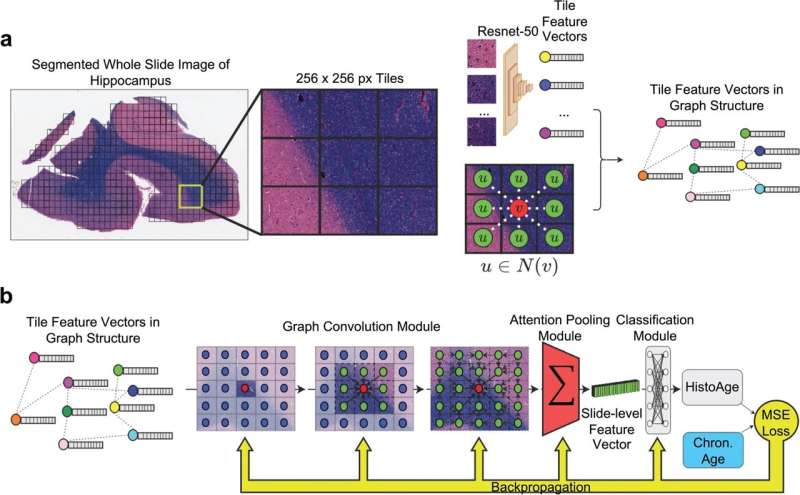
Researchers have, for the first time ever, used AI to develop an algorithm they term “HistoAge” which predicts age at death based on the cellular composition of human brain tissue specimens with an average accuracy of within 5.45 years. This powerful tool can also identify neuroanatomical regions vulnerable to age-related changes, an indicator of potential cognitive diseases.
Scientists have uncovered why night shift work is associated with changes in appetite. The findings could help the millions of people who work through the night and struggle with weight gain.
The brain circuitry disrupted in Alzheimer’s disease appears to influence memory through a type of brain wave known as theta oscillation, a team of researchers report. The findings, published in Nature Communications, could help researchers design and evaluate new treatments for Alzheimer’s, a condition that affects millions of people around the globe and has no cure.
A new study suggests that a healthy heart may help prevent Alzheimer’s—and this gives hope for new treatments.
Researchers have shown the potential of a new gene therapy approach to silence human sensory neurons (nerve cells) as a means of treating persistent pain. Many current drugs for chronic pain are highly addictive, which makes it important to discover new alternatives.
Scientists have developed new tools, based on AI language models, that can characterize subtle signatures in the speech of patients diagnosed with schizophrenia.
Can plant-derived nutrients alter gut bacteria to affect brain function? A team of scientists investigated this question in a study of overweight adults. Their findings, published in the journal Gut, suggest that dietary fiber can exert influence on both the composition of gut bacteria and the reward signals in the brain and associated food decision-making.
New guidance has been issued for clinicians on the determination of brain death, also known as death by neurologic criteria
Researchers have shown it is possible to detect tell-tale signs of Parkinson’s disease 20–30 years before symptoms appear. Their work opens the door to screening programs and preventative treatments long before irreversible damage is done.
Finally this week, there is evidence that some form of conscious experience is present by birth, and perhaps even in late pregnancy, an international team of researchers has found.









