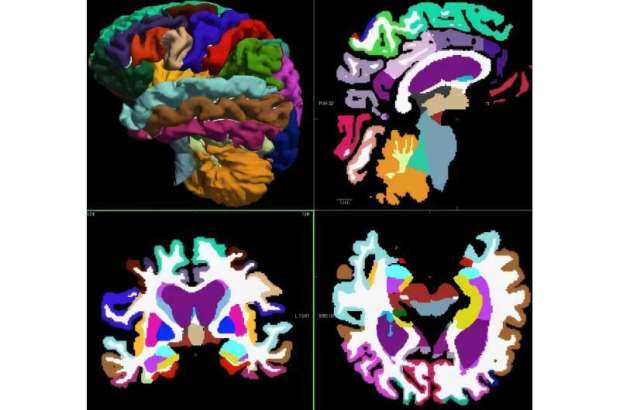
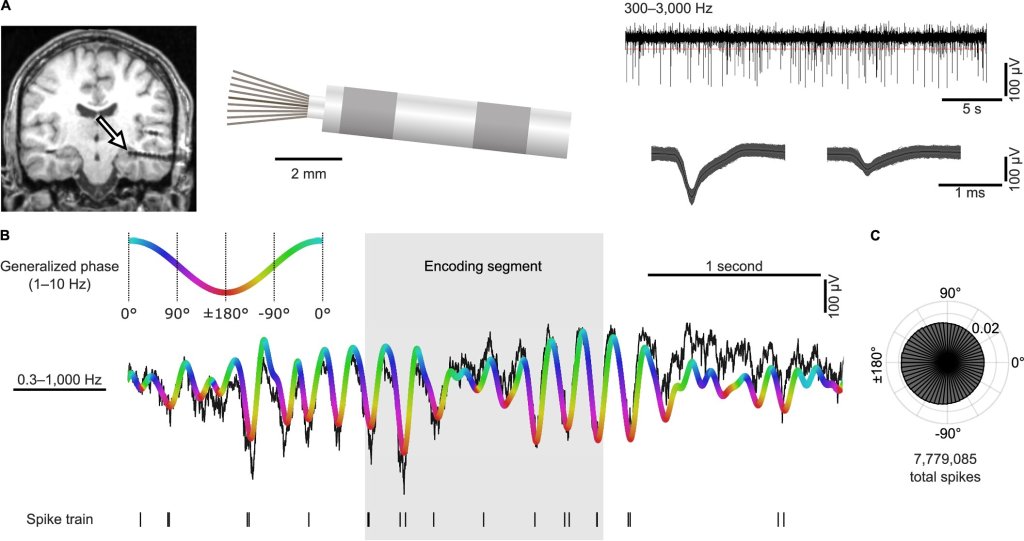
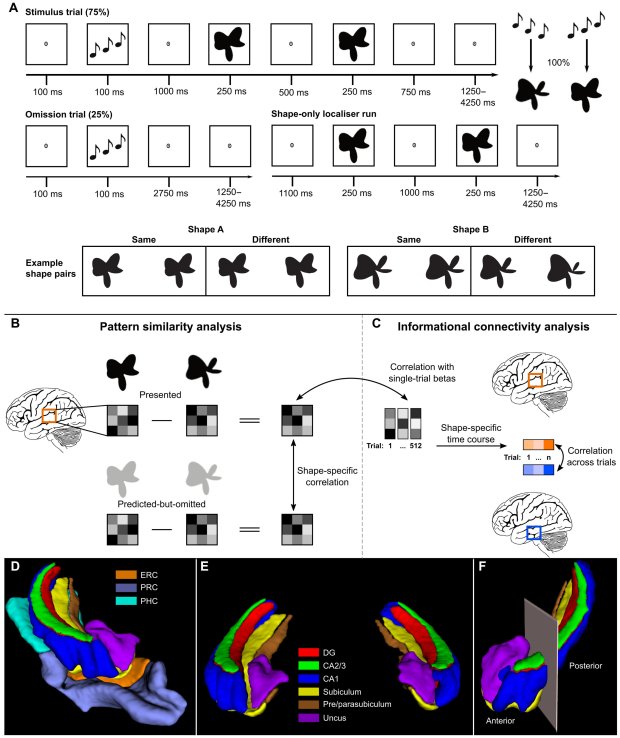
Researchers utilised AI to examine anatomical brain changes, achieving a 93% accuracy in predicting Alzheimer’s disease. Their findings indicate that these changes, including brain volume loss, vary by age and sex.
Lithium—a decades-old treatment for bipolar disorder—may hold potential neuroprotective benefits beyond mood stabilisation. An exploratory clinical trial suggests that low-dose oral lithium may help slow the decline of verbal memory, or ability to remember and recall words and sentences, in older adults with mild cognitive impairment, particularly among those with evidence of amyloid beta—one of the hallmark biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease.
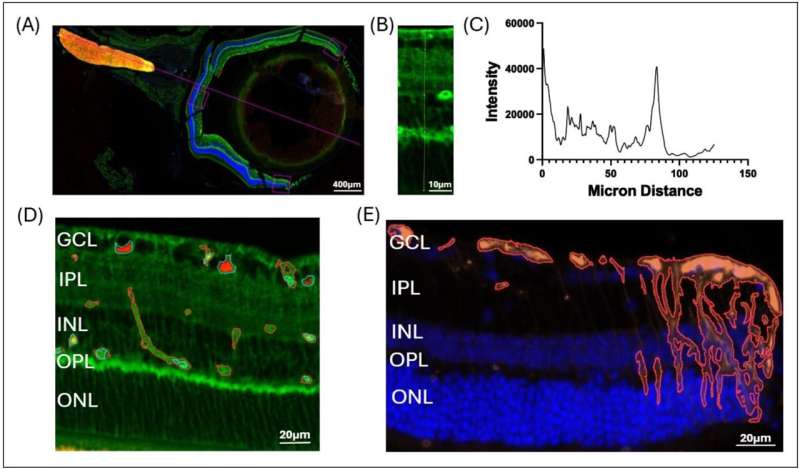
Scientists have discovered new diagnostic markers for multiple sclerosis (MS), a disease that affects 3 million people worldwide.
