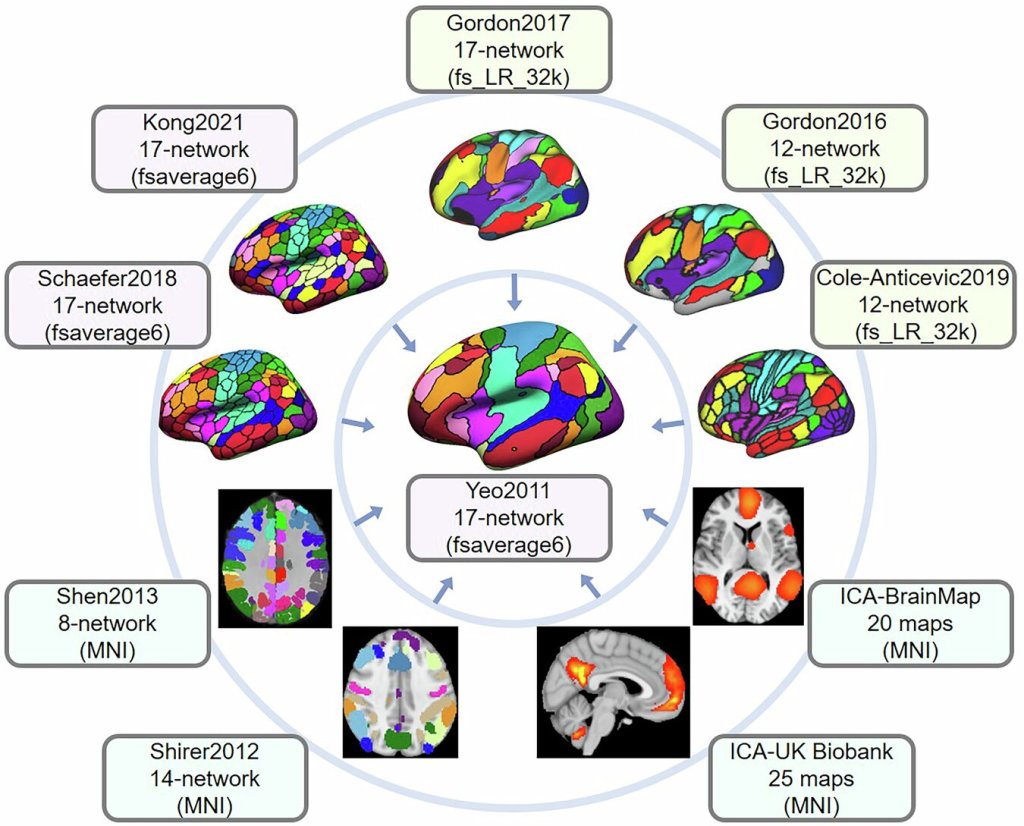
UCLA Health researchers have helped to develop a new digital toolbox to create a “common language” for brain network studies, potentially accelerating new discoveries and treatments for neurological and psychiatric conditions.
New research published in The Journal of Neuroscience suggests that relieving psychological stress by targeting specific neurons in the brain can lower blood pressure and reduce anxiety.
People who have early signs of heart problems may also have changes in brain health that can be early signs of dementia, such as loss of brain volume, according to a meta-analysis published online in Neurology. The meta-analysis does not prove that early heart problems cause loss of brain cells; it only shows an association.
Scientists have gained greater clarity in the brain regions and neurons that control metabolism, body temperature and energy use.
A recent study published in Science challenges assumptions about infant memory, showing that young minds do indeed form memories. The question remains, however, why these memories become difficult to retrieve later in life.
The brain’s appetite signalling pathways can be disrupted by consuming non-caloric sweeteners, according to new research.
Analysis of stroke patients from 1971 to 2019 showed college graduates exhibited stronger overall cognitive abilities immediately post-stroke. However, stroke survivors with any higher education saw a more rapid deterioration of executive functions, such as working memory and problem-solving, compared to those with lower levels of education.
New research suggests that psychopaths have a distinct pain experience, which can differ from what their bodies register.
A study published in the journal Scientific Reports suggests that virtual reality (VR) may offer a promising avenue for pain management in cancer patients. By immersing patients in realistic underwater environments using VR headsets, researchers observed a significant reduction in self-reported pain. This subjective improvement was further corroborated by real-time brain imaging, which revealed notable alterations in the neural pathways associated with pain perception.
A new review highlights how unpredictable sensory experiences, beyond traditional stressors like abuse and neglect, can disrupt brain development.
Scientists have uncovered a fundamental principle of how brain cells stay connected, and their discovery could change how we understand Alzheimer’s disease. Published in Cell Reports, this study reveals that neurons—the cells that make up our brain—use simple physics to maintain their connections, and that these processes change in Alzheimer’s patients.
New research shows that the brain’s numerical processing involves both absolute and relative quantity, with relative size processing increasing as information moves from the back to the front of the brain.
A pilot study of a post-stroke population has revealed some potential benefits of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) on attention and fatigue. Study findings are published in Frontiers in Human Neuroscience.
Finally this week, marathon runners experience a temporary decline in brain myelin during races, with levels returning to normal after recovery, according to a study published in Nature Metabolism.
