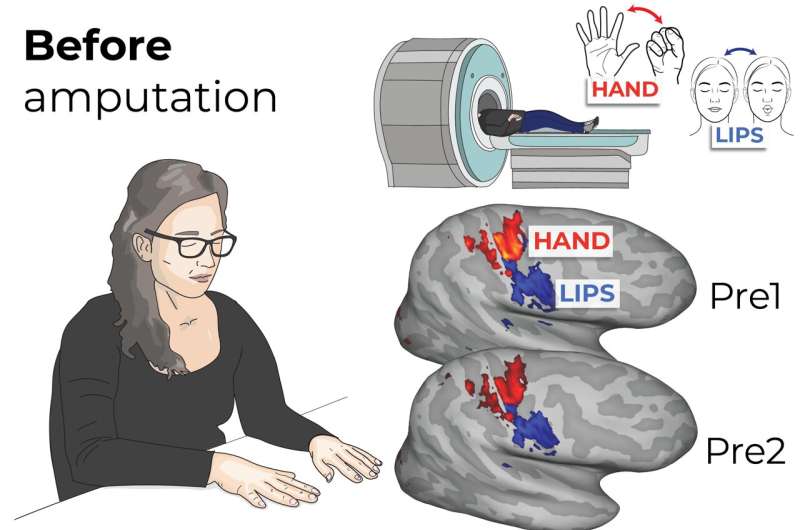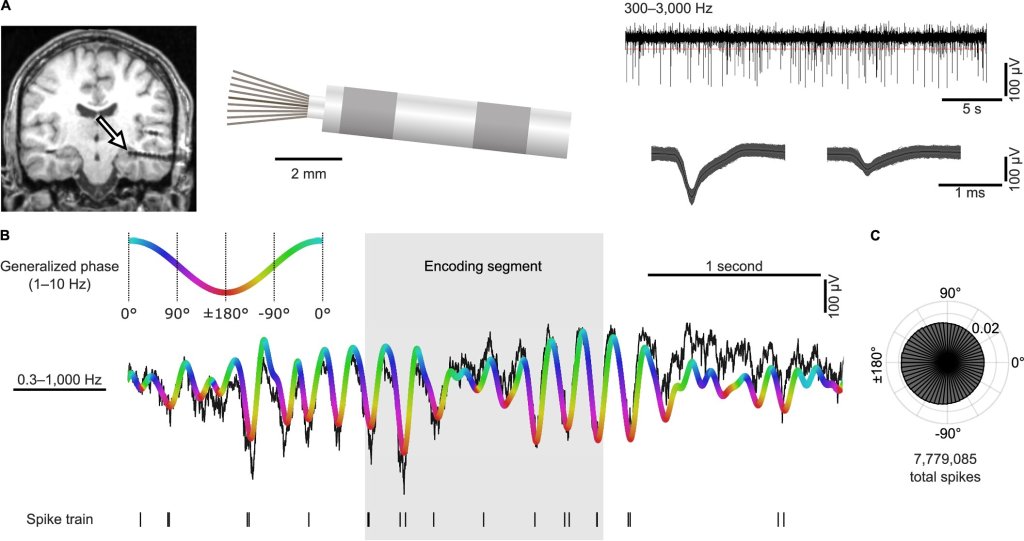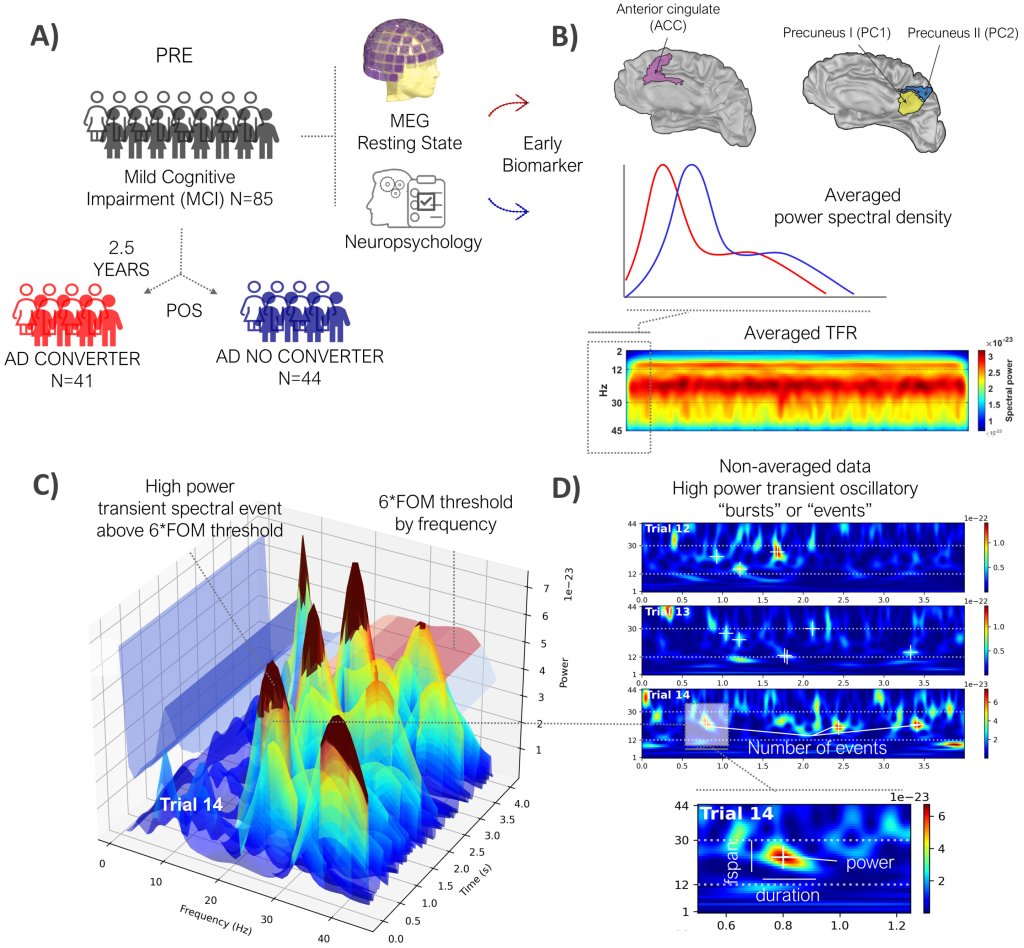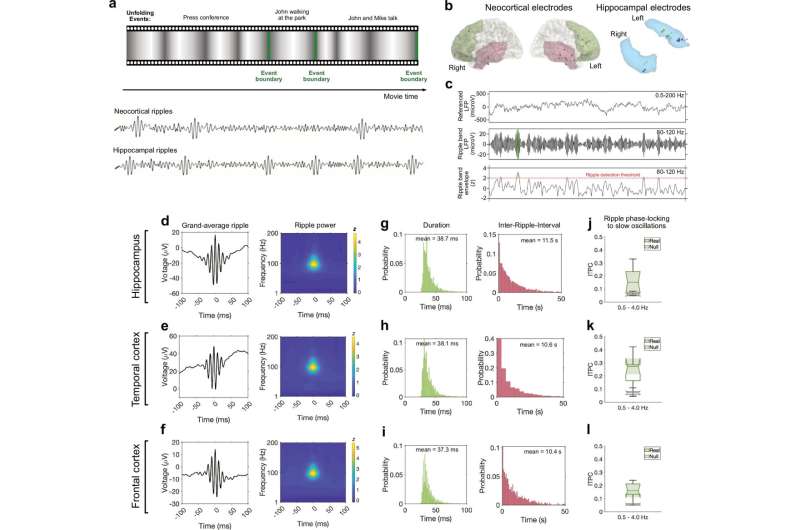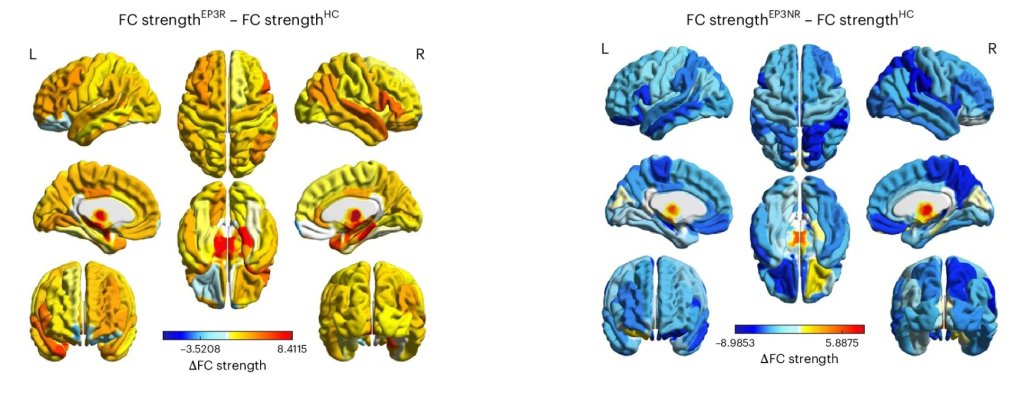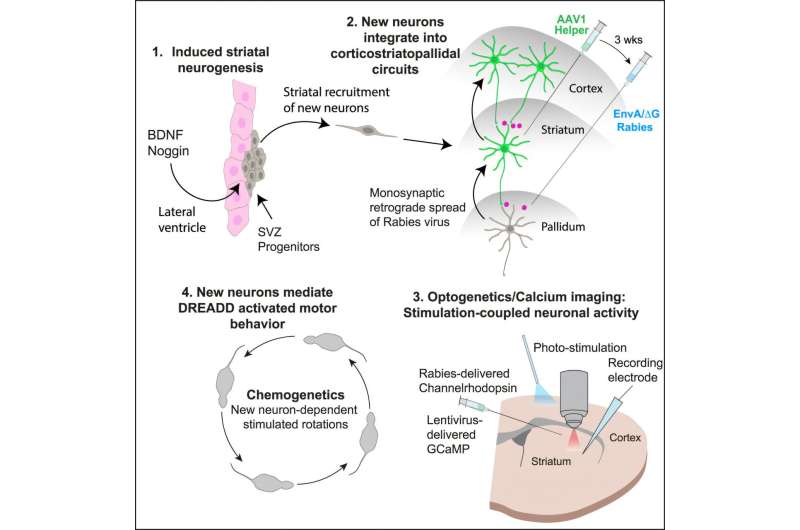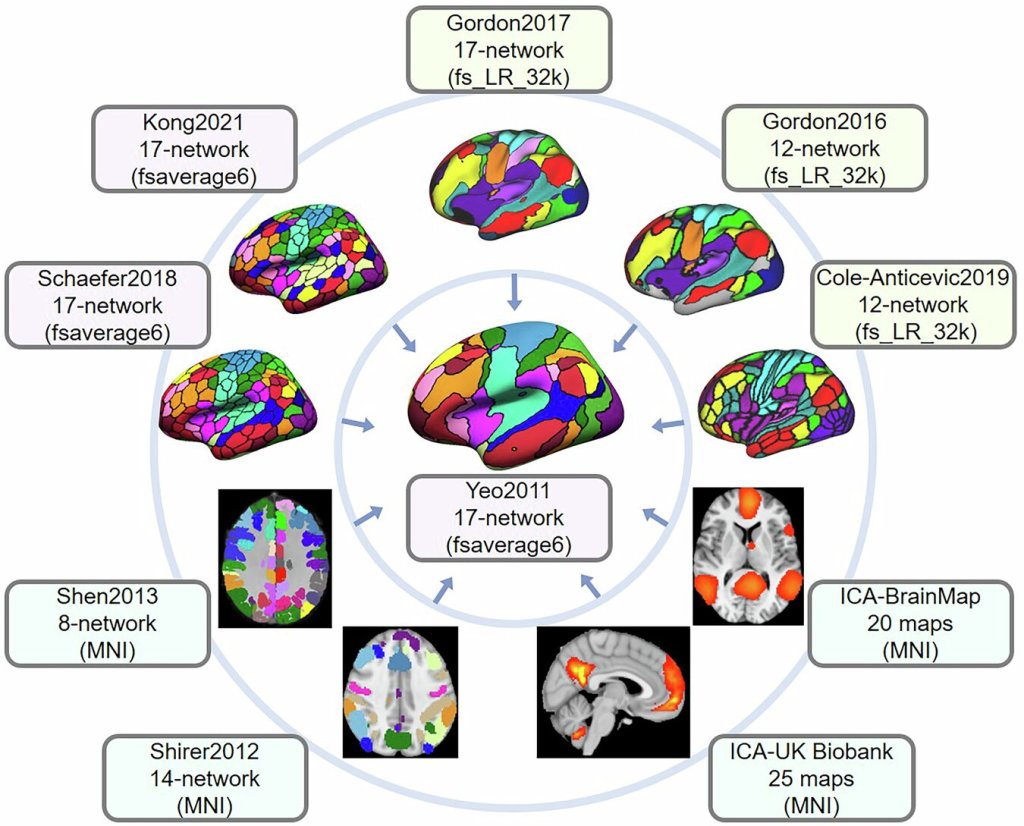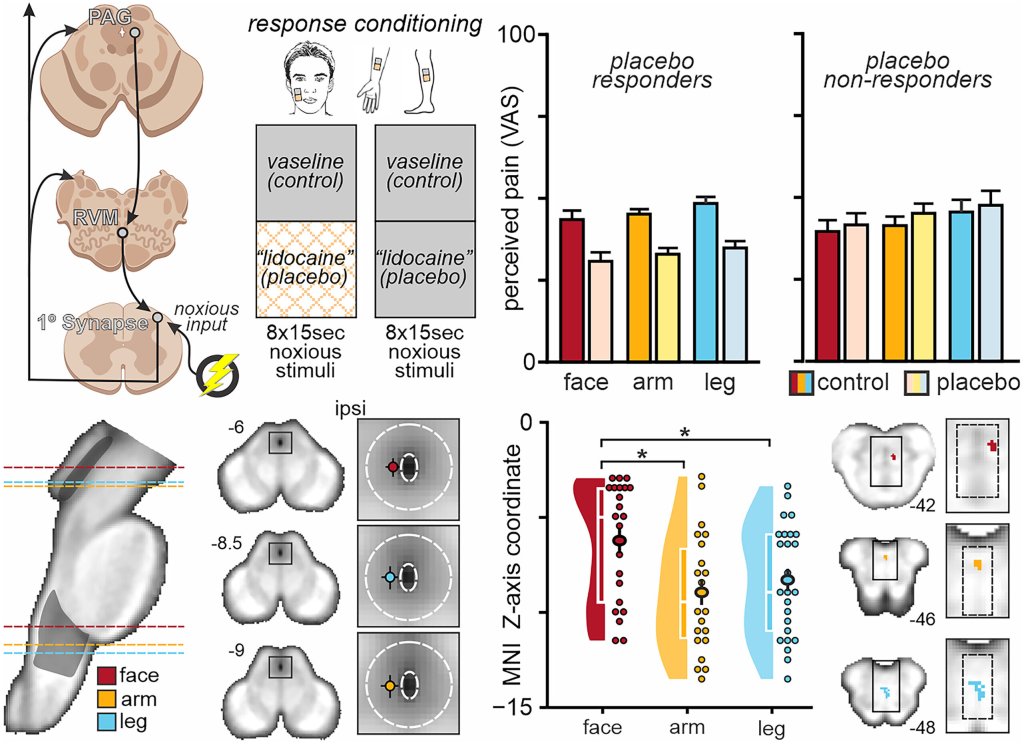
Researchers have used placebo pain relief to uncover a map-like system in the brainstem that controls pain differently depending on where it’s felt in the body. The findings may pave the way for safer, more targeted treatments for chronic pain that don’t rely on opioids.
