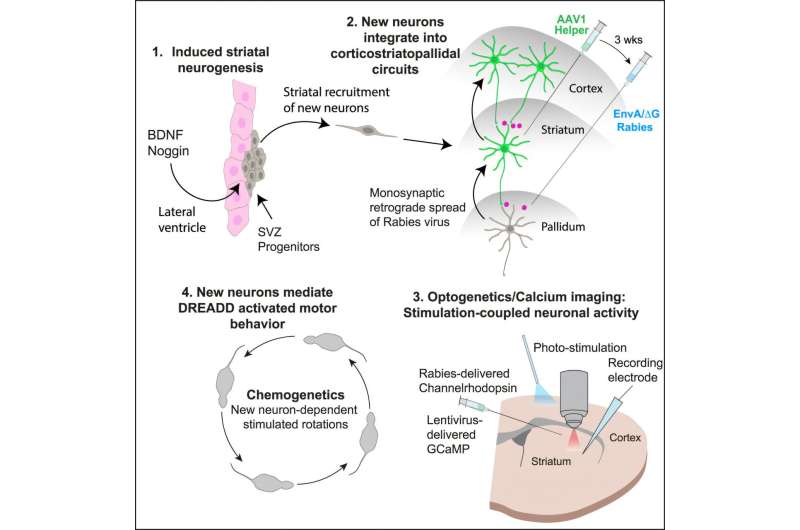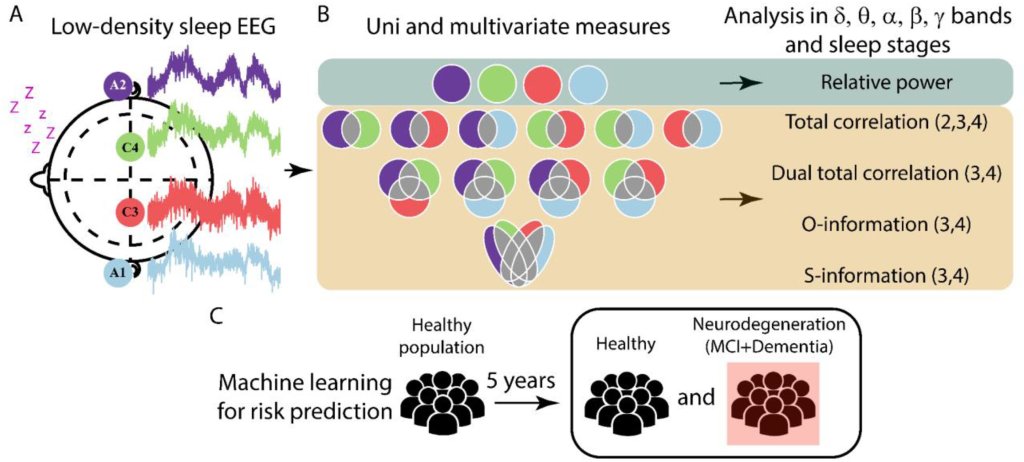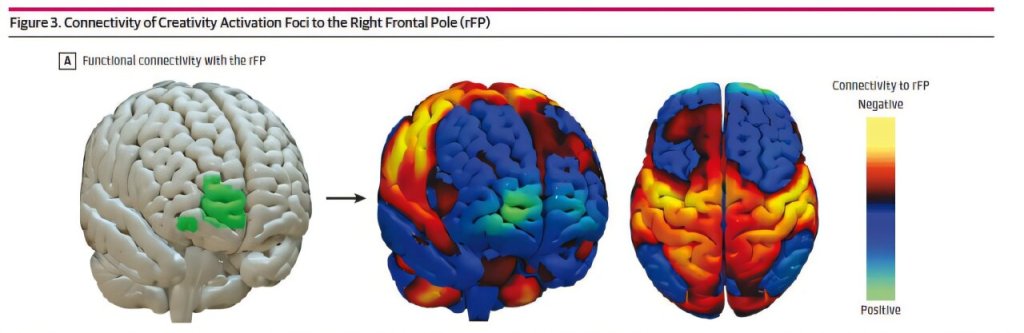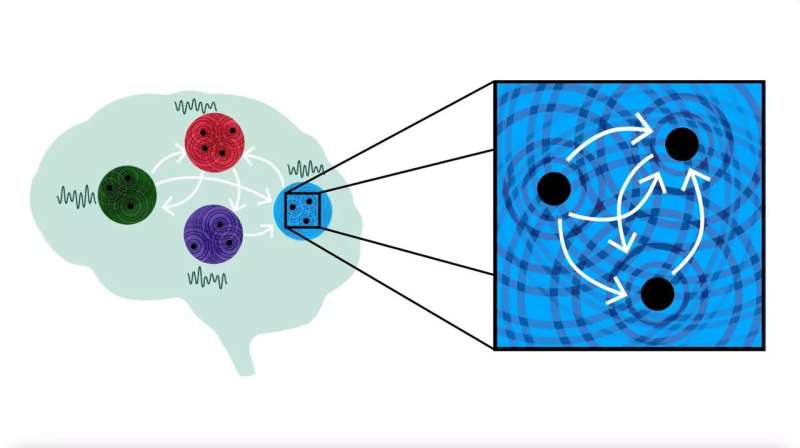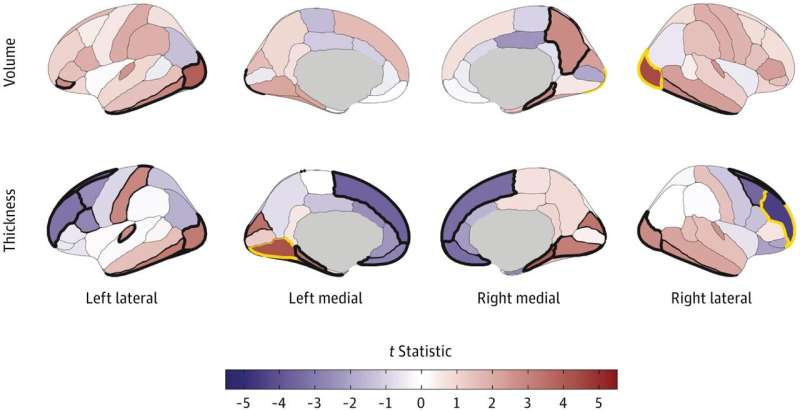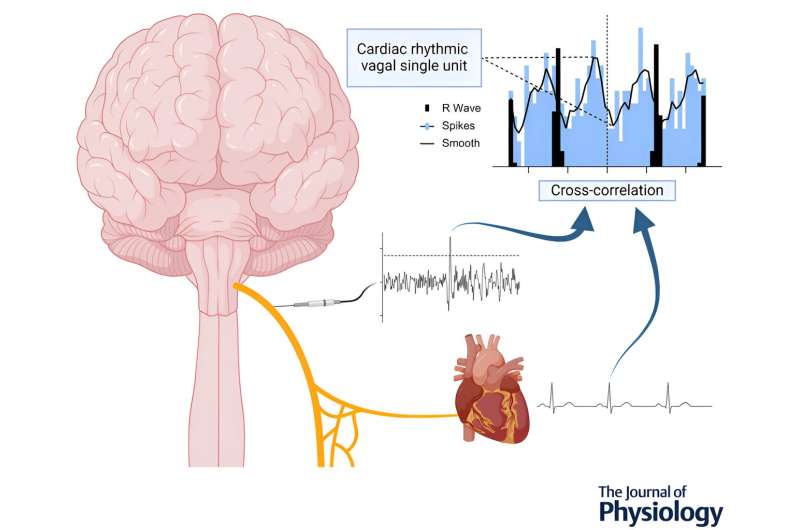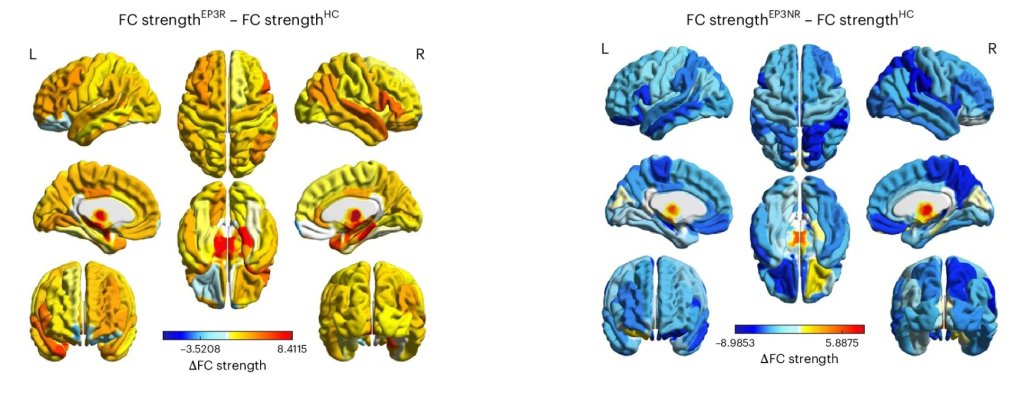
Pioneering research has identified the brain mechanisms that enable psychosis to remit. These findings could significantly inform the development of novel intervention strategies for patients with psychosis.
