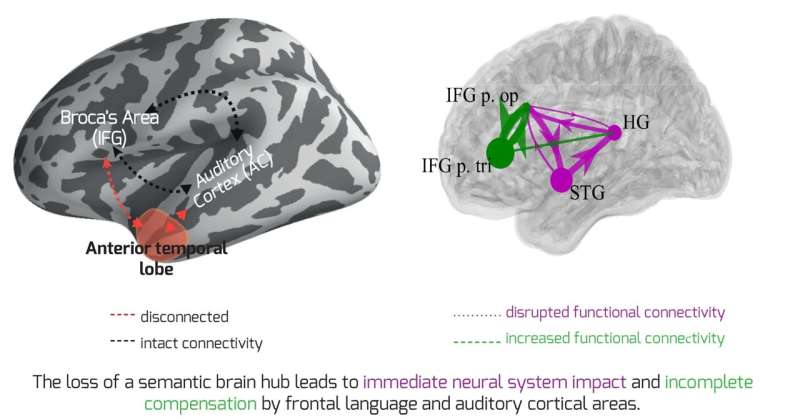
A new study that is the first to compare inflammation and brain stress responses in long COVID-19 patients with individuals who have fully recovered shows that those with continued brain fog and other cognitive issues have a lower ability to adapt to stress and higher levels of inflammation in their brains.
Researchers have identified a remarkably small but critical piece of genetic code that helps determine how brain cells connect, communicate, and function.
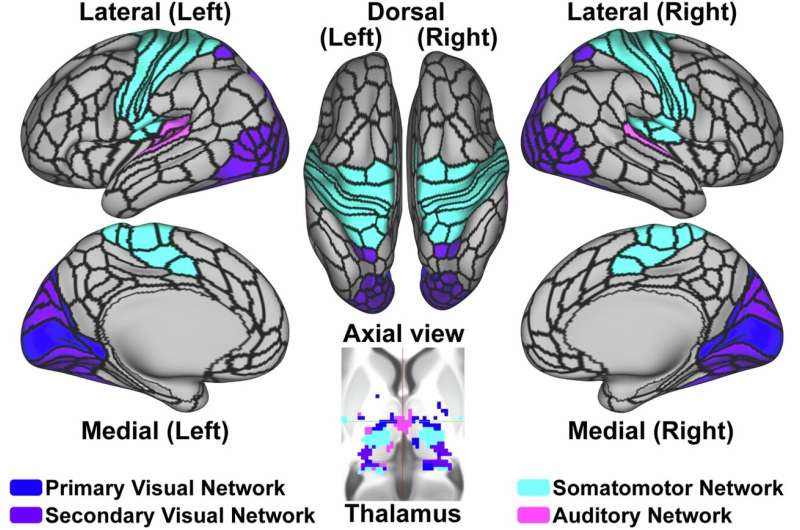
Conditions such as Tourette syndrome (TS), schizophrenia, and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) have sex differences with unknown mechanisms. These sex-specific mechanisms may inform the development of more effective treatments.
A new study reveals that type 2 diabetes is associated with thinning of the brain’s cortex in older adults, particularly in regions responsible for memory and cognition.
Specific cannabinoids produced by the human body may help to quell excessive fear responses in people with post-traumatic stress disorder and anxiety, according to a Northwestern Medicine-led study published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation.
People taking antidepressants for more than two years are more likely to experience withdrawal symptoms compared to short-term users when they come off the medication, finds a new study.
Researchers have identified nine blood-based microRNAs that are elevated in teens diagnosed with depression, offering a potential biomarker for early detection. These molecules, absent in adult depression, may signal unique biological processes in adolescents.
People who have obstructive sleep apnea may have an increased risk of dementia if left untreated, according to a new study of UK electronic health care records.
New research reveals that acute stress can impair key brain functions involved in emotion regulation, particularly in individuals with distress-related disorders like depression, anxiety, and borderline personality disorder. The study found that executive functions—such as working memory, impulse control, and cognitive flexibility—are more likely to be disrupted in these individuals during high-stress moments.
A large-scale study of over 2,500 toddlers found no significant clinical differences in autistic traits between males and females at the time of early diagnosis.
A research team has uncovered the cause and molecular mechanism of chronic brain inflammation that results in repetitive behavioural disorders. The research team demonstrated that an inflammatory response by immune cells in the brain induces overactivity in certain receptors, which may, in turn, lead to the meaningless repetitive behaviours observed in people with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD).
Measuring the interaction of brain networks could help identify teens at risk for dangerous drinking, according to a novel study that explored how brain signals relate to future drinking behaviour.
In a demographically diverse sample of healthy people, researchers found dramatic changes over the human lifespan in the brain’s “blue spot”—a tiny region involved in cognition and believed to be the first affected by neurodegenerative conditions including Alzheimer’s disease.
Researchers at Karolinska Institutet have identified three types of nerve cells connected to the intestinal villi, suggesting that previously unknown neural networks regulate fluid balance in the gut.
A study in rural China found that intensively lowering blood pressure significantly reduces the risk of dementia and cognitive decline in people with hypertension. Over 48 months, patients who received targeted care saw a 15% reduction in dementia and a 16% drop in cognitive impairment risk.
A new adaptive brain modeling framework offers fresh hope for objective diagnosis of neuropsychiatric disorders, which currently lack reliable neuroimaging biomarkers.
People who naturally stay up late, are more likely to experience faster cognitive decline than those who are early risers, according to a long-term study. Researchers found that unhealthy behaviors common in the evening, such as poor sleep, smoking, and drinking, may explain part of this risk.
A comprehensive new analysis reveals that depression significantly increases the risk of developing dementia, whether it begins in midlife or later in life.
Researchers have discovered how an ion channel in the brain’s neurons has a kind of “molecular memory,” which contributes to the formation and preservation of lifelong memories. The researchers have identified a specific part of the ion channel at which new drugs for certain genetic diseases could be targeted. The study, led by Linköping University in Sweden, has been published in Nature Communications.
A decade-long brain health study has released its full dataset, offering rare longitudinal insights into how cognition and brain structure change across adulthood.
Neuroscientists have discovered that the brain uses a dual system for learning through trial and error. This is the first time a second learning system has been identified, which could help explain how habits are formed and provide a scientific basis for new strategies to address conditions related to habitual learning, such as addictions and compulsions.
Finally, this week, parental education may protect offspring’s cognitive health later in life, according to a study published online May 30 in JAMA Network Open.