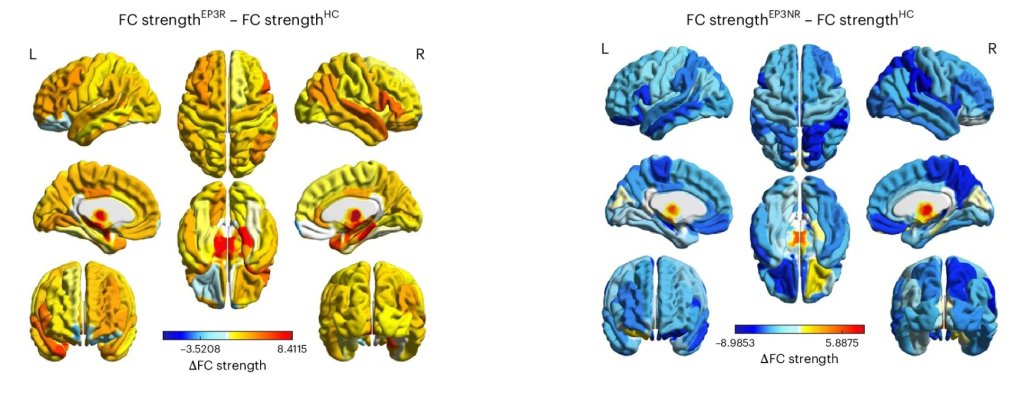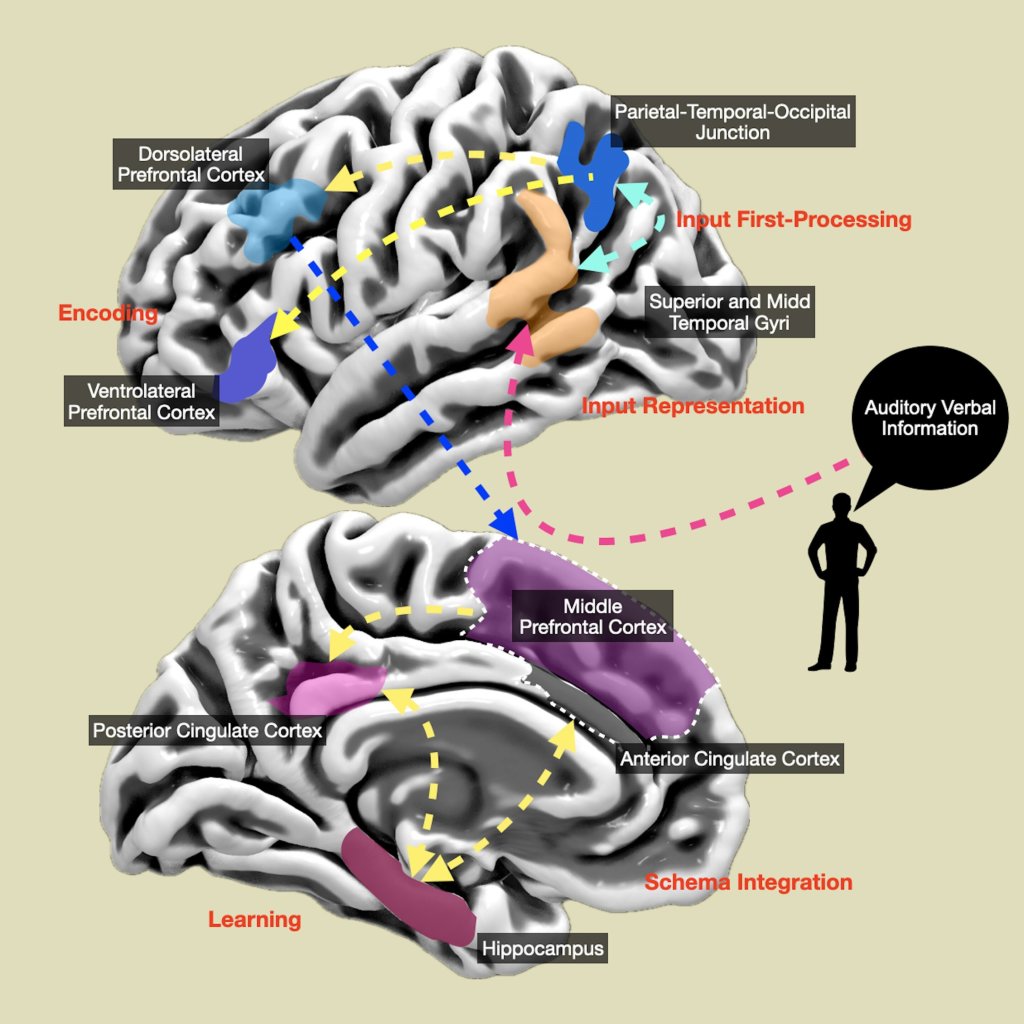
An extensive study has shed new light on the global lifespan changes in the brain’s functional connectivity. Their findings reveal developmental patterns in the brain that could provide valuable information for future investigations into various neuropsychiatric and cognitive disorders.
A new meta-analysis reveals that Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) reduces suicide risk by 34% and all-cause mortality by 30% in individuals with severe depression.
The difference between the brain’s predicted age and actual chronological age, called a brain age gap, may influence the relationship between cognitive impairment risk factors, like high blood pressure and diabetes, and a person’s cognitive performance, also known as thinking and memory skills, according to a study published in Neurology.
Scientists have developed a groundbreaking 3D brain model that closely mirrors the architecture and function of the human brain.
New findings challenge the idea that curiosity simply fades with age. Instead, “state curiosity”—a specific drive to learn—actually intensifies later in life. This increased interest in personally relevant topics among older adults may be a key factor in maintaining cognitive health.
A recent study reveals that prenatal exposure to common air pollutants is associated with subtle but measurable changes in fetal brain structure during the second and third trimesters.
New research shows that the brain’s cortex can rapidly reorganize itself after losing neurons, allowing other nerve cells to take over lost functions. Scientists studied neural networks in the auditory cortex and found that although sound-processing patterns were briefly disrupted, the brain formed nearly identical patterns within days.
A novel study aimed at disentangling the neurological underpinnings of depression shows that multiple brain profiles may manifest as the same clinical symptoms, providing evidence to support the presence of both one-to-one and many-to-one heterogeneity in depression.
Heading a soccer ball alters the brain, research spearheaded by the University of Sydney has found, despite having no immediate impact on cognition.
Results from a new clinical trial reveal that a single dose of psilocybin—a naturally occurring psychedelic compound found in mushrooms—can provide sustained reductions in depression and anxiety in individuals with cancer suffering from major depressive disorder. The findings are published in Cancer.
Finally, this week, new research has found a compelling link between the composition of the gut microbiome and the risk of cognitive impairment in adults.