Scientists have highlighted the most effective treatments for neurological diseases by overcoming one of medicine’s most difficult challenges: the blood–brain barrier. The findings offer new hope for patients with conditions including Alzheimer’s, and Parkinson’s disease, brain tumors, and epilepsy.
A study conducted in Finland showed that changes in the functioning of opioid neurotransmitters in the brain may underlie anorexia.
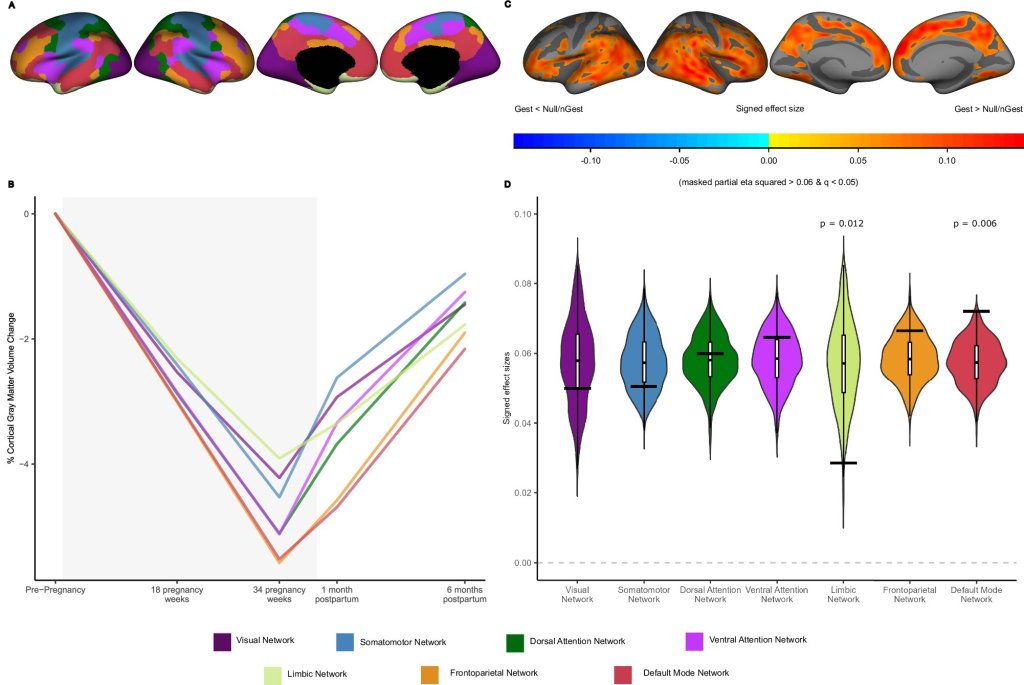
Poorer cardiovascular health in childhood and adolescence may be linked to early differences in brain structure, particularly in areas of the brain known to be affected in dementia in later life, according to a new scientific study.
Researchers have uncovered how specific patterns in brain activity can predict an individual’s sensitivity to pain, expanding opportunities for improved pain management strategies.
Delayed rapid eye movement (REM) sleep may be an early indicator of Alzheimer’s disease. Researchers found that participants with delayed REM sleep had higher levels of toxic proteins associated with Alzheimer’s and reduced levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which supports memory.
The microbial ecosystems in our mouths may impact cognitive function as we age, with pathogenic bacteria linked to cognitive decline.
New research suggests that mood swings in bipolar disorder are regulated by two clocks: the body’s 24-hour circadian rhythm and a dopamine-based clock that influences alertness. When these clocks align at specific intervals, they may trigger shifts between mania and depression.
A study in the Journal of Neuroscience reveals a new mechanism for how brain cells transmit signals from their tips to their nucleus, triggering gene activation crucial for learning and memory.
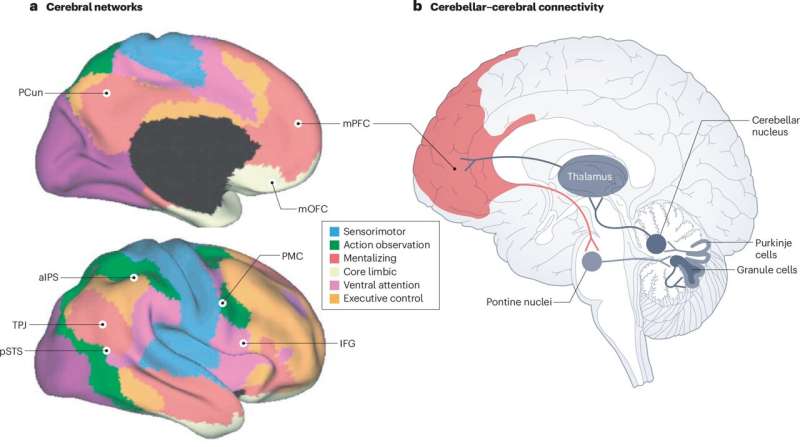
Investigators have discovered that activity in two widely distributed brain networks previously considered separate are actually correlated with each other and together play a key role in recognition memory, according to a study published in Cell Reports.
Cannabinoids offer new hope for safe and effective pain relief.
Researchers analyzed the genetic connection of retinal cells and several neuropsychiatric disorders. By combining different datasets, they found that schizophrenia risk genes were associated with specific neurons in the retina. The involved risk genes suggest an impairment of synapse biology, so the ability of neurons to communicate with each other. This impairment might also be present in the brains of schizophrenia patients.
Researchers at the University of Barcelona have identified a deficit in contrast perception in people with schizophrenia.
A study of nearly 1,000 people with post-COVID-19 syndrome (PCS) revealed that two-thirds still experienced significant symptoms, including reduced exercise capacity and cognitive performance, two years after infection. Persistent symptom clusters included fatigue, neurocognitive disturbances, and post-exertional malaise, with worse outcomes in individuals with obesity, lower education, or severe initial infections.
Finally this week, new research shows diets high in processed meat, fast food, and sugary drinks accelerate biological aging, even in young adults.