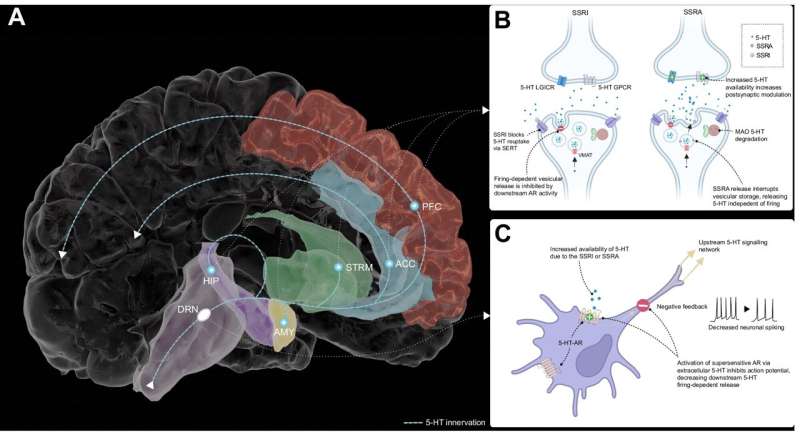
Scientists have determined that more than 60% of people who contracted COVID-19 have neurological symptoms that impact their cognitive function and quality of life, even two and three years after COVID-19.
Lip-read words can be decoded from the brain’s auditory regions similarly to heard speech, according to a new report that looked at how vision supports verbal perception.
Exercising is healthy, but not always appealing. Now research may have found a “switch” that activates the desire to get moving, as it shows that during exercise the muscle activates proteins which encourage further activity. The paper is published in Science Advances.
Researchers have demonstrated that a simple blood test that reflects brain health can predict which people are most at risk of suffering a stroke.
Our brain interprets visual information by combining what we see with what we already know. A study published in the journal Neuron, reveals a mechanism for learning and storing this existing knowledge about the world.
A newly developed brain-computer interface translates brain signals into speech with up to 97% accuracy, making it the most precise system of its kind.
Researchers have discovered that spontaneous brain activity during early development drives neural wiring before sensory experiences shape the brain. This spontaneous activity in neurons strengthens connections, following Hebb’s rule, where “cells that fire together wire together.”
According to new research, cognitive impairments in psychotic disorders, such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder, are linked to brain network organization.
A recently published study has unveiled significant findings that could enhance brain-computer interface (BCI) technologies, marking a crucial step towards more intuitive neuroprosthetic control and advanced rehabilitation therapies.
Researchers have discovered that the hippocampus stores multiple copies of a single memory, each within different neuron groups that develop at different stages.
Scientists have developed a promising preventative therapeutic approach against Alzheimer’s disease, targeting the amyloid beta biomolecule that typically triggers nerve cell hyperactivity in the early stages of the brain disease.
A new study finds that COVID-19 proteins left in the brain may lower cortisol levels, leading to heightened inflammation and an exaggerated response to stressors.
Through a large-scale brain imaging study, an international research team has identified five patterns of age-related degeneration in older people experiencing mental decline. In their study, the team conducted the multi-year study of thousands of MRI scans using machine learning applications to find patterns in brain degeneration as people age.
A new machine learning model, AutMedAI, can predict autism in children under two with nearly 80% accuracy, offering a promising tool for early detection and intervention.
Researchers have discovered the neurons responsible for “item memory,” deepening our understanding of how the brain stores and retrieves the details of “what” happened and offering a new target for treating Alzheimer’s disease.
Contrary to previous research, a new study of female participants finds no link between migraine and the risk of developing Parkinson’s disease.
Children who have persistently raised inflammation are at a higher risk of experiencing serious mental health disorders including psychosis and depression in early adulthood, according to a study published today in JAMA Psychiatry.
Researchers have identified a link between brain overgrowth and the severity of social and communication symptoms in children with autism spectrum disorder.
People with multiple sclerosis (MS) are far less likely than those without the condition to have the molecular hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease, according to new research. The discovery suggests a new avenue of research through which to seek Alzheimer’s treatment.
Scientists have discovered a new method to regulate the receptors responsible for the sense of touch, potentially leading to more effective treatments for chronic pain.
Researchers have found that nondeceptive placebos—placebos given with the full knowledge that they are placebos—can effectively manage stress, even when administered remotely. In a two-week randomized controlled trial, participants experiencing prolonged stress were divided into two groups: one group received nondeceptive placebos, while the other served as a control.
Return to work two years after a breast cancer diagnosis is associated with higher cognitive speed performance before and after treatment, according to a study published in JAMA Network Open.
Researchers have discovered a mutation in the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein that enhances its ability to infect the central nervous system, potentially explaining neurological symptoms and long COVID. The mutation was found to allow the virus to better infiltrate the brain, with implications for future treatments targeting COVID-19’s effects on the brain.
Finally, this week, while everyone knows that a good night’s sleep restores energy, a new study finds it resets another vital function: memory.