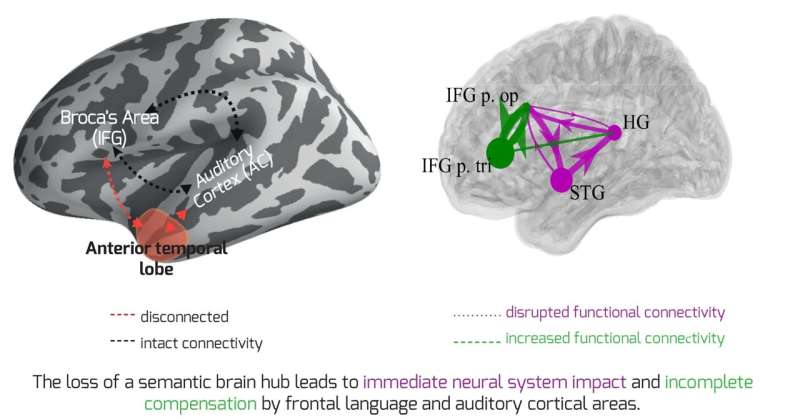
Researchers have developed a precise map of what is happening in the cerebral cortex when someone hears a melody.
Scientists have made a groundbreaking discovery, identifying a rare lipid as a crucial factor in ferroptosis, a unique form of cell death. The findings provide new detail on how cells die during ferroptosis and could improve understanding of how to stop ferroptosis in contexts where it is harmfully occurring– in neurodegenerative diseases, for example– or induce it in contexts where it could be useful, such as using it to kill dangerous cancer cells.
Our brains are “programmed” to learn more from people we like – and less from those we dislike. This has been shown by researchers in cognitive neuroscience in a series of experiments.
An intensive meditation-based intervention (iMI) significantly improves positive symptoms, particularly refractory hallucinations and delusions, in male patients with schizophrenia, according to a new study.
Indigenous people may be more likely to have a stroke than non-Indigenous people, according to a systematic review that looked at populations around the world.
A new study highlights the critical link between sleep, circadian rhythms, and psychiatric disorders, suggesting that disturbances in sleep and internal body clocks can trigger or exacerbate mental health issues. The research underscores the prevalence of sleep-circadian disturbances across all psychiatric disorders, pointing to the need for holistic treatments that address these factors.
For individuals with post-COVID-19 condition, cognitive symptoms are common, according to a study published online Feb. 14 in JAMA Network Open.
Researchers have developed an artificial intelligence model that accurately determines the sex of individuals based on brain scans, with over 90% success. This breakthrough supports the theory that significant sex differences in brain organization exist, challenging long-standing controversies.
A new population-based study reveals the roles of maternal and fetal genes in the growth of a baby’s cerebral cortex.
A new study explains how dopamine influences movement sequences, offering hope for Parkinson’s disease (PD) therapies. Researchers observed that dopamine not only motivates movement but also controls the length and lateralization of actions, with different neurons activating for movement initiation and reward reception.
New research sheds light on what goes on inside people’s heads as they make decisions to obtain information about the future.
Moderate/severe and penetrating traumatic brain injury (TBI) are associated with an increased risk for subsequent development of brain cancer, according to a study published online Feb. 15 in JAMA Network Open.
For the first time, researchers have mapped out the proteins implicated in the early stages of motor neuron disease (MND).
In a study published in the Journal of Neuroscience, scientists demonstrated the effectiveness of using low-intensity focused ultrasound to modulate the activity in a critical region in the brain that processes and regulates pain signals.
Finally this week, new research shows how empathy can be socially transmitted.