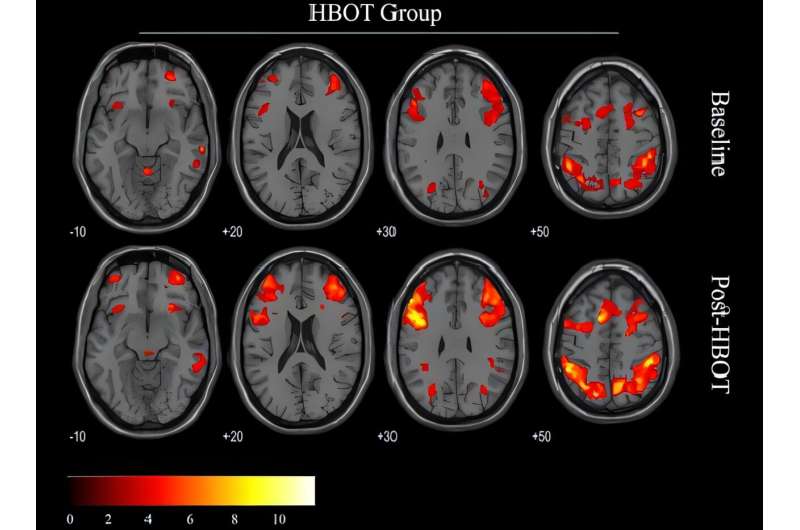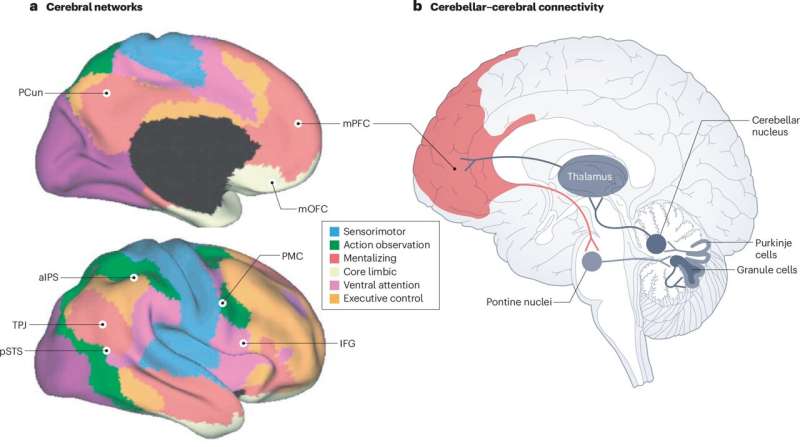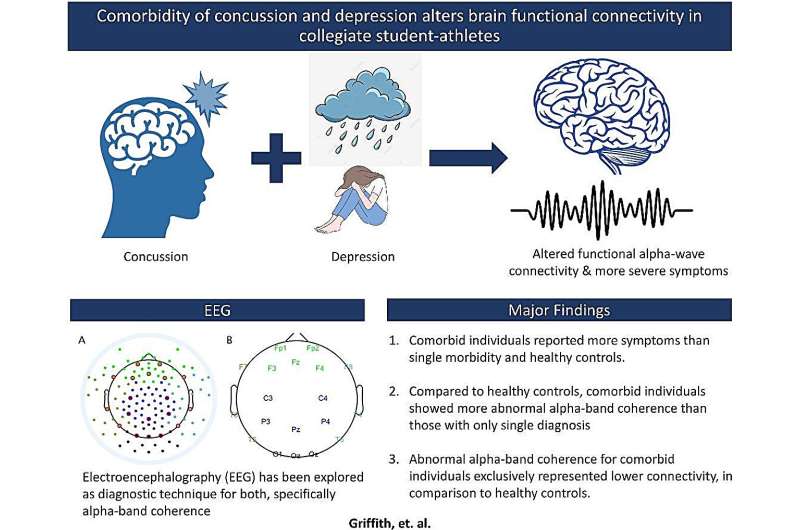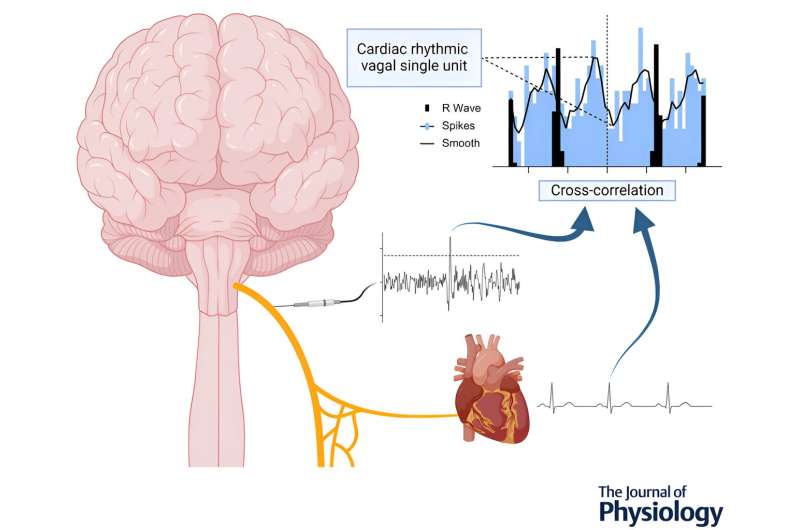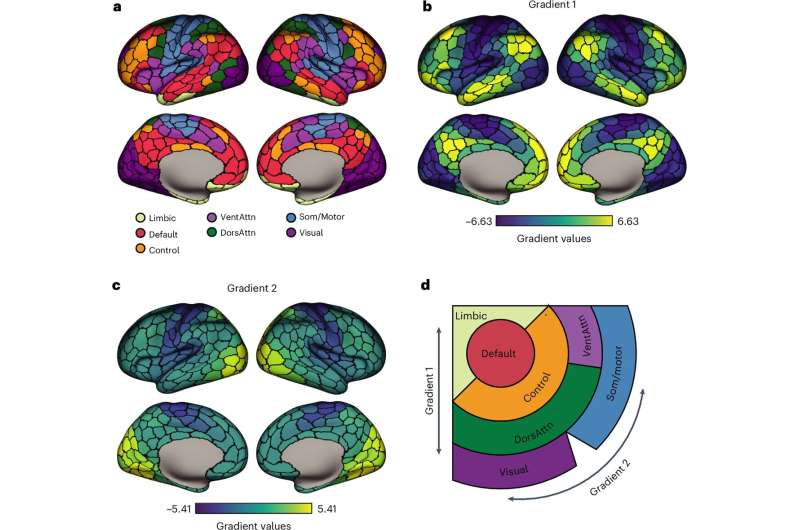
Scientists have uncovered how different types of brain cells work together to form large-scale functional networks in the human brain—interconnected systems that support everything from sensory processing to complex decision-making—paving the way for new insights into brain health and disease.
A new neuroimaging marker of cerebral small vessel disease is related to general cognition and may serve to identify persons at risk of dementia in future clinical trials, a landmark study has found.
A recent study reveals that the genetic mutation causing Huntington’s disease (HD) enhances brain development and intelligence in early life, but leads to degeneration in adulthood. Children with the HD gene exhibit larger brains and higher IQs than those without the mutation.
In what could one day become a new treatment for epilepsy, researchers have used pulses of light to prevent seizure-like activity in neurons.
A team of researchers has found that certain factors are linked to faster brain shrinkage and quicker progression from normal thinking abilities to mild cognitive impairment (MCI). People with type 2 diabetes and low levels of specific proteins in their cerebrospinal fluid showed more rapid brain changes and developed MCI sooner than others.
A new study explores how brain waves reflect melody predictions while listening to music.
Neuroscientists have identified the binding site of low-dose ketamine, providing critical insight into how the medication, often described as a wonder drug, alleviates symptoms of major depression in as little as a few hours with effects lasting for several days.
New research indicates that cannabis use causes cellular damage that increases the risk of highly cancerous tumors by disrupting mitochondria and damaging DNA.
Fampridine, used for improving walking in multiple sclerosis, may also enhance working memory in individuals with schizophrenia or depression. A study found that the drug significantly improved working memory in participants with initially poor performance, but had no effect on those with strong baseline memory.
A recent study links satellite and brain imaging data to identify how environmental factors can impact mental health, cognition and brain development in young people.
