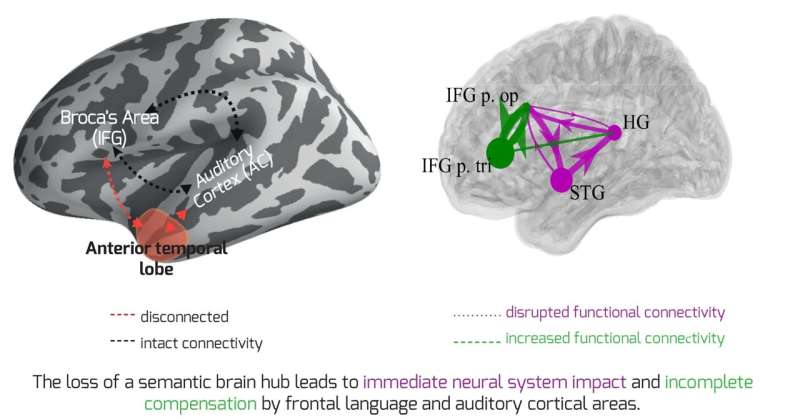
A new way of mapping activity and connections between different regions of the brain has revealed fresh insights into how higher-order functions like language, thought and attention, are organized.
Researchers at the University of Copenhagen have demonstrated that the brain’s ability to learn certain skills can be significantly enhanced if both the brain and nervous system are primed by carefully-calibrated, precisely-timed electrical and magnetic stimulations. This new research has the potential to open entirely new perspectives in rehabilitation and possibly elite sports.
A study of patients with epilepsy shows how making new neurons benefits cognition.
New AI software can read the brain scans of patients who have had a stroke to more accurately pinpoint when it happened and help doctors work out whether it can be successfully treated. It is hoped that the new technology will ultimately enable faster and more accurate emergency treatment of patients in a hospital setting.
Researchers have discovered the structural details of a brain receptor called GPR6, which could lead to new treatments for Parkinson’s disease.
Living in disadvantaged neighbourhoods is associated with higher blood pressure and lower cognitive performance, even in individuals without mild cognitive impairment. Researchers analyzed over 500 adults, finding that poor social and economic resources in neighborhoods exacerbate cardiometabolic health issues and reduce brain function.
Scientists have developed a new approach to learning through noninvasive manipulation of brain activity patterns.
A new study is helping solve the mystery as to why the brain shrinks in a unique pattern, known as atrophy, in chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE). Published in Acta Neuropathologica, this research provides novel evidence that cumulative repetitive head impacts are driving the specific patterns of brain degeneration found at the base of the folds of the surface of the brain, known as the cortical sulcus.
A global research collaboration has revealed a hidden cause of a rare intellectual disorder associated with severe language delay, epileptic seizures, motor impairment and brain abnormalities.
A multi-sensory digital treatment protocol, incorporating sensory integration, sensory substitution, and sensory masking (e.g., blindfolding), significantly improved participants’ performance on spatial memory tasks. Resting-state fMRI analysis showed that these improvements were associated with enhanced connectivity between memory-related brain regions, executive frontal areas, and the default mode network (DMN).
People with high blood pressure who also lack sleep may be at increased risk of reduced cognitive performance and greater brain injury, new research has found.
Researchers have uncovered a groundbreaking mechanism called Electro-Calcium (E-Ca) coupling that integrates electrical and calcium signaling in brain capillaries. This process ensures precise blood flow delivery to active neurons, crucial for brain health and cognitive function.
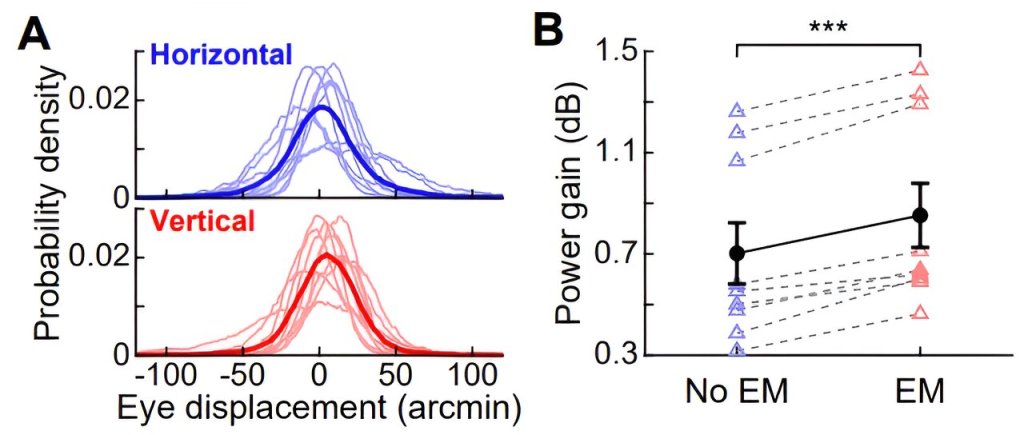
Researchers at the University of Helsinki have made a breakthrough in understanding what neural mechanisms allow the extreme sensitivity of human vision in darkness.
New research reveals that music can do more than trigger memories—it can alter their emotional tone. When participants recalled neutral stories while listening to emotionally charged music, they later remembered the stories as matching the music’s mood. These findings hint at music’s potential for therapeutic interventions, like reframing negative memories in depression or PTSD.
Finally this week a recent study has found that high blood sugar may impair brain health even in people without diabetes.