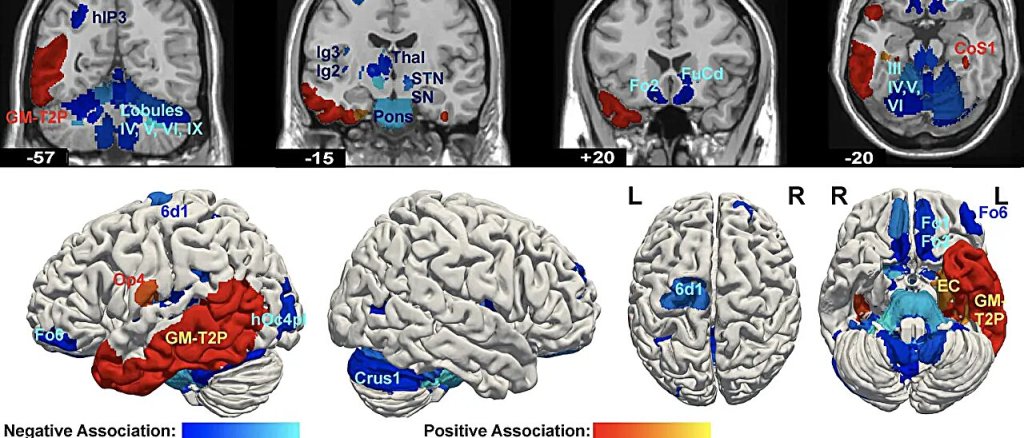
A recent study has shed light on the brain structure differences associated with psychopathy—a condition known to be one of the strongest predictors of persistent violent behaviour. The findings are published in the journal European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience.
Researchers are using a new approach to brain imaging that could improve how drugs are prescribed to treat Parkinson’s disease.
An analysis of over 375 trials shows that structured exercise significantly reduces depression and anxiety in children and teens. Low-intensity resistance activities like light weights were most effective for easing anxiety, while moderate mixed-mode programmes worked best for depression, especially when lasting under 12 weeks.
A new technology that uses clinical MRI machines to image metabolic activity in the brain could give researchers and clinicians unique insight into brain function and disease.
Diets rich in phosphate additives, commonly found in processed foods, can increase blood pressure by triggering a brain signaling pathway and overactivating the sympathetic nervous system that regulates cardiovascular function, UT Southwestern researchers discovered. Their findings could lead to treatment strategies for patients with hypertension caused by overconsumption of foods containing high levels of phosphates.
The long-standing belief that left-handed people are more creative has been challenged by a new meta-analysis of over a century of research.
New research proposes a unified theory of brain function based on criticality—a state where the brain teeters between order and chaos, allowing it to learn, adapt, and process information optimally. When the brain strays from this delicate balance, cognitive performance weakens, and neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s may begin to take hold.
A drug used for Parkinson’s disease has been shown to be effective in reducing the symptoms of difficult to treat depression, according to a study led by the University of Oxford.
A recent study shows that older adults may compensate for age-related cognitive decline by enhancing activity in a specific brain region linked to attention—the locus coeruleus (LC). In a brain imaging study, older participants showed stronger LC responses when interpreting ambiguous facial expressions, compared to younger adults.
Individuals with versus those without tinnitus have significantly lower scores on cognitive function tests, according to a recent study published in Frontiers in Neurology.
New research shows how the brain navigates emotional transitions, using music as a tool to map changing neural patterns. Scientists found that emotional responses in the brain depend heavily on the listener’s prior emotional state.
A clinical trial has revealed that Ambroxol, a common cough medicine in Europe, may help slow cognitive decline in people with Parkinson’s disease dementia.
In a study of 200 former professional rugby players (aged 30–61 years old), researchers from Imperial College London, University College London and the UK Dementia Research Institute found no cases of early-onset dementia.
Finally this week, new research findings show how synaptic connections in the cerebral cortex can strengthen during sleep, offering insight into how the brain continues learning even while we rest.