A new Alzheimer’s test collects just a few drops of blood from a finger prick, which can be mailed to a lab for analysis. The test measures biomarkers like pTau217 and has shown similar accuracy to traditional venous blood sampling.
Children born to mothers who take antiseizure medications during pregnancy may face increased risks of neurodevelopmental conditions, according to new data.
Researchers have shed light on the puzzling relationship between dopamine and rest tremor in Parkinson’s disease, finding that preserved dopamine in certain brain regions may actually contribute to tremor symptoms, challenging common beliefs.
New research has revealed the diverse assembly and regulation of Type-A GABA receptors (GABAARs), which are crucial for balancing brain activity.
A recent study has found fascinating similarities in how the human brain and artificial intelligence models process language. The research, published in Nature Communications, suggests that the brain, like AI systems such as GPT-2, may use a continuous, context-sensitive embedding space to derive meaning from language, a breakthrough that could reshape our understanding of neural language processing.
A team of researchers has investigated the composition and communication of cells in so-called subcortical lesions, tissue damage to deep brain structures at different stages of multiple sclerosis.
Care for stroke survivors urgently needs to focus on non-motor skill outcomes such as fatigue, anxiety and reduced social participation to improve survivors’ quality of life and minimize care needs, according to a new study.
An international research collaboration has discovered how unusual spherical structures form in the brains of people with a mutation that causes a form of inherited Alzheimer’s disease.
A new study identifies previously hidden brain network patterns in schizophrenia by focusing on nonlinear connectivity, offering potential biomarkers for early diagnosis. Traditional imaging methods often overlook these patterns, but researchers developed advanced statistical tools to uncover this new dimension of brain organization.
Finally this week, research published in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society has identified several community-level factors that may increase people’s risk of experiencing cognitive impairment.