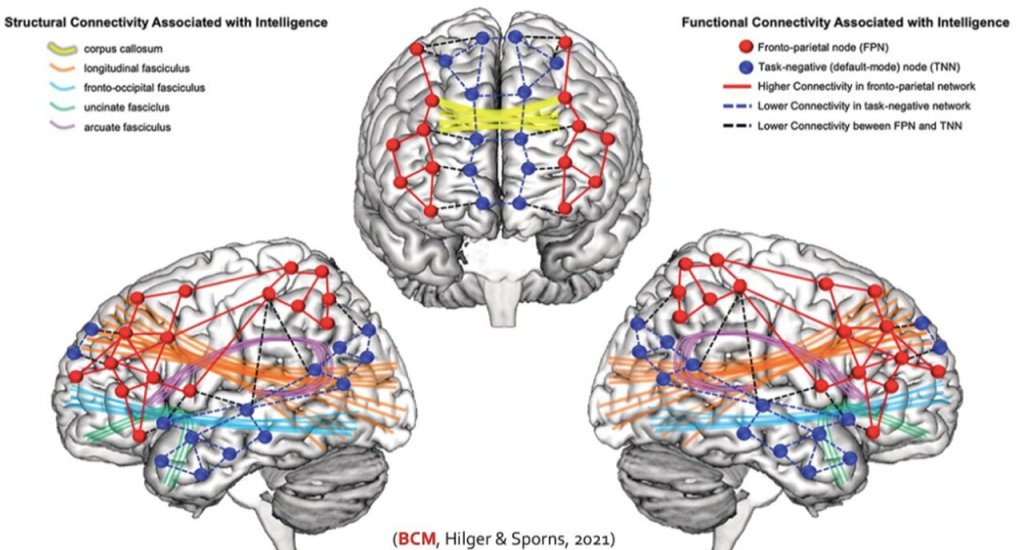
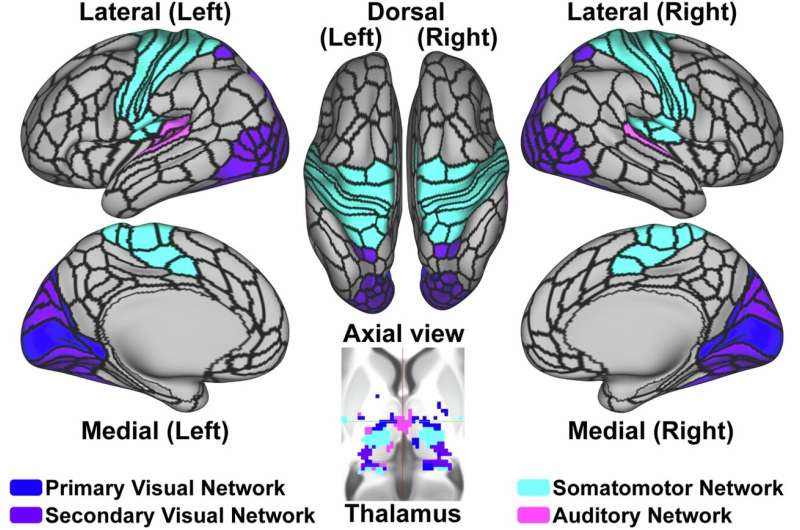
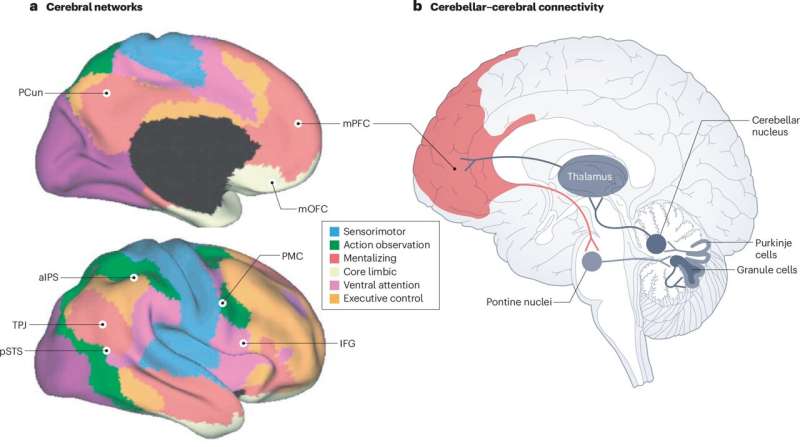
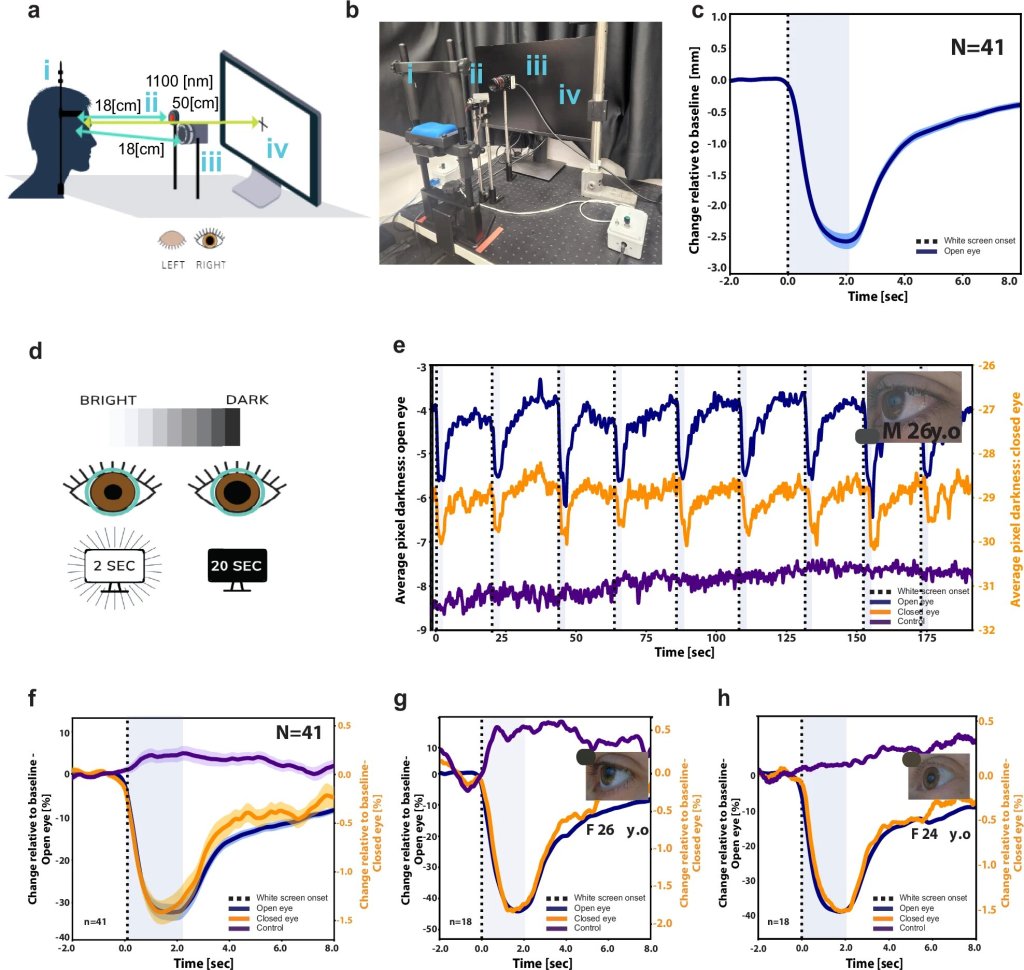
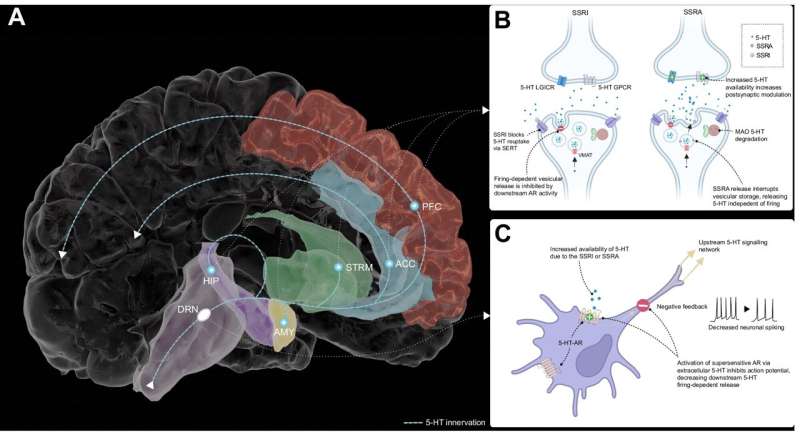
The link between poor sleep and mental health problems could be related to deficits in brain regions that keep unwanted thoughts out of the mind, according to hew research.
