Credit: eLife (2024)
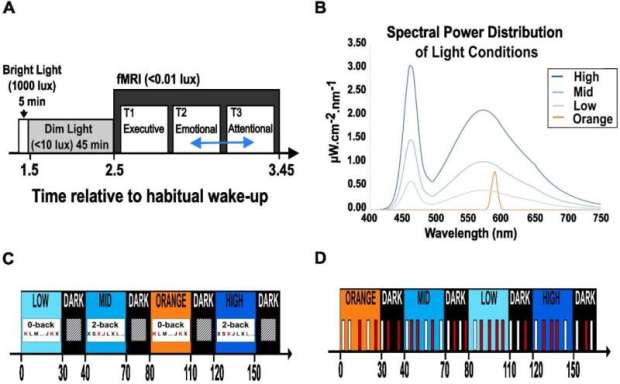
Exposure to higher levels of light can help people feel more awake and increase cognitive performance, probably by influencing the activity of parts of a brain region called the hypothalamus, according to new research.
Researchers have developed a new tool to better understand how chemicals like dopamine and epinephrine interact with neurons.
Bursts of brain rhythms with “beta” frequencies control where and when neurons in the cortex process sensory information and plan responses. Studying these bursts would improve understanding of cognition and clinical disorders, researchers argue in a new review.
Why do we move slower the older we get? A new study delivers answers.
People with a history of cognitively stimulating occupations during their 30s, 40s, 50s, and 60s had a lower risk of mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and dementia after age 70, according to a new study. The findings highlight the importance of cognitive stimulation during midlife for maintaining cognitive function in old age.
An inpatient, epilepsy-related rehabilitation program shows lasting effects on several aspects of adaptation to epilepsy and quality of life, according to a study published in the journal Epilepsia.
A recent study reveals that high body mass index (BMI) is associated with changes in physiological brain pulsations. These pulsations play a crucial role in maintaining brain fluid circulation and the clearance of metabolic waste from the brain.
Researchers have discovered that a high single dose of dietary supplement creatine can temporarily improve cognitive performance that is reduced by sleep deprivation.
Engaging in conversation with others can activate various brain functions in socially isolated older adults, even if the interactions occur via the internet. This finding comes from a recent clinical trial conducted by Massachusetts General Hospital, with the results published in The Gerontologist.
A new study suggests a common brain network exists between heart rate deceleration and depression.
Neuroscientists have revealed that recency bias in working memory naturally leads to central tendency bias, the phenomenon where people’s (and animals’) judgements are biased towards the average of previous observations. Their findings may hint at why the phenomenon is so ubiquitous.
A new study has found that a brain network condition called “explosive synchronization” could be the cause of extreme pain crises in people with sickle cell disease.
Researchers have developed tiny, flexible devices that can wrap around individual nerve fibers without damaging them. These devices could be used for the diagnosis and treatment of a range of disorders, including epilepsy and chronic pain, or the control of prosthetic limbs.
Scientists have discovered the mechanism that allows adult brain stem cells to express genes that maintain their identity and those for neuronal differentiation without conflicts in cellular activity.
A new study aims to examine the role of napping in brain development among infants and preschoolers. By tracking changes in the hippocampus, the research aims to prove how critical naps are for memory retention and brain growth in young children.
Finally this week, neuroscientists have confirmed that different strategies are employed when choosing between primary and secondary rewards, with impulsivity being a key factor.