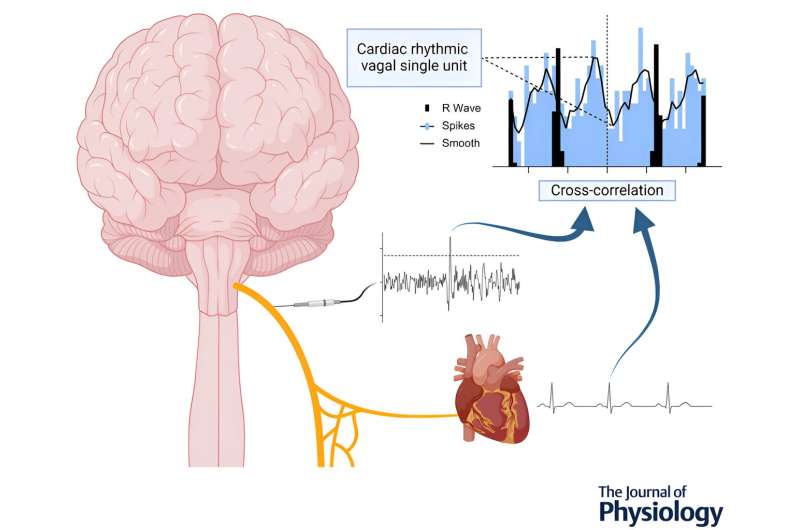
The team that first recorded vagus nerve signals in humans has now isolated the electrical activity of individual neurons responsible for cardiovascular regulation. Published in the Journal of Physiology, the Monash University-led discovery paves the way for more research into how and why cardiovascular disease develops.
New research reveals that dopamine is not directly responsible for the formation of placebo analgesia, contrary to previous beliefs.
Scientists have developed a new brain-mapping tool called START, which combines transcriptomics and viral tracing to map the connections between specific neuronal subtypes with unprecedented detail. This technology allows researchers to identify distinct patterns of connectivity in inhibitory neurons within the cerebral cortex, providing a blueprint of the brain’s circuits.
A new study has demonstrated that emotion enhances memory for contextual details, challenging the view that emotion impairs the ability to remember such information.
Researchers compared the diagnostic accuracy of GPT-4 based ChatGPT and radiologists using 150 brain tumor MRI reports. ChatGPT achieved 73% accuracy, slightly outperforming neuroradiologists (72%) and general radiologists (68%).
Deep brain stimulation may provide immediate improvement in arm and hand strength and function weakened by traumatic brain injury or stroke.
People with Parkinson’s disease (PD) who experience visual hallucinations have reduced brain responses to unexpected visual changes, a marker known as visual mismatch negativity (vMMN). Using EEG, researchers compared brain activity in PD patients with and without hallucinations and discovered that those with hallucinations showed weaker vMMN signals
Lower attention ability in adolescence can predict cigarette and cannabis use in young adulthood, according to new research from Trinity College Dublin.
New research has found that frequent consumption of fizzy drinks and fruit juice significantly increases the risk of stroke. The study, which analyzed data from nearly 27,000 participants across 27 countries, showed a 22% increased risk of stroke from drinking fizzy drinks, with the risk rising further with multiple servings per day. Additionally, drinking more than four cups of coffee daily raised stroke risk by 37%, while tea consumption was associated with a reduced stroke risk.
New research shows that even pollution levels that are below government air-quality standards are associated with differences in children’s brains.
University of Queensland researchers have made a significant step towards enabling women with epilepsy safer access to a common and highly effective anti-seizure medication.
A new study shows that brain synchronization between a neurotypical person and someone with autism is weaker compared to two neurotypical individuals interacting. Using EEG hyperscanning, researchers observed reduced inter-brain synchrony during hand movement imitation between mixed pairs, with autistic individuals more likely to follow than lead.
Certain immune cells play an important role in the early stages of multiple sclerosis, a twin study shows.
New evidence from the Centre for Healthy Brain Ageing indicates that older adults who experience a stroke for the first time will have substantial immediate and accelerated long term-cognitive decline. The new research, published in JAMA Network Open, looked at finding out exactly how a stroke impacts a person’s cognitive abilities.
A new study shows how individual brain cells in the hippocampus respond to pronouns.
Scientists are examining the brains of individuals with asymptomatic Alzheimer’s disease who, despite having amyloid plaque and tau buildup—the primary indicators of Alzheimer’s—did not show diagnosable dementia symptoms while alive. They’ve identified crucial mechanisms that may safeguard against cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease.
Finally this week, In a first-of-its-kind study, University of South Florida researchers are finding that music can help boost cognition in patients undergoing chemotherapy.
