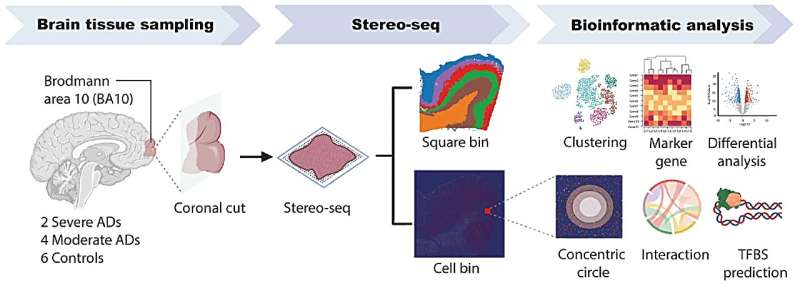
Scientists have developed a novel, detailed map at the subcellular level of a brain region frequently impacted by Alzheimer’s disease. This groundbreaking achievement represents a significant advancement in understanding the mechanisms underlying the development of this neurodegenerative condition.
New research shows that AI can identify complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS) with over 90% accuracy by analyzing gut microbiome patterns.
Mindfulness exercises paired with music were found to engage both neural and cardiac systems, potentially reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression. A recent study showed that live and virtual music mindfulness sessions lowered stress and altered states of consciousness, though only live sessions fostered social connection.
A long-term study shows that teenagers who maintain or increase physical activity levels are less likely to develop symptoms of depression.
Researchers have developed a brain-computer interface (BCI) that enables computer cursor control and clicking, using neural signals from the speech motor cortex. One participant with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) used the interface for daily life activities, including independent control of a personal desktop computer and text entry.
New research shows that targeting emotional processing is key to treating and managing chronic pain.
In a first-of-its-kind clinical study, researchers have shown that patients with treatment-resistant PTSD were symptom-free up to six months after completing traditional therapy paired with vagus nerve stimulation (VNS).
Scientists using living human brain tissue have shown for the first time how a toxic form of a protein linked to Alzheimer’s can stick to and damage the connections between brain cells.
People whose biological age is higher than their chronological age may be more likely to develop dementia than people whose biological age matches or is lower than their chronological age, according to a study published online in Neurology. Biological age is based on biomarkers of aging such as lung function, blood pressure and cholesterol.
A recent study reveals that oxygen tension elevation during weeks four to six promotes neurogenesis in brain organoids, regulated by neuroglobin. The research is published in Science Advances.
Obstructive sleep apnea, a condition that causes lower oxygen levels during sleep, is linked to degeneration of brain regions associated with memory through damage to the brain’s small blood vessels, according to a study published in Neurology.
A new theory suggests that psychedelics promote empathy, insight, and psychological flexibility by making the brain’s right hemisphere temporarily dominant over the left.
A revolutionary microscopy method called LICONN enables scientists to reconstruct brain tissue and map synaptic connections using standard light microscopes. By embedding brain tissue in hydrogel, expanding it, and imaging at nanoscale resolution, researchers achieve a detailed view of neuronal architecture previously only possible with electron microscopy.
A new music therapy-based tool called MuSICCA may transform how healthcare teams assess consciousness in children with severe brain injuries.
Research from Emory University has identified a biological connection between inflammation and deficits in motivation in individuals with schizophrenia, offering new hope for treating symptoms that have long been resistant to existing therapies.
A Yale-led study shows that the senses stimulate a region of the brain that controls consciousness—a finding that might inform treatment for disorders related to attention, arousal, and more.
Finally this week, a new study has debunked the common myth that autistic people are less effective communicators than non-autistic individuals. Researchers found no difference in how well information was shared between autistic-only, non-autistic-only, or mixed groups.




 It may be possible to categorise the brain strategies used by professional musicians based on how they prioritise sight vs. sound when learning to play new music, according to a
It may be possible to categorise the brain strategies used by professional musicians based on how they prioritise sight vs. sound when learning to play new music, according to a 
