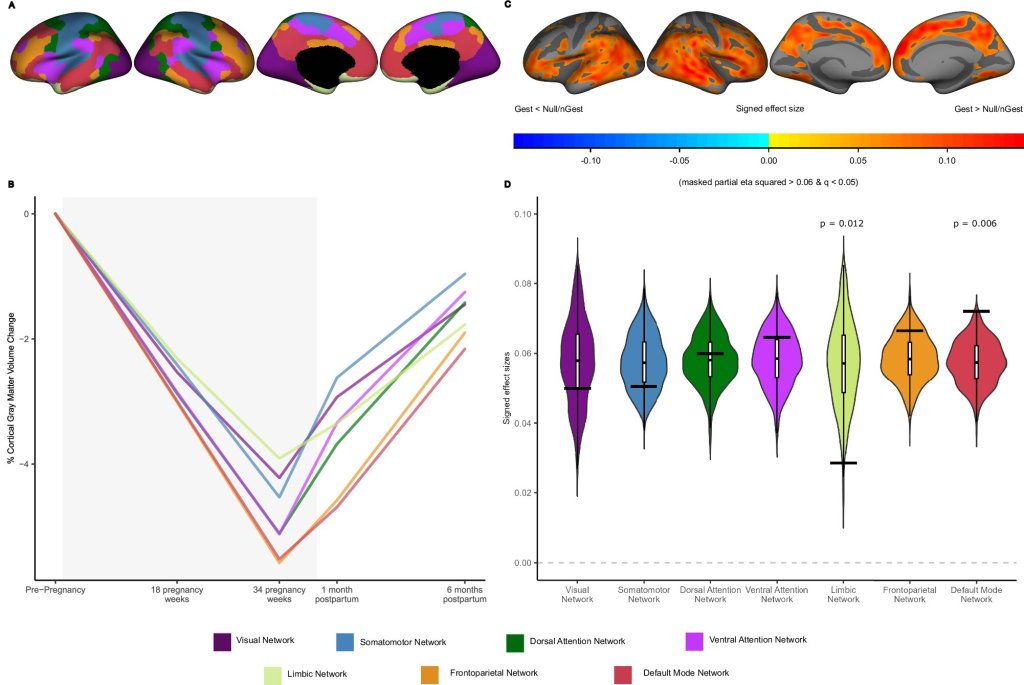
A new study has analyzed the brains of women during pregnancy for the first time using neuroimaging techniques. The research shows that there is a reduction and partial recovery of almost 5% of gray matter in 94% of the total gray matter volume of the brain, especially in regions linked to social cognition.
An international team has shown the relationship of activity of neurotransmitters to how humans process the emotional content of language.
More than half of 23-year-olds in a European study show restrictive, emotional or uncontrolled eating behaviours, according to new research led by the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience (IoPPN) at King’s College London. Structural brain differences appear to play a role in the development of these eating habits.
A new framework links brainwaves to individual cognitive states.
In a recent study, scientists have shown neurotransmitters in the human brain are active during the processing of the emotional content of language, providing new understanding into how people interpret the significance of words.
A new study shows stem cell therapy ‘jump-start’ brain repair after stroke.
Researchers have developed a flexible, biodegradable electrode capable of stimulating neural precursor cells in the brain, offering a safer and more precise alternative for neural repair. The electrode dissolves naturally after seven days, eliminating the need for surgical removal while promoting tissue regeneration.
Music supports babies in neonatal intensive care units, according to a recent neuroimaging study.
A study analyzing data from over 130 million individuals found that antibiotics, antivirals, vaccines, and anti-inflammatory medications are associated with a reduced risk of dementia. This supports the idea that infections and inflammation contribute to dementia and highlights the potential of repurposing existing drugs for prevention or treatment.
New research has uncovered psychological profiles associated with mental and brain health in middle-aged and older adults.
An experimental treatment for depression that triggers seizures with magnets significantly improved mental health in patients without some cognitive effects associated with electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), according to a clinical trial led by UT Southwestern Medical Center.
A research team has gathered new insight into the neural underpinnings of human cooperation.
A new study has identified three psychological profiles that influence brain health, cognitive decline, and dementia risk in aging adults. Profiles with high protective traits, like purpose and openness, show better cognition and brain integrity, while those with low protective traits or high negative traits face accelerated brain atrophy and mental health issues.
Stanford Medicine scientists are generating a periodic table of sorts for psychiatric disorders, providing a better understanding of these conditions and paving the way toward targeted treatment.
A study analyzing data from over 2 million veterans found that GLP-1 receptor agonists, popular weight-loss drugs like Ozempic and Wegovy, provide significant neurological and behavioral health benefits, including reduced risks of addiction, Alzheimer’s, and dementia. However, they also pose risks for pancreatitis and kidney conditions.
Finally, this week, a brain signal that lights up when we anticipate rewards may hold the secret to helping people overcome depression, and researchers are working to unlock its potential.






 What is the point about living our lives?
What is the point about living our lives?