Scientists have identified how depression alters the brain’s response to positive and negative stimuli, particularly in the amygdala, a key emotional processing center. The study found that depression reduces neural activity linked to positive perceptions while increasing it for negative perceptions.
People with atrial fibrillation (AF) who have a stroke could benefit from blood thinning treatments, known as anticoagulants, at an earlier stage than is currently recommended, finds a new study.
Researchers from the University of Oxford have identified a key biochemical mechanism relevant to the development of Huntington’s disease. This discovery opens up the possibility of studying the disease before its clinical onset and eventually stopping its progression.
Childhood attention issues, coupled with genetic predispositions, increase the likelihood of experiencing psychotic-like symptoms in adolescence.
UCLA Health researchers have found that people who experienced discrimination had pro-inflammatory bacteria and gene activity in their gut microbiome that was different from those who did not experience discrimination. The researchers could also predict with 91% accuracy which study participants faced discrimination by only analyzing their gut microbiome using stool samples.
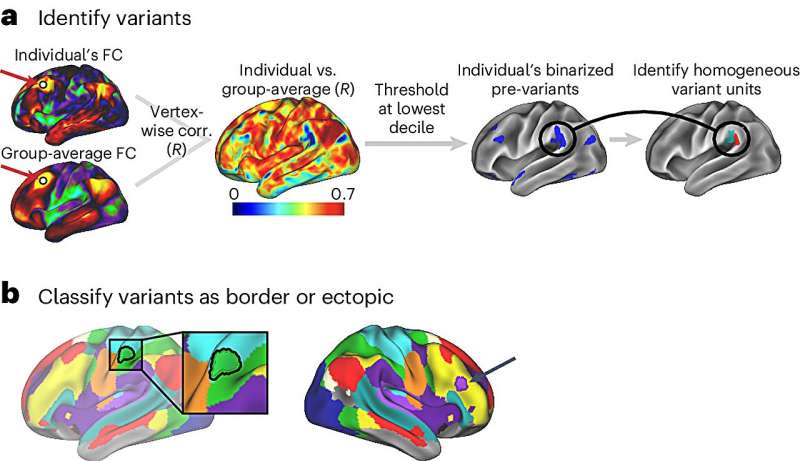
A new study links hundreds of brain proteins to differences in how brain regions communicate, revealing how microscale molecules can influence macroscale brain connectivity.
Lifetime cannabis use is associated with several changes in brain structure and function in later life, suggests an observational study, but these associations may not be causal, finds a genetic analysis of the same data, published in the open access journal BMJ Mental Health. Meanwhile, new research shows that prenatal exposure to cannabis can negatively impact children’s thinking and behavioral skills, including impulse control, attention, and aggression.
A type of therapy that involves applying a magnetic field to both sides of the brain has been shown to be effective at rapidly treating depression in patients for whom standard treatments have been ineffective. The treatment—known as repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS)—involves placing an electromagnetic coil against the scalp to relay a high-frequency magnetic field to the brain.
Scientists have identified new cell clusters in the amygdala for anxiety treatment.
Just one or two sessions of physical activity at the weekend may be just as likely to lower the risk of cognitive decline, which can often precede dementia, as more frequent sessions, concludes research published online in the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
A new study finds a link between genetic markers and neuropathic pain.
Finally this week, ultrasound, once used almost exclusively to take images of the body, is quickly developing into a targeted therapy that can have a potentially life-changing impact on our brains, according to the authors of a new article.