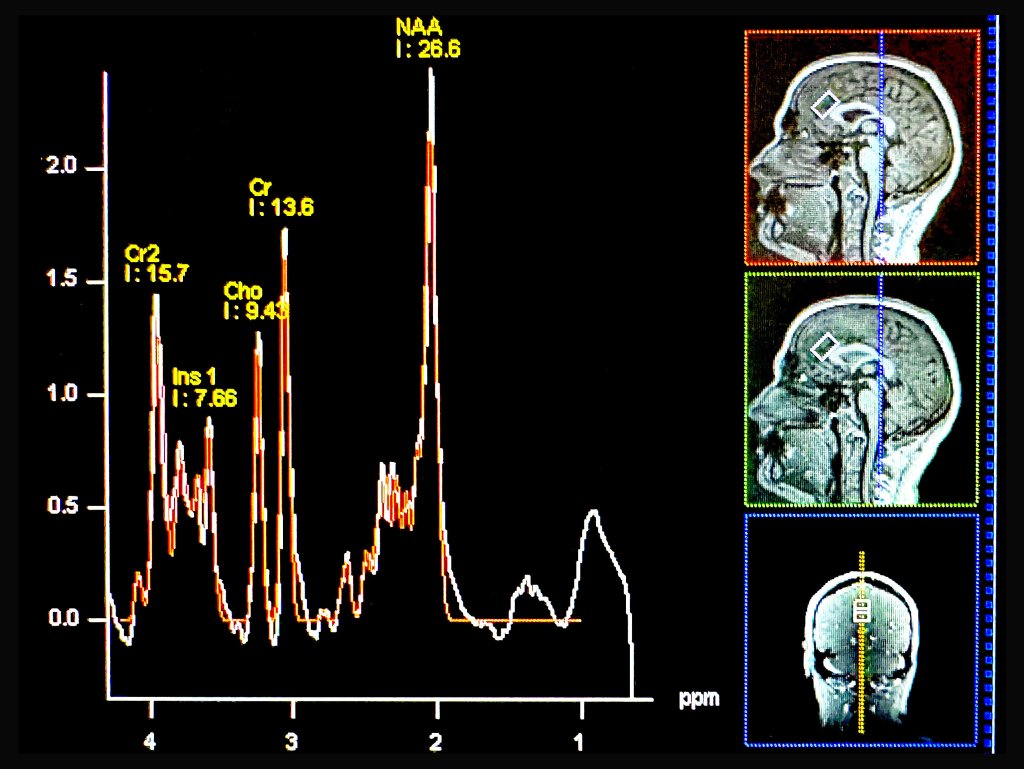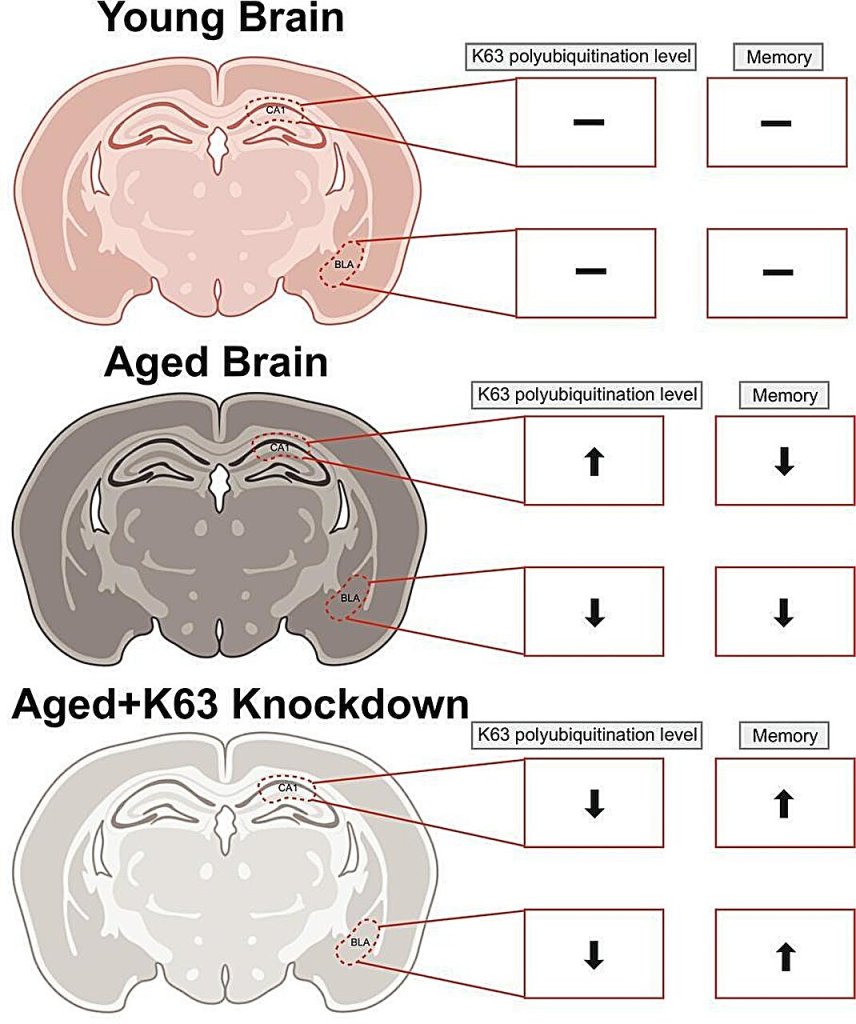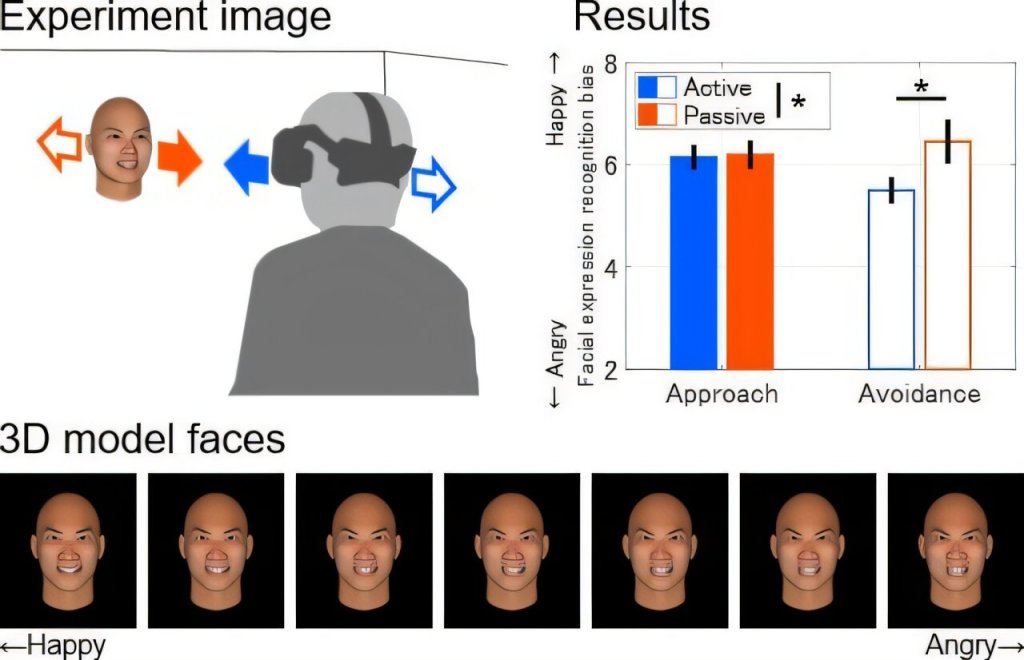
A recent study explores how physiological signals can reveal cognitive arousal—the level of mental alertness and emotional activation—without relying on subjective reporting.
New research reveals that women with long COVID show distinct biological disruptions — including gut inflammation, anaemia, and abnormal hormone levels — that may explain their heightened and persistent symptoms. These findings emerged from immune, biomarker, and genetic analyses in people one year after infection.
A new software enables brain simulations which both imitate the processes in the brain in detail and can solve challenging cognitive tasks.
University of Auckland researchers report that an 8-week, twice-weekly LSD microdosing regimen for major depressive disorder was feasible and well-tolerated, with Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS) scores reduced by 59.5% at the end of treatment and sustained to six months.
Dance styles engage the brain in different ways depending on the movements, aesthetics, and emotions associated with the dance, according to a study published in Nature Communications.
New research shows that depression beginning before age 25 has a much stronger hereditary component than depression that emerges later in life. By analysing genetic data from over 150,000 people with depression, researchers identified distinct genetic regions linked specifically to early-onset cases.
Scientists have developed an innovative, non-invasive brain stimulation therapy to significantly improve visual function in stroke patients who have suffered vision loss following a stroke.
