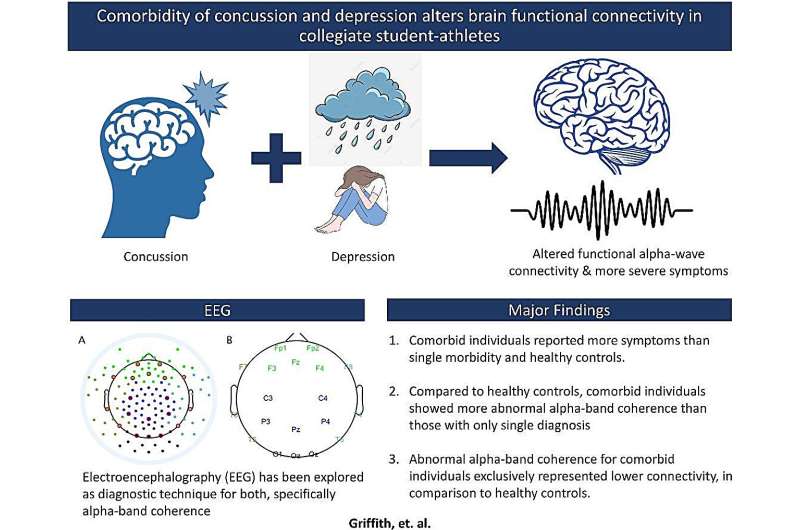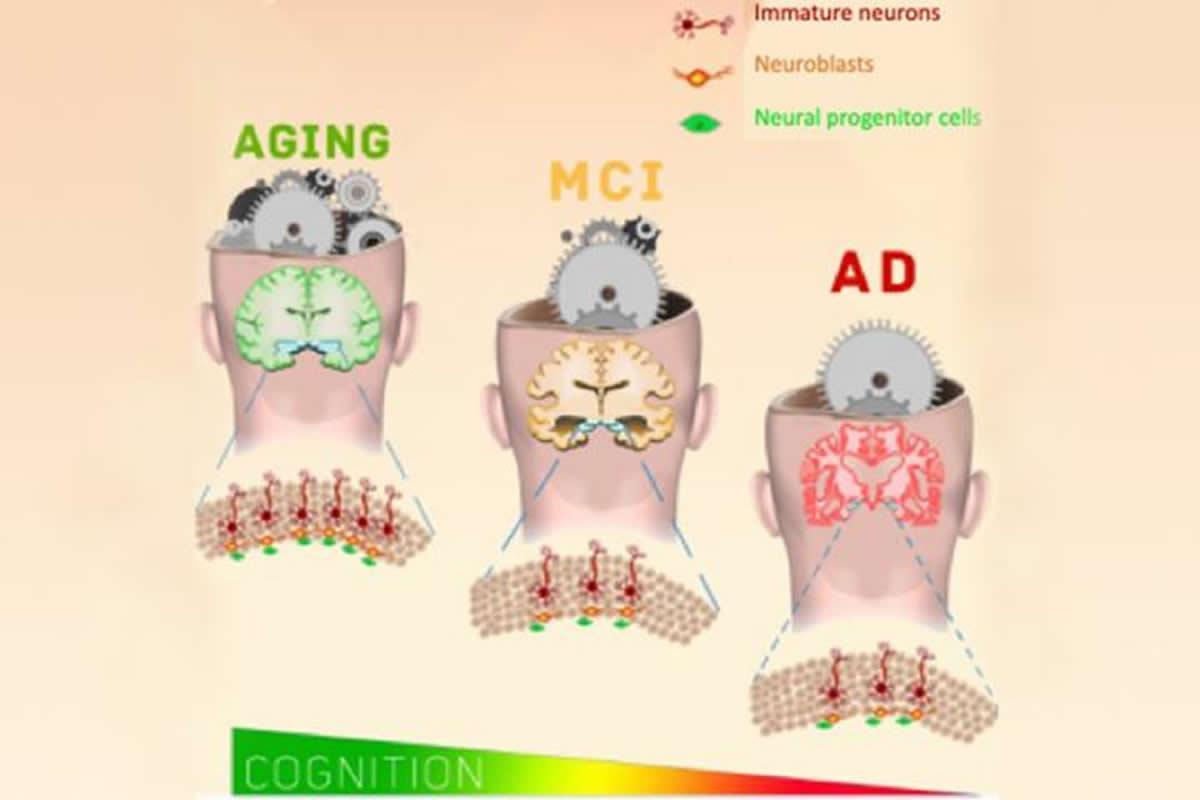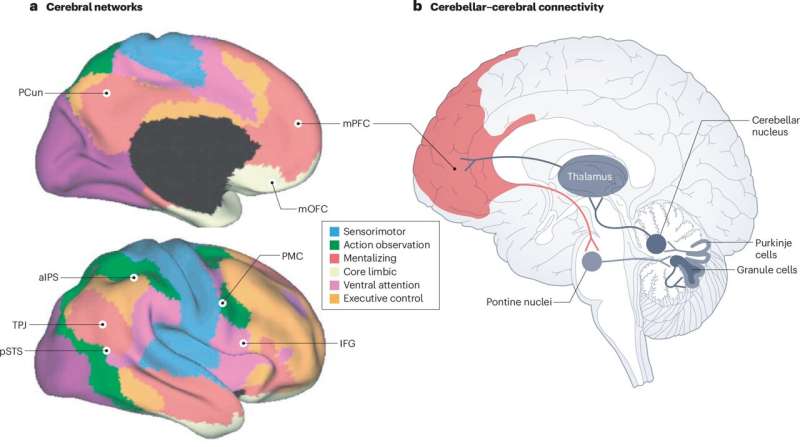
A recent publication in Nature Reviews Neuroscience sheds light on the often-overlooked role of the cerebellum in both motor and social-cognitive processes.
New research has shown that Alzheimer’s disease impacts the brain in two primary phases: an early, gradual phase that damages select cell types and a late phase marked by rapid, widespread damage as symptoms emerge.
Playing video games may boost your cognitive abilities and exercise can improve your mental health, but not the other way around, a large-scale study has found.
A large meta-analysis of over 600,000 people shows that experiencing loneliness significantly raises the risk of developing dementia by 31%. Researchers found that loneliness is a key factor in cognitive decline, contributing to conditions like Alzheimer’s disease, regardless of age or sex.
Researchers have found that senescent cells—non-dividing “zombie” cells—accumulate in the skin as people age and may influence aging in other parts of the body.
A new study reveals that visual clutter alters how information flows between neurons in the brain’s primary visual cortex, but not the order in which it’s processed. Researchers found that the efficiency of information transfer changes depending on the location of clutter in the visual field.
An innovative study, published in Nature Communications, reveals the mechanism behind two seemingly contradictory effects of fear memories: the inability to forget yet the difficulty to recall.
After only one to three days of a whiplash injury, scientists can predict which patients will develop chronic pain based on the extent of cross “talk” between two regions of the brain, and the person’s anxiety level after the injury, according to a new Northwestern Medicine study.
