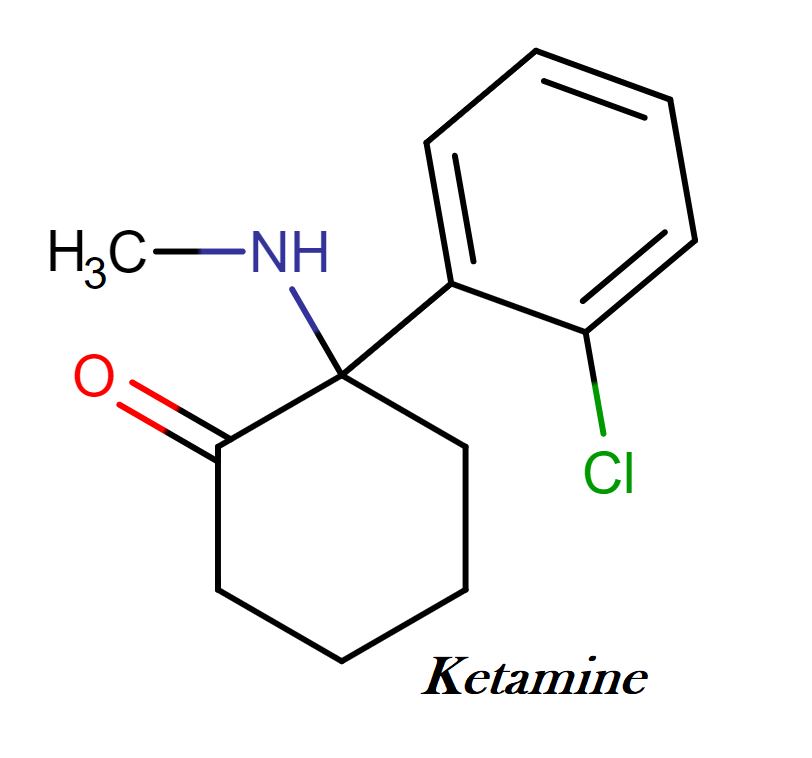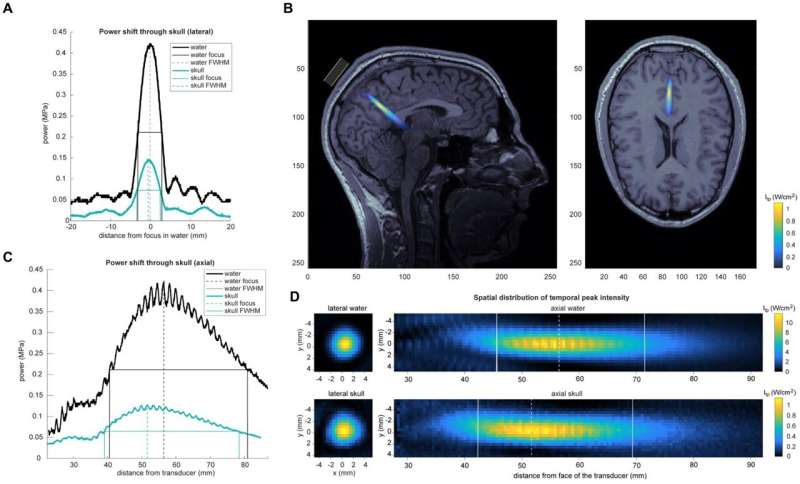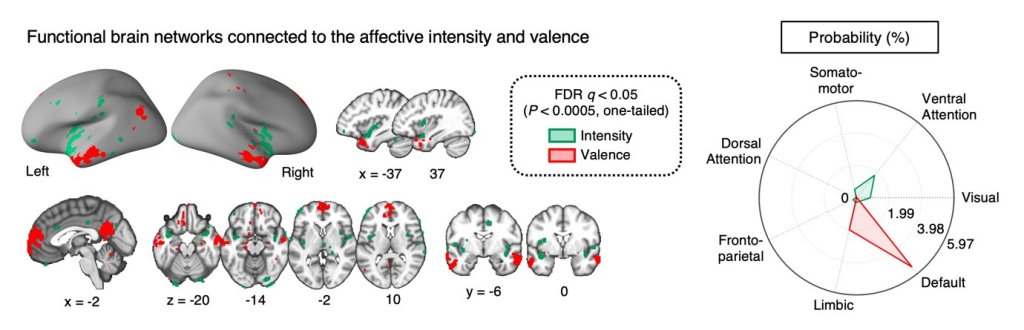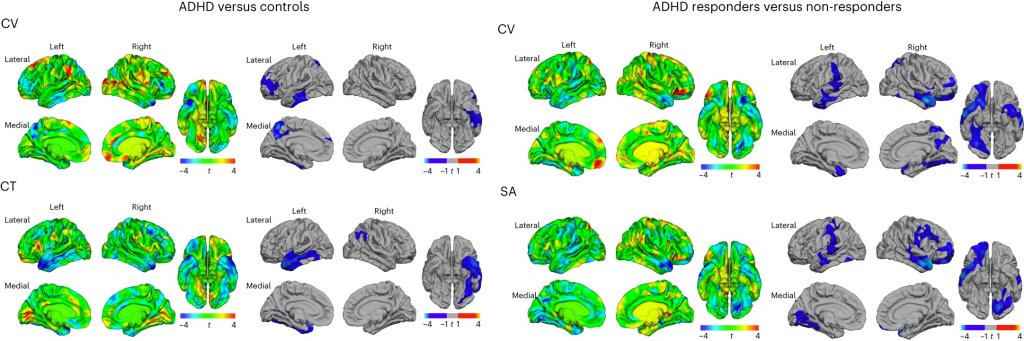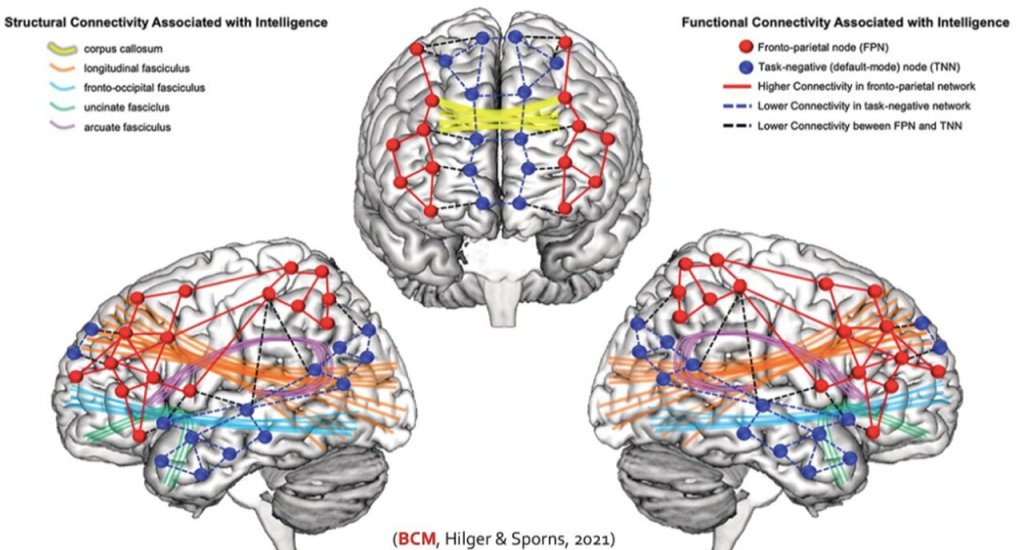
Neuroscientists have developed machine learning models to predict human intelligence.
Researchers have found that incorporating specific nutrients into a regular diet may reduce iron buildup in the brain—a factor associated with cognitive decline in normal aging. The research team said the findings offer valuable insights for future clinical trials aimed at evaluating the impact of similar nutritional intake on brain iron accumulation and cognitive function.
The short-term boost our brains get after we do exercise persists throughout the following day, suggests a study led by UCL (University College London) researchers.
Thirteen proteins linked to brain aging in humans are identified in a Nature Aging paper. Changes in the concentrations of these blood proteins may peak at 57, 70, and 78 years old in humans, and suggest that these ages may be important for potential interventions in the brain aging process.
Brain scans show vulnerability to gaming addiction in teens.
A team of scientists has uncovered a novel mechanism that reshapes our understanding of how blood flow is regulated in the brain. The study, published in The Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences introduces Electro-Calcium (E-Ca) Coupling, a process that integrates electrical and calcium signaling in brain capillaries to ensure precise blood flow delivery to active neurons.
Researchers at the Yale School of Medicine found structural and functional alterations in specific brain regions of individuals with opioid use disorder. The study’s results were published in Radiology.
A new study has identified a unique brain network that links varied patterns of brain atrophy, or shrinkage, associated with schizophrenia. By combining neuroimaging data from multiple studies involving more than 8,000 participants, the research team found a specific connectivity pattern of atrophy that was present across different stages and symptoms of schizophrenia—and distinct from brain networks associated with other psychiatric disorders.
New research provides valuable insights into the brain-body immune connection, identifying key communication hubs in the dural sinuses and skull bone marrow at the back of the head.
