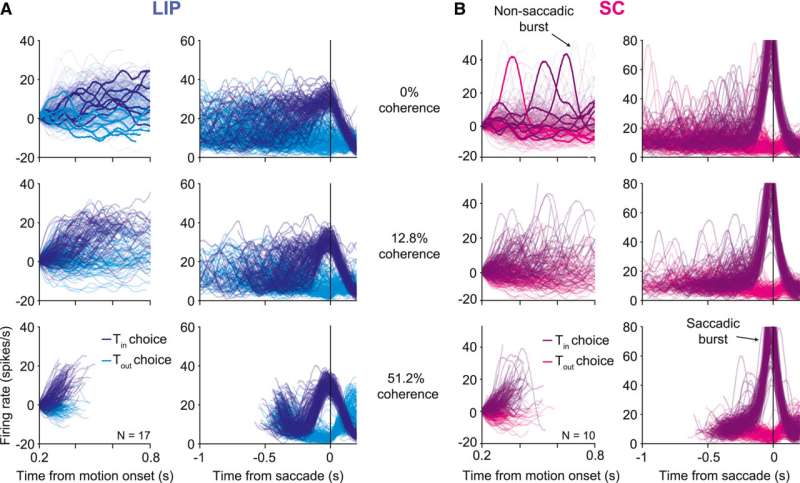
A new paper, published in Neuron, highlights the role of the superior colliculus (SC), a structure in the midbrain, in terminating decisions.
Degeneration of dopaminergic neurons is widely accepted as the first event that leads to Parkinson’s, but a new study suggests that a dysfunction in the neuron’s synapses—the tiny gap across which a neuron can send an impulse to another neuron—leads to deficits in dopamine and precedes the neurodegeneration.
Depression, a challenging condition to diagnose early, may now be detected more promptly using a simple 1-minute Electroencephalogram (EEG) test at home.
Scientists have confirmed that human brains are naturally wired to perform advanced calculations, much like a high-powered computer, to make sense of the world through a process known as Bayesian inference.
New research shows how repeated traumatic brain injury contributes to Alzheimer’s disease.
Racial disparities can be seen in dementia severity, functional impairment, and neuropsychiatric symptoms among patients with frontotemporal dementia (FTD), according to a study recently published in JAMA Neurology.
A new study identifies a potential new approach to PTSD treatment.
Any head injury—even a mild one—raises a person’s risk of later having an ischemic stroke. Having multiple injuries increases that risk, even more so than the severity of a single traumatic brain injury, researchers have found.
New research finds that cerebrospinal fluid net flow is markedly decreased in Huntington’s disease, with the decrease being greater in the later stages of the disease.
The targeted use of ultrasound technology can bring about significant changes in brain function that could pave the way towards treatment of conditions such as depression, addiction, or anxiety, a new study suggests.
Finally this week, new research finds that antidepressants may actually reduce negative memories in individuals suffering from depression while improving overall memory function.
