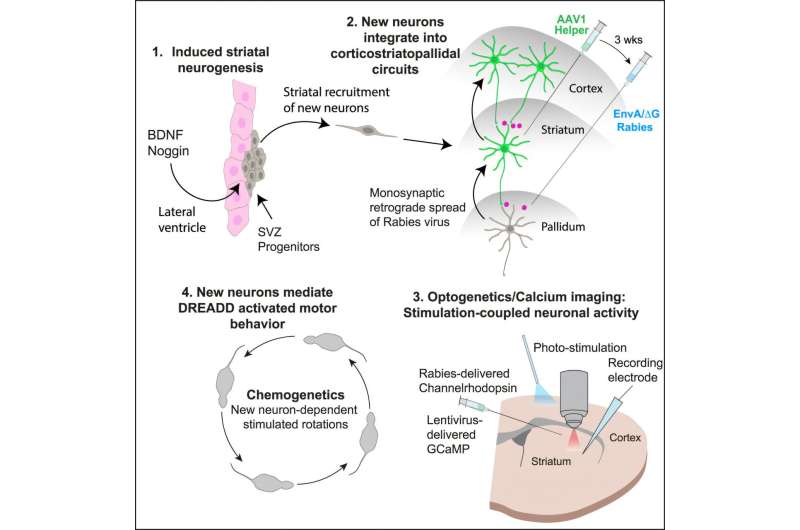
New research shows that the adult brain can generate new neurons that integrate into key motor circuits. The findings demonstrate that stimulating natural brain processes may help repair damaged neural networks in Huntington’s and other diseases.
A study published in Brain Communications highlights a new approach to treating drug-resistant epilepsy.
A novel human study with intracranial recordings demonstrates the thalamus’s pivotal role, especially its higher-order regions, in the onset of conscious perception, with activation preceding that of the prefrontal cortex.
New findings reveal that long-term obesity patterns have distinct impacts on brain structure, function, and cognition.
Researchers have discovered new potential therapeutic targets for multiple sclerosis (MS). While current treatments prevent further damage, the current findings may form the starting point for the development of new treatments for tissue recovery in MS. The research is published in the journal Brain.
Research published in the Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging has uncovered changes in brain connectivity during chemotherapy in patients with breast cancer.
Mass General Brigham investigators have linked difficult early life experiences with reduced quality and quantity of the white matter communication highways throughout the adolescent brain. This reduced connectivity is also associated with lower performance on cognitive tasks.
A team of engineers has developed a microscale brain–computer interface that is small enough to be placed between hair follicles on a user’s head.
Researchers have identified specific high-order thalamic nuclei that drive human conscious perception by activating the prefrontal cortex. Their findings enhance understanding of how the brain forms conscious experience, offering new empirical support for theories that assign a central role to thalamic structures rather than cortical areas alone.
A natural compound found in everyday fruits and vegetables may hold the key to protecting nerve cells—and it’s showing promise as a potential treatment for ALS and dementia.
New research highlights how smartphones are transforming memory science by capturing real-world data on sleep, emotion, and daily experiences. Studies show that replaying memories before sleep, experiencing novel events, and feeling positive emotions can all strengthen autobiographical memory.
An artificial intelligence tool that can help interpret and assess how well treatments are working for patients with multiple sclerosis has been developed by UCL researchers.
A recent study indicates that brain cells possess a higher degree of plasticity than previously understood. This suggests that the brain’s ability to adapt and change throughout life is more extensive than earlier scientific models suggested.
Researchers have discovered that increased blood flow leads to stiffness in the hippocampus, a region of the brain that plays important roles in learning and memory.
By mapping the presynaptic inputs to single neurons within the primary somatosensory cortex researchers have shown how these neurons integrate brain-wide signals related to behavior, offering a more nuanced understanding of cortical activity.
Seventeen modifiable risk factors are shared by stroke, dementia, and late-life depression, according to a review published in the Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry.
A recent study has shown how aspects of brain function change with age, revealing that excitatory processes in the brain decrease, while inhibitory processes increase as children get older. The findings are an important step in understanding disorders like autism.
Finally this week, research shows that a blow to the head can significantly impact a child’s or adolescent’s future education. Even a mild concussion can have far-reaching consequences.





 A
A  Electrically stimulating the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex can enhance our ability to ‘think outside the box’, a
Electrically stimulating the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex can enhance our ability to ‘think outside the box’, a 