New research shows that slow-wave sleep strengthens synaptic connections in the neocortex, making it more receptive to long-term memory formation. Researchers found that during deep sleep, synapses in the neocortex reach peak efficiency at precise moments within slow-wave oscillations.
A new study suggests how brain, with sleep, learns meaningful maps of spaces.
A large-scale study revealed that genetic variants linked to dyslexia are associated with differences in brain areas controlling motor coordination, vision, and language. Using data from over a million individuals, researchers calculated genetic “polygenic scores” for dyslexia and analyzed their relationship to brain structures. Higher genetic risk for dyslexia was tied to lower volumes in brain regions related to speech processing and movement, and increased volumes in the visual cortex. Differences in the brain’s internal capsule, which connects regions, were also observed.
Cognitive impairment, especially in learning and memory, is more likely among people with epilepsy, according to a newly published study.
A recent study explores how connections across the entire brain predict human intelligence, moving beyond traditional focus on specific brain areas like the prefrontal cortex. Using fMRI data from over 800 individuals, researchers analyzed communication between brain regions to predict fluid, crystallized, and general intelligence scores. Findings reveal that distributed brain-wide connections play a crucial role, surpassing existing models that emphasize localized regions. This research highlights intelligence as a global property of the brain, offering fresh perspectives for understanding cognitive processes.
The chromosomal disorder 22q11.2 deletion syndrome (22q) has emerged as one of the strongest risks for schizophrenia.
New research reveals that brain structure varies with reading ability, particularly in the left hemisphere. Better readers have distinct traits, including a larger anterior temporal lobe for integrating word meaning and a thicker left Heschl’s gyrus for phonological processing.
Night shifts and poor sleep quality are associated with an increased risk for incident epilepsy, according to a study published in BMC Public Health.
People with severe, treatment-resistant depression who received a nerve-stimulating therapy showed significant improvement in depressive symptoms, quality of life and ability to complete everyday tasks after a year, according to the results of a national, multicenter clinical trial.
Finally this week, researchers have found a relationship between lifestyle choices that affect dementia risk and early signs of aging in the brain.