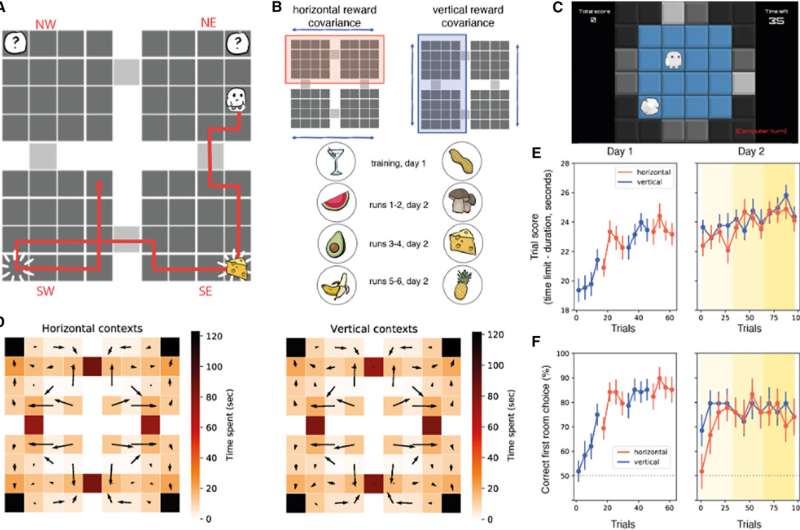
Researchers carried out a study exploring the impact of context on goal-directed decision-making. Their findings, published in Neuron, suggest that goal-seeking ‘compresses’ spatial maps in the hippocampus and orbitofrontal cortices in the brain.
Learning a second language strengthens neural connections in the language network, a new study shows.
A recent review highlights significant advancements in wearable electroencephalogram (EEG) technologies for non-invasive brain-computer interfaces (BCIs). This review is particularly valuable for researchers and clinicians new to BCI applications, offering insights into mainstream wearable non-invasive BCIs and the latest research reports.
New research may create some respite for patients of two medically unexplained fatigue-inducing conditions: myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) and fibromyalgia (FM).
A new study has found that people with obesity who underwent bariatric surgery had stable cognition two years later suggesting that bariatric surgery may mitigate the natural history of cognitive decline expected in people with obesity.
New research has found an association between a reduction in gray matter in the brain and early-onset psychosis.
Researchers have discovered that a protein called phosphorylated α-synuclein, which is associated with several neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s disease and Lewy body dementia, is also involved in the normal processes of how neurons communicate with each other in a healthy brain.
Adults with posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) have smaller cerebellums, according to new research from a brain imaging study.
A recent study published in Molecular Psychiatry has identified previously unknown alterations in neural connectivity that promote psychomotor disturbance—a slowing or reduction in movement—in individuals with major depressive disorder.
Finally this week, new research explores the potential of aesthetic chills, intense emotional responses characterized by shivers and goosebumps, as a novel intervention for depression.