Women who began an aerobic exercise program during chemotherapy for breast cancer reported improved cognitive function and quality of life compared to those who received standard care.
A new study reveals that setting reminders can eliminate some age-related declines in memory. The findings offer a significant breakthrough in addressing the cognitive challenges faced by older adults, particularly in the context of prospective memory, which is the ability to remember to perform an intended action at the right moment, like taking medication or attending appointments.
Concussion researchers have recognized a new concussion sign that could identify up to 33% of undiagnosed concussions.
In a study published in the journal Bilingualism: Language and Cognition, Concordia researchers use neuroimaging methods to examine brain resilience in regions of the brain linked to language and aging. They found that the hippocampus in bilinguals with Alzheimer’s disease was noticeably larger than those who were monolingual when matched for age, education, cognitive function and memory.
People in early middle age who have poor sleep quality, including having difficulty falling or staying asleep, have more signs of poor brain health in late middle age, according to a recent study.
New research shows that prolonged mental exertion weakens connectivity between the brain’s frontal and parietal lobes, impacting cognitive efficiency. However, the brain has built-in compensatory mechanisms that adjust neural connections to preserve function under fatigue.
Finally this week, cannabis use may lead to thinning of the cerebral cortex in adolescents, according to a recent study published in The Journal of Neuroscience.