New research reports an association between taking GLP-1 receptor agonists and lower overall cancer risk in adults with obesity, with a reduced risk for ovarian cancer.
Some regions of the brain in people with Alzheimer’s reorganize more often while at rest than in people without the disease–– and in healthy people, this frequent reshuffling sometimes predicts who will develop the condition later, according to a new study.
Researchers have demonstrated for the first time that psychotherapy leads to measurable changes in brain structure by using cognitive behavioural therapy.
Listening to music while doing something can make that activity more enjoyable. But listening to music after an experience or activity can make it more memorable if you have the optimal emotional response while listening to it, according to new research.
A new study reveals that the brain employs two distinct mechanisms to drive exploration under conditions of uncertainty.
A team of scientists has discovered a built-in “brake” that controls when key brain cells mature. In multiple sclerosis (MS), this brake appears to stay on too long, leaving the cells unable to repair the damage the disease causes.
New research suggests a link between a history of traumatic brain injury (TBI) and the risk of developing a malignant brain tumour.
Breathwork while listening to music may induce a blissful state in practitioners, accompanied by changes in blood flow to emotion-processing brain regions, according to a study published in the journal PLOS One.
The type of estradiol-based hormone therapy taken during and after menopause, such as patches or pills, may be associated with differences in memory performance, according to a new study.
Researchers have identified two specific types of brain cells that are altered in people with depression. The study, published in Nature Genetics, opens the door to developing new treatments that target these cells and deepens our understanding of depression.
Finally, this week, a new AI framework can detect neurological disorders by analyzing speech with over 90% accuracy.