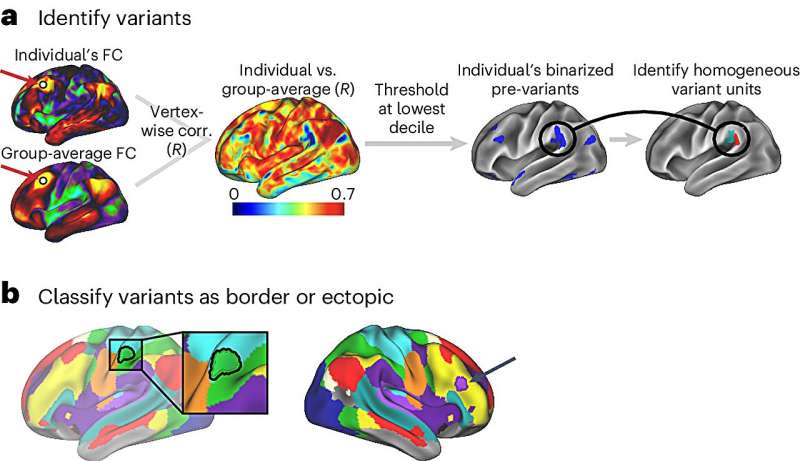
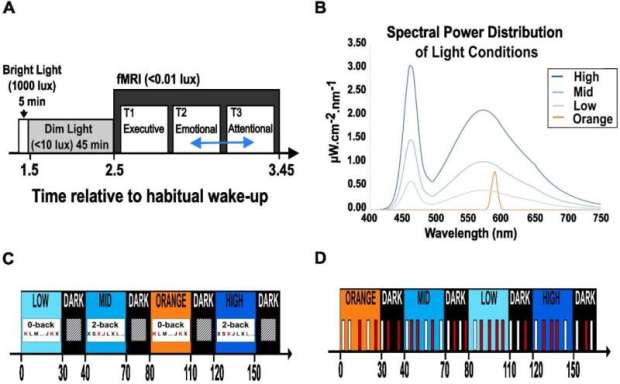
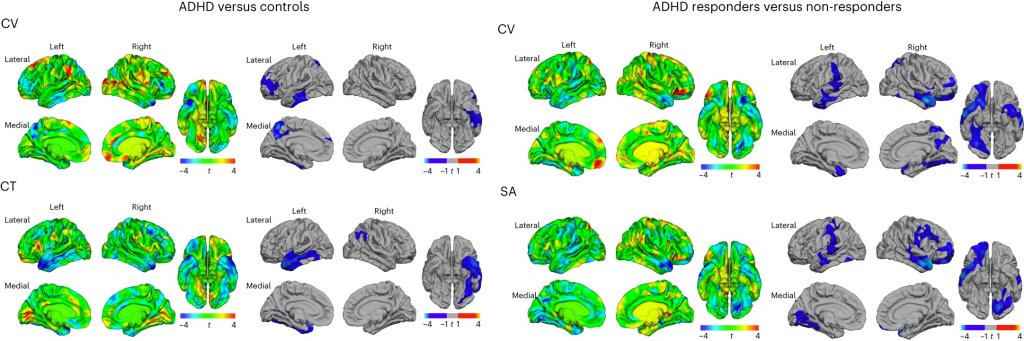
As the clock strikes midnight on January 1st, millions around the world set ambitious resolutions to transform their lives. Yet, research shows that most resolutions fail within a few weeks. Why is it so difficult to stick to our goals? Let’s turn to the workings of the brain for some possible answers.
The Burden of Cognitive Load
The prefrontal cortex, the brain region responsible for decision-making, planning, and self-control, has limited cognitive resources. Think of it as a battery that can be depleted with overuse. Every time we make a decision, resist a temptation, or even remember something trivial, we drain these resources. This phenomenon is known as cognitive load.
When cognitive resources are stretched thin, such as after a long day of work or when juggling multiple tasks, the brain struggles to exert self-control. Stress hormones like cortisol exacerbate this effect. High cortisol levels impair the prefrontal cortex’s function, making it harder to resist temptations or make rational decisions. This is why people often abandon their resolutions in moments of stress or fatigue.
Willpower and the Dopamine Connection
Willpower is not just a matter of grit; it’s deeply rooted in the brain’s reward system. The neurotransmitter dopamine plays a pivotal role in motivation and self-control. Engaging in self-disciplined behavior—such as sticking to a resolution—releases dopamine, which reinforces the behavior and provides a sense of accomplishment.
However, dopamine levels fluctuate based on our physical and emotional state. When we’re tired or stressed, dopamine levels drop, weakening our resolve and making it harder to resist temptations. This is why maintaining energy and managing stress are crucial for sustaining willpower.
Habits: The Brain’s Shortcut
Habits are automated behaviors that bypass the prefrontal cortex, conserving cognitive resources. They rely on established neural pathways in the brain. Forming new habits involves creating and strengthening these pathways, which makes desired behaviors more automatic over time.
For instance, brushing your teeth every morning doesn’t require conscious effort because it’s a well-formed habit. Similarly, turning your resolutions into habits reduces reliance on willpower and increases the likelihood of long-term success.
Practical Strategies for Success
To harness the power of neuroscience in achieving your New Year’s resolutions, consider these strategies:
1. “Exercise” Willpower in Small Ways
Willpower, like a muscle, can be strengthened with practice. Here are some simple ways to build it:
- Resist the urge to check your phone during a meeting.
- Complete a challenging task without procrastination.
- Skip a sugary snack in favor of a healthier option.
Each small victory trains your brain to exert self-control, making it easier to tackle bigger challenges over time.
2. Leverage the Power of Habits
Building habits is key to reducing cognitive load and sustaining resolutions. Try these techniques:
- Habit stacking: Link a new habit to an existing one. For example, “After I brush my teeth, I will meditate for 5 minutes.”
- Use cues and triggers: Set up reminders or environmental prompts. For example, place a water bottle on your desk to encourage hydration.
3. Focus on Intrinsic Motivation
Intrinsic motivation, driven by genuine personal desires, is more sustainable than external rewards. Reflect on why your resolution matters to you. For example:
- If your goal is to exercise more, focus on how it boosts your mood and energy levels rather than just losing weight.
Engaging in activities that align with your values and bring you joy releases dopamine, reinforcing positive behavior and making it easier to stay motivated.
The “Why” Behind Resolutions
Understanding the underlying motivations for your resolutions can make all the difference. Ask yourself:
- Are you pursuing this goal because of external pressures or because it aligns with your genuine aspirations?
For example, resolving to eat healthier might stem from a desire to feel more energetic and vibrant rather than societal expectations. Connecting with the deeper “why” increases intrinsic motivation and improves the likelihood of success.
Keeping New Year’s resolutions is not just about willpower; it’s about working with your brain’s natural tendencies. By managing cognitive load, leveraging dopamine, and building habits, you can turn fleeting resolutions into lasting changes. Remember, the path to success lies not in perfection but in persistence. With small, consistent steps, you can rewire your brain and make your goals a reality.