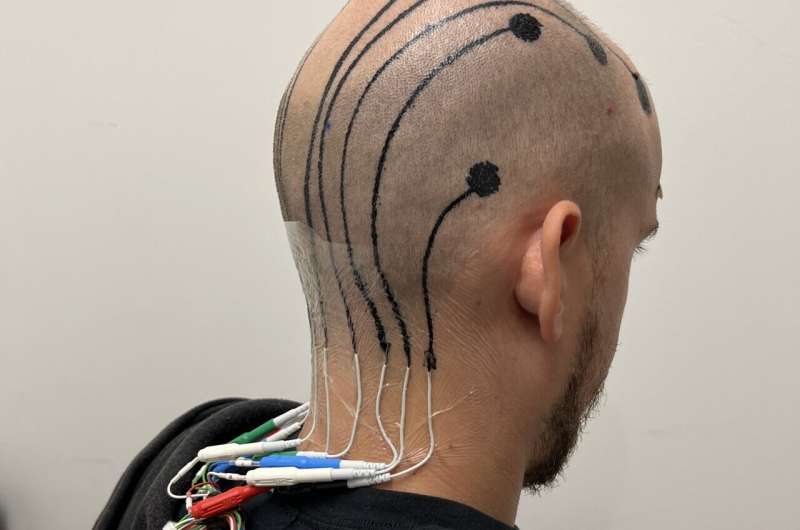
For the first time, scientists have invented a liquid ink that doctors can print onto a patient’s scalp to measure brain activity. The technology offers a promising alternative to the cumbersome process currently used for monitoring brainwaves and diagnosing neurological conditions. It also has the potential to enhance non-invasive brain-computer interface applications.
People who have chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) who have a family history of mental illness may have a higher risk of aggression in middle age, according to a new study.
A loss of brain volume associated with new immunotherapies for Alzheimer’s disease may be caused by the removal of amyloid plaques, rather than the loss of neurons or brain tissue, finds a study led by UCL researchers.
A common heart drug may slow the progression of Huntington’s disease according to new research.
Men with cardiovascular disease risk factors, including obesity, face brain health decline a decade earlier—from their mid 50s to mid 70s—than similarly affected women who are most susceptible from their mid 60s to mid 70s, suggest the findings of a long term study, published online in the Journal of Neurology Neurosurgery & Psychiatry.
In a new study published in Briefings in Bioinformatics, researchers have found that depression can increase the chances of a person experiencing menstrual pain (dysmenorrhea).
Researchers have achieved a major milestone in the treatment of spinal cord injuries (SCI). By applying deep brain stimulation (DBS) to an unexpected region in the brain—the lateral hypothalamus (LH)—the team has improved the recovery of lower limb movements in two individuals with partial SCI, greatly improving their autonomy and well-being.
Soccer heading may cause more damage to the brain than previously thought, according to a study presented at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
New research reveals subtle changes in the visual pathways of individuals with chronic mild traumatic brain injury (TBI), even when standard eye examinations show no abnormalities. These findings include structural and functional deficits despite participants showing normal visual acuity during clinical examination.
A recent study identifies research strategies for tying brain function and structure to behaviour and health.
COVID-19 may be a risk factor for multiple sclerosis (MS). This has been shown by new research at Örebro University and Örebro University Hospital, Sweden. The study is published in the journal Brain Communications.
A study appearing in Nature Neuroscience has linked distinct neural and behavioral characteristics in autism spectrum disorder (ASD) to a simple computational principle.
Everyday physical activity, like going for a short walk or playing with the kids, may provide short-term benefits for cognitive health, equivalent to reversing four years of cognitive aging. That was a key finding a new study, published in the journal Annals of Behavioral Medicine.
Voice experiments in people with epilepsy have helped trace the circuit of electrical signals in the brain that allow its hearing center to sort out background sounds from their own voices.
A study led by University College London researchers found that large language models, a type of AI that analyzes text, can predict the results of proposed neuroscience studies more accurately than human experts.
Skeletal muscle loss is a risk factor for developing dementia, according to a study presented at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
A pioneering study has meticulously mapped the brain’s intricate neural pathways, shedding light on how specific regions work together to control impulsive actions. By employing advanced neuroimaging and noninvasive brain stimulation techniques, researchers uncover the mechanisms that allow us to halt unwanted actions.
Finally this week, new research reveals the unique human ability to conceptualize numbers may be rooted deep within the brain.