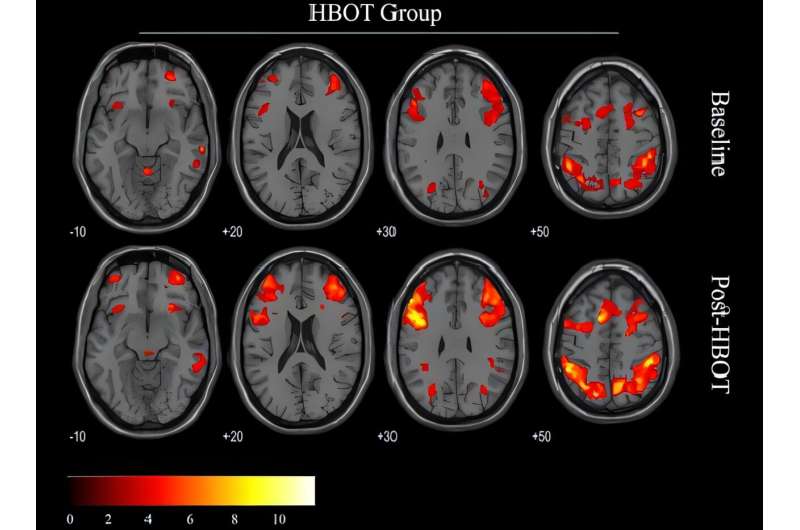
Researchers have demonstrated that hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) improves the condition of PTSD sufferers who have not responded to psychotherapy or psychiatric medications.
Scientists have discovered for the first time a neural mechanism for memory integration that stretches across both time and personal experience. These findings, reported in Nature, demonstrate how memories stored in neural ensembles in the brain are constantly being updated and reorganized with salient information, and represent an important step in deciphering how our memories stay current with the most recently available information.
An international study has found frailty increases a person’s risk of dementia, but early intervention may be the key to prevention.
Neuroscientists have discovered brain cells that form multiple coordinate systems to tell us “where we are” in a sequence of behaviours. The findings help us understand the algorithms used by the brain to flexibly generate complex behaviors, such as planning and reasoning, and might be useful in understanding how such processes go wrong in psychiatric conditions such as schizophrenia.
New research finds that even single bouts of intense exercise can improve cognitive performance in young adults, particularly in memory, attention, and executive functioning.
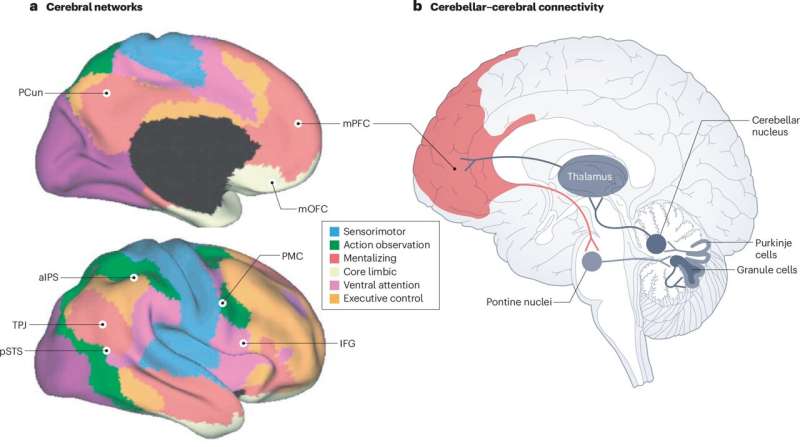
By scanning the brains of people while they watched movie clips, neuroscientists have created the most detailed functional map of the brain to date. The fMRI analysis, published in Neuron, shows how different brain networks light up when participants viewed short clips from a range of independent and Hollywood films, including Inception, The Social Network, and Home Alone.
Asthma is associated with memory difficulties in children, and early onset of asthma may exacerbate memory deficits, according to a new study.
Older adults with significant fluctuations in cholesterol levels are at increased risk for dementia and cognitive decline, even without medication changes. Researchers studied nearly 10,000 older adults, tracking their cholesterol levels and cognitive function over six years. High variability in total and LDL (“bad”) cholesterol was associated with a 60% increase in dementia and 23% increase in cognitive decline.
Scientists have successfully reprogrammed astroglia, a type of brain support cell, into neurons that mimic specific interneurons critical for brain function.
Exercise has been shown to improve brain health and reduce the risk of cognitive decline and dementia over the long-term. But engaging in everyday physical activity has immediate benefits for brain health, according to a new study.
A team of researchers has identified a potential biomarker of Parkinson’s disease progression.
New research highlights neuroglia (or glia cells) as critical players in mental health, potentially influencing conditions like depression and schizophrenia. Glia cells, long considered “support cells” in the brain, have now been shown to communicate through unique calcium signaling, impacting neuronal function and stress responses. Studies suggest that compromised astrocyte function, a glial cell type, may relate to depressive symptoms and schizophrenia.
Using deep brain stimulation techniques, neuroscientists are looking for early signals in the brain to help stop seizures.
A study investigated how cannabis use influences metabolomic patterns linked to psychotic-like experiences in adolescents. Blood samples revealed that non-cannabis users showed inflammatory metabolic changes associated with hallucinations, while cannabis users exhibited shifts in energy-related metabolites tied to brain ketogenesis.
Finally this week, a new study links satellite data with brain imaging to reveal how environmental factors like light pollution, green spaces, and urban density affect the mental health and brain development of children.