In a new study published in Nature Communications, researchers investigated the genetic and modifiable influences on fragile brain regions by looking at the brain scans of 40,000 UK Biobank participants aged over 45.
Scientists have shown for the first time that a type of thinking that has been described for over a century as a developmental milestone of adolescence may grow teenagers’ brains over time.
A team of neurologists, stem cell specialists and molecular biologists affiliated with several institutions in the U.S. and led by a group at Stanford University School of Medicine has found evidence that the root cause of Alzheimer’s disease may be fat buildup in brain cells. The study is published in the journal Nature.
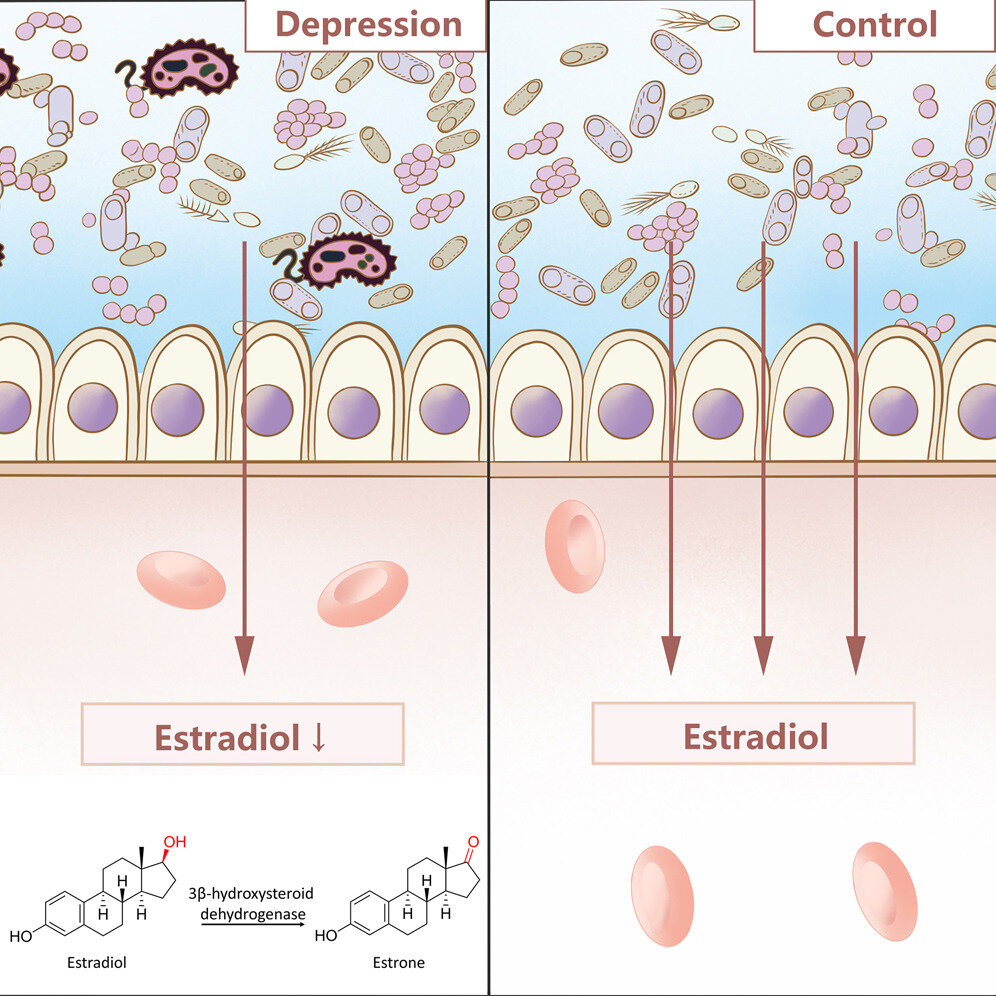
New research highlights the critical role of unique gut bacteria in newborns, producing serotonin to educate immune cells and prevent allergic reactions early in life.
People continuously exposed to bright, artificial light at night may be at increased risk of developing conditions that affect blood flow to the brain and having a stroke, according to research published in Stroke.
Researchers reveal new findings on the complexity of age-related memory decline and neural dedifferentiation, challenging existing theories on cognitive aging.
A new study has found that amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD) exhibit strikingly similar cellular and molecular characteristics, despite affecting different brain regions and showing distinct clinical symptoms.
New research reveals how the human brain processes vital signals from the heart and lungs, offering new insights into the complex brain-body integration essential for health and cognition.
In a new study, AI processed text from health histories and neurologic examinations to locate lesions in the brain. The study, which looked specifically at the large language model called generative pre-trained transformer 4 (GPT-4), is published in the online issue of Neurology Clinical Practice.
New research shows that disturbed gut flora during the first years of life is associated with diagnoses such as autism and ADHD later in life.
Bilingualism may serve as a powerful tool against age-related cognitive decline, particularly in social cognition areas such as the theory of mind. A new study demonstrates that early bilingualism leads to beneficial structural changes in the brain, including increased gray matter volume and cortical thickness, which contribute to a stronger cognitive reserve.
In a study published in Nature Mental Health, scientists have found that individuals suffering from chronic musculoskeletal pain (CMP) may face a higher risk of brain aging.
A new analysis involving over 13,000 people has found changes to blood vessels in the brain that can increase the risk of stroke and dementia are common in people with a range of heart conditions, regardless of whether they have experienced a stroke.
A Canadian-led study has identified genes that may be partially responsible for the development of cerebral palsy.
Researchers have introduced a new, refined method for analyzing brain signals, enhancing our understanding of brain functionality. This research has the potential to improve treatments for neurological conditions such as Parkinson’s disease, pain, epilepsy and depression.
A study reveals that Lewy body disease, a major neurodegenerative disorder, may start developing in individuals as early as middle age, well before symptoms manifest.
Researchers have shown that the brain chemical GABA regulates activity in the retina of the eye in autistic and non-autistic individuals differently. Autistic people have larger responses to single light flashes in the retina of the eye and this new study shows that increasing GABA activity can reduce this response.
Finally this week, a study by the University of Sheffield has cast doubt on the efficacy of non-invasive brain stimulation techniques in improving visual working memory.