A rare intracranial brain-recording study revealed that tirzepatide, a GLP-1 and GIP receptor agonist, temporarily silences craving-related neural activity in a key reward circuit of the brain. Researchers observed that the drug initially shut down signaling in the nucleus accumbens of a patient with treatment-resistant obesity. However, after five months, both the “food noise” and the corresponding neural patterns returned, suggesting the effect was short-lived. The findings highlight how these metabolic drugs influence human brain circuits and underscore the need for more durable treatments targeting impulsivity in eating disorders.
Researchers report that ketogenic diets are associated with modest reductions in depressive symptoms in adults, while evidence for anxiety remains uncertain.
An international study has uncovered similar structural changes in the brains of young people diagnosed with anxiety disorders, depression, ADHD and conduct disorder, offering new insights into the biological roots of mental health conditions in children and young people.
A randomised, placebo-controlled trial shows that cannabis with active THC reduces immediate alcohol cravings and lowers drinking levels in heavy-drinking young adults.
New research shows that the brain distinguishes between “what an odour is” and “how it feels,” processing them at different times. After smelling, the brain sends a quick signal that identifies molecular features for differentiation.
“Drains” in the brain, responsible for clearing toxic waste in the organ, tend to get clogged up in people who show signs of developing Alzheimer’s disease, a new study shows.
Researchers have discovered how the brain keeps time for precise movements, revealing a neural “hourglass” mechanism between the motor cortex and striatum. The motor cortex sends timing signals that accumulate in the striatum until they reach a threshold that triggers action.
Finally this week, a new brain imaging study reveals that music activates the same chemical system in the brain that is responsible for the pleasure associated with food and social bonding.