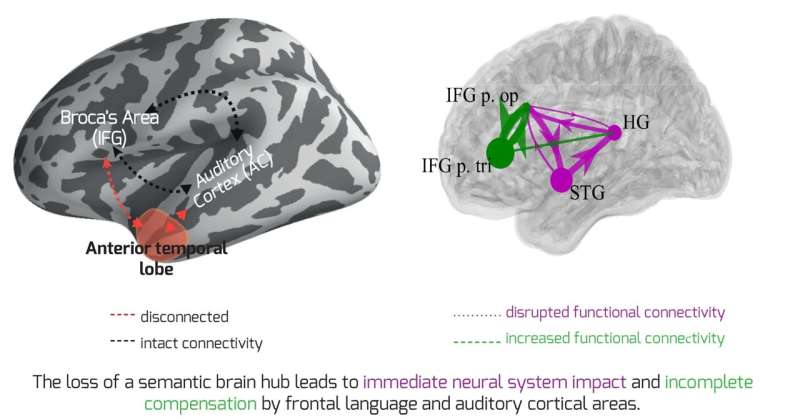
A team of international neuroscientists has obtained the first direct recordings of the human brain in the minutes before and after a brain hub crucial for language meaning was surgically disconnected. The results reveal the importance of brain hubs in neural networks and the remarkable way in which the human brain attempts to compensate when a hub is lost, with immediacy not previously observed.
A new study, published in Cell Reports, describes a novel molecular link between vitamin B12 and multiple sclerosis that takes place in astrocytes—important non-neuronal glial cells in the brain.
Australian researchers have flagged potential concerns over the use of social chatbots, calling for more studies into the impact of AI software on neurodiverse people and those who find human interaction difficult.
An exploratory study has shown that light, regular exercise can improve the cognitive as well as physical health of adults with Down syndrome.
Researchers at Linköping University, Sweden, have examined the brains of 16 patients previously hospitalised for COVID-19 with persisting symptoms. They have found differences in brain tissue structure between patients with persisting symptoms after COVID-19 and healthy people.
Scientists have discovered a new way a ribonucleic acid (RNA) impacts fear-related learning and memory.
Comparing PET scans of more than 90 adults with and without mild cognitive impairment (MCI), researchers say relatively lower levels of the so-called “happiness” chemical, serotonin, in parts of the brain of those with MCI may play a role in memory problems including Alzheimer’s disease.
A new study reveals a significant association between adverse childhood experiences and symptoms of muscle dysmorphia in adolescents and young adults.
Using electrochemical techniques and machine learning, scientists measured dopamine levels in real time during a computer game involving rewards and penalties. The findings shed light on the intricate role of dopamine in human behavior and could have implications for understanding psychiatric and neurological disorders.
Researchers have identified a potential treatment target for a genetic type of epilepsy.
A new study sheds light on the significant role of patients’ beliefs in the effectiveness of neurostimulation treatments for conditions like depression and ADHD. Analyzing five studies, the research team found that patients’ perceptions of receiving real or placebo treatments often had more impact on outcomes than the treatments themselves.
New research has found that smoking causes the brain to shrink and age prematurely, a condition not reversible even after quitting smoking.
Researchers have discovered a key player in alcohol addiction: pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP). This peptide, found in the “bed nucleus of the stria terminalis” (BNST), is linked to heavy alcohol drinking and withdrawal.
Finally this week, new research reveals that moderate exercise improves cognitive performance even under conditions of sleep deprivation and low oxygen levels.