New research shows that learning to read fundamentally changes how the brain responds to spoken language, even when no written words are present. While previous brain imaging studies have demonstrated that literacy strongly affects how the brain responds to written words, this study is among the first to show differences in brain activity during listening alone.
Chronic alcohol consumption profoundly alters gene expression in key brain regions involved in reward, impulse control, and decision-making, according to a recent study.
Babies as young as two months old are able to categorize distinct objects in their brains—much earlier than previously thought—according to new research from neuroscientists at Trinity College Dublin. The research, which combined brain imaging with artificial intelligence models, enriches our understanding of what babies are thinking and how they learn in the earliest months of life.
A new study reveals that certain brain regions are more active in people with obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) during cognitively demanding tasks. The findings could help inform new ways in which the condition is treated and assessed.
A type of therapy that stimulates specific brain pathways with electromagnetic pulses combined with physical therapy significantly reduced overall disability in stroke survivors compared to survivors who received sham (inactive) electromagnetic stimulation combined with physical therapy, according to a preliminary study presented at the American Stroke Association’s International Stroke Conference 2026.
The increased size of, and lesser blood supply to, a key brain structure in patients with long COVID tracks with known blood markers of Alzheimer’s disease and greater levels of dementia, a new study finds.
A new international study on Buddhist monks shows that meditation is a state of heightened cerebral activity in which brain dynamics are profoundly altered. More specifically, the study found that practicing meditation is associated with modulations in neural oscillations, an increase in the complexity of brain activity and an alteration in “brain criticality,” a state of equilibrium between chaos and order. These changes are thought to reflect a brain that is more alert, flexible, adaptive and efficient.
An AI-powered model can read a brain MRI and diagnose a person in seconds, a study suggests. The model detected neurological conditions with up to 97.5% accuracy and predicted how urgently a patient required treatment.
An international research team has uncovered the next frontier in monitoring brain health, and the key is in technology that millions of people are already using every day—earbuds. The world-first study found that commercially available earbuds have the capability to detect and classify brain activity, simply by measuring subtle changes in users’ hearing. The team used acoustic sensors in earphones to assess cognitive load—the mental effort that shapes learning, task performance and early cognitive decline.
Finally this week, a new study has found that moderate consumption of caffeinated coffee (two to three cups a day) or tea (one to two cups a day) reduced dementia risk, slowed cognitive decline, and preserved cognitive function.
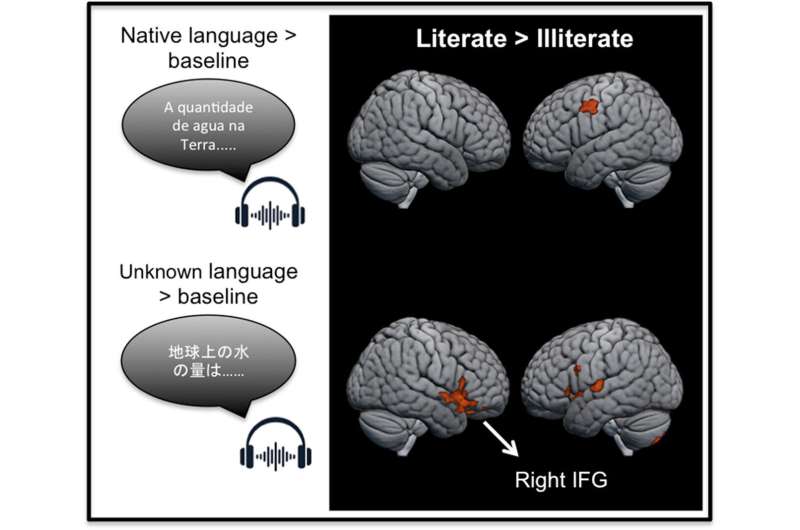
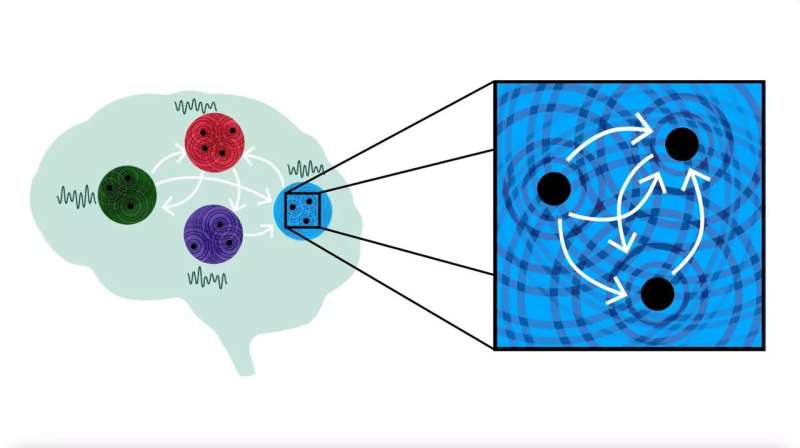


 Researchers have discovered differences in the
Researchers have discovered differences in the