Researchers from Trinity College Dublin have collaborated with international partners to explore if societal inequality affects the brain. The study reveals a direct link between structural inequality—such as socioeconomic disparities measured by a country-level index (GINI)—and changes in brain structure and connectivity associated with aging and dementia.
New research has explained how the body’s internal clock influences the inflammatory process of the immune system.
Researchers used AI to analyze brain images from 70-year-olds, estimating their biological brain age and uncovering connections to lifestyle and health factors. Diabetes, inflammation, and high glucose levels were linked to older-looking brains, while regular exercise and healthy habits were associated with younger-looking brains.
An international research team, including researchers at Karolinska Institutet, has mapped the genes expressed in the brain cells of people with multiple sclerosis.
Gestational hypertension, preeclampsia, and eclampsia are associated with an increased risk for neurological outcomes in the months or years after giving birth, according to a recent study published in JAMA Neurology.
People with breathing problems during sleep may have a larger hippocampus, the area of the brain responsible for memory and thinking, according to a new study.
Researchers have discovered a connection between Alzheimer’s disease and herpes simplex virus-1 (HSV-1), suggesting viral infections may contribute to neurodegeneration. The study found that tau protein, typically seen as harmful in Alzheimer’s, might initially protect the brain from the virus but later exacerbate damage.
COVID-19 infection is not associated with immediate changes in multiple sclerosis (MS) symptom severity or disability, according to a study published in Neurology.
A study of nearly 10,000 adolescents found that those who initiated substance use before age 15 exhibited distinct differences in brain structures compared to their peers. Many of these differences were present before substance use, suggesting a role in predisposing factors like genetics and environment.
A new study reveals that humans think at a rate of 10 bits per second, while sensory systems process a billion bits per second—100 million times faster.
New research in epigenetics reveals how early-life experiences influence gene expression and brain development. By bridging the gap between nature and nurture, this work shows that environmental factors leave lasting biological imprints, shaping long-term health and resilience.
For patients with neurodevelopmental disorders, a genomics-informed model can provide clinical benefits, directly affecting management, according to a new study.
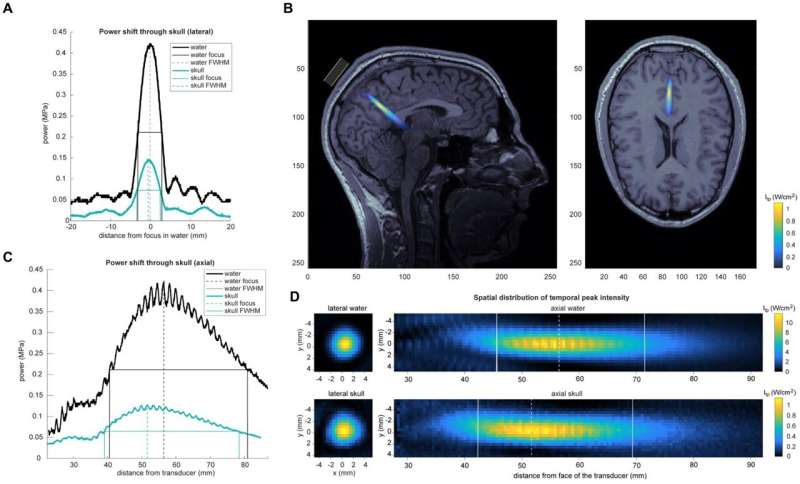
A new “molecular lantern” technique allows researchers to monitor molecular changes in the brain non-invasively using a thin light-emitting probe. This innovative tool utilizes Raman spectroscopy to detect chemical changes caused by tumors, injuries, or other pathologies without altering the brain beforehand.
Finally this week, researchers have found that the pupil is key to understanding how, and when, the brain forms strong, long-lasting memories.