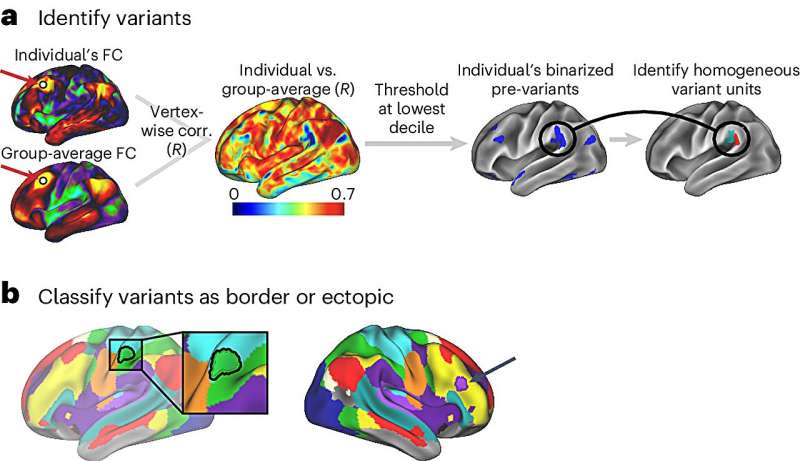
A new study has revealed brain differences that may explain why humans demonstrate a variety of cognitive abilities and behaviors. The research shows that two forms of individual differences may predict cognitive abilities, explain behavioral differences and even pinpoint biomarkers of brain disease.
A team of neuroscientists has found that so-called superagers maintain memory as they grow older because they do not experience a decline in the integrity of their white brain matter.
Researchers have developed an artificial intelligence technique that can effectively estimate an individual’s brain age based on electroencephalogram (EEG) brain scans. The technology could help to make early, regular screening for degenerative brain diseases more accessible.
A simple blood test could allow doctors to determine whether a person may be at higher risk for stroke or cognitive decline during their lifetime, according to a new study.
A brief episode of anger triggered by remembering past experiences may negatively impact the blood vessels’ ability to relax, which is essential for proper blood flow, according to new research published in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
Using neuroimaging, researchers have identified a brain network crucial to human consciousness.
An individual’s experience of pain from medical treatment can be heightened by witnessing other people’s responses to the same treatment, with this negative experience subsequently spreading to others, scientists have discovered.
Listening to music benefits older adults’ cognitive health, even if it’s music they haven’t heard before or don’t enjoy very much, according to a new study.
Researchers have found a way to better control the preclinical generation of key neurons depleted in Parkinson’s disease, pointing toward a new approach for a disease with no cure and few effective treatments.
An international research team led by Karolinska Institutet has mapped the early genetic development of the brain and can now present an atlas of embryonic development between weeks 6 and 13.
Researchers have identified a key mechanism in brain stem cells that prevents identity conflicts during gene expression. This mechanism allows the cells to retain stemness while being primed for neuronal differentiation. The discovery includes finding that keeping neuronal gene messengers within the nucleus, while allowing stem cell gene messengers to be translated, avoids premature differentiation.
A new study demonstrates the potential of virtual reality in treating major depressive disorder.
Exercise prompts muscles to release molecular cargo that boosts brain cell function and connection, but the process is not well understood. Now new research has found that the nerves that tell muscles to move also prompt them to release more of the brain-boosting factors.
A pattern of brain activity that helps prevent us from getting lost has been identified in a new study, published in Nature Human Behaviour.
A new study highlights a novel mechanism of brain plasticity involving chondroitin sulfate clusters outside nerve cells. Researchers identified these cartilage-like structures as crucial for the brain’s ability to adapt and store information.
Finally this week, a new computer model may have cracked the code on helpful memory cues.