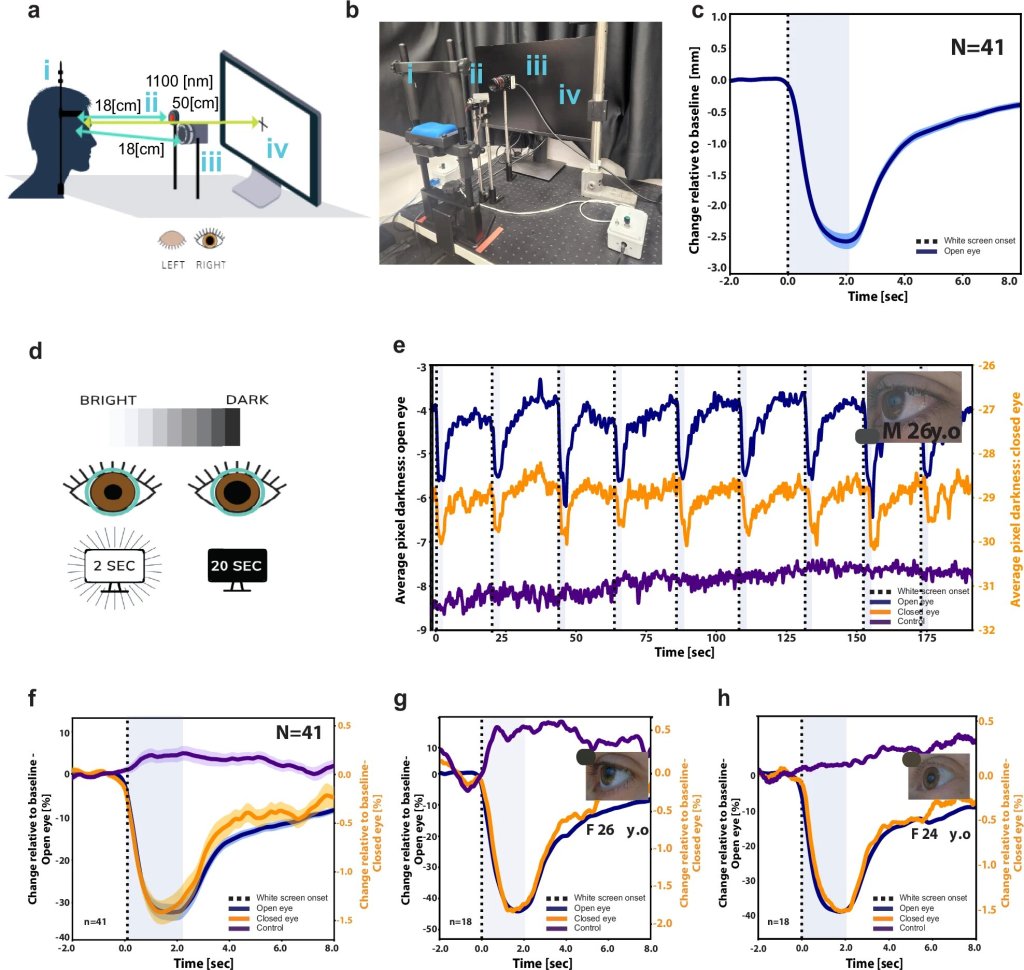
A new technological advancement now enables researchers to observe changes in pupil size and gaze direction behind closed eyelids for the first time, using non-contact infrared imaging. This capability is expected to aid in identifying wakefulness states during sleep, anesthesia, and intensive care by monitoring pupil size variations. It could also be instrumental in gauging sedation levels, detecting seizures and nightmares, and acknowledging pain or responsiveness following trauma or within intensive care settings.
Neuroscientists have uncovered serotonin’s role in resilience.
A recent study using artificial intelligence has yielded a new understanding of how the brain anticipates future occurrences and processes data. It was found that the brain’s inherent activity, even in the absence of external stimuli, is crucial to our cognitive and emotional processes.
New research shows that varied cognitive training, rather than repetitive tasks, helps older adults improve working memory.
Scientists have mapped how propofol, a widely used anesthetic, alters brain connectivity to induce unconsciousness. Using fMRI, they found that propofol disrupts connections in the thalamus, reducing complex information processing and limiting sensory integration.
Research on older individuals indicates that vision impairment may be responsible for one in five dementia cases.
A new technology that uses harmless light waves to measure activity in babies’ brains has provided the most complete picture to date of brain functions like hearing, vision and cognitive processing outside a conventional, restrictive brain scanner.
Heat waves can worsen abnormal excitability of the brain in people with epilepsy, finds a new small-scale patient study.
Scientists have developed an innovative approach to studying brain connections using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). Recently published in Cell Systems, this work introduces a new way of understanding brain architecture through dynamic functional networks, challenging the traditional static approach.
New research identifies potential therapeutic target for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
A new study published in Nature Communications examines how the brain initiates spontaneous actions. In addition to demonstrating how spontaneous action emerges without environmental input, this research has implications for the origins of slow ramping of neural activity before movement onset—a commonly-observed but poorly understood phenomenon.
Researchers have published a novel study exploring the effects of delayed feedback on learning in individuals with moderate-to-severe traumatic brain injury (TBI).
A breakthrough in medical imaging is making it possible for researchers to observe brain activity during movement and pick up the early signs of disorders that affect brain-to-body coordination, such as Parkinson’s disease.
A new study investigated the origin of ataxia in the brain of patients with stroke and found a significant number of the stroke lesions in the patients were located outside the cerebellum.
Researchers have developed a noninvasive technique that could dramatically improve the way doctors monitor intracranial hypertension, a condition where increased pressure in the brain can lead to severe outcomes like strokes and hemorrhages.
Robotic ‘coaches’ aiding upper limb rehabilitation for stroke and brain injury survivors have been successfully trialed in Vienna, Austria.
Scientists have created a dynamic technique to monitor swift changes in brain activity, particularly those associated with cravings. This method differs from conventional neuroimaging by offering a continuous perspective on the variations in craving intensity. The research revealed that individuals with intense cravings tend to remain longer in brain states that intensify these cravings and do not activate the brain networks that could diminish them.
A recent study highlights the interaction between brain structure and social context, suggesting that some children are more vulnerable to social stressors than others.
With maps of the connections between neurons and artificial intelligence methods, researchers can now do what they never thought possible: predict the activity of individual neurons without making a single measurement in a living brain.
A review highlighting recent advances in genetically encoded fluorescent tools for labeling and selectively manipulating synapses has been published in Nature Reviews Neuroscience.
Researchers have investigated the correlations between outdoor nighttime light pollution and Alzheimer’s disease, finding that excessive light pollution may elevate the risk of Alzheimer’s, particularly in younger individuals.
Finally this week, brain waves can be manipulated while in rapid eye movement (REM) sleep, a sleep stage associated with memory and cognition, a new study from the University of Surrey finds.