Contrary to fears of “digital dementia,” new research finds that using digital technology is linked to a reduced risk of cognitive decline in older adults. A large-scale meta-analysis of over 400,000 participants revealed that digital engagement correlates with a 58% lower risk of cognitive impairment.
A simple method of brain stimulation has been shown to change how people make decisions. These were the findings of a new study published in the Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience.
A team of researchers has identified the key brain regions that are essential for logical thinking and problem solving. The findings help to increase our understanding of how the human brain supports our ability to comprehend, draw conclusions, and deal with new and novel problems—otherwise known as reasoning skills.
Medial temporal lobectomy is effective in improving seizure outcomes among patients with drug-resistant temporal lobe epilepsy, according to a recent study.
New research links fatty, sugary diets to impaired brain function. The findings build on a growing body of evidence showing the negative impact of high-fat, high-sugar (HFHS) diets on cognitive ability, adding to their well-known physical effects.
A recent study reveals that the basolateral amygdala plays a key role in calibrating prosocial behavior based on emotional closeness.
New research reveals that gut imbalances in children with autism may influence brain activity and behaviour by disrupting the production of key neurotransmitters like serotonin. Scientists found that changes in gut-derived metabolites are linked to differences in brain structure and function in children with autism.
Chronic pain is closely intertwined with depression. Individuals living with pain’s persistent symptoms may be up to four times more likely to experience depression according to a new study.
Our brains can adapt to filter out repeated distractions, according to a new EEG study. Participants learned to ignore frequent visual distractions, such as a red shape in the same location, while searching for a target.
Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation is showing promise in Alzheimer’s treatment.
A new international study reveals a possible connection between GLP1 receptor agonists—used in drugs like Ozempic—and increased risk of depression and suicidal ideation, especially in people with low dopamine function.
Researchers have found a potential link between the trauma of climate-related events, exemplified by devastating wildfires, and persistent effects on cognitive function.
Researchers have developed a personalized blood test that may offer a faster, less invasive way to track high-grade glioma progression. By identifying unique DNA junctions from each patient’s tumour, the test can detect tumor DNA in the bloodstream, even before changes appear on MRI scans.
A new study demonstrates for the first time that listening to favorite music activates the brain’s opioid receptors.
Promising a more personalized approach to treating major depressive disorder (MDD), a new study reveals that brain connectivity patterns, especially in the dorsal anterior cingulate cortex, can significantly predict patient response to antidepressant medications. This finding was validated in two large, independent clinical trials using brain imaging and clinical information.
Contrary to potential assumptions, recent research demonstrates that the spatial working memory of older people with autistic traits and neurotypical individuals shows no difference in change over time.
A major international study has provided the most comprehensive evidence to date on treatments for neuropathic pain —defined as pain caused by disease of the nervous system, affecting up to 10% of the population worldwide.
Finally, this week, exercise appears to be vital for maintaining sharp minds, even when a key brain energy source is lacking, according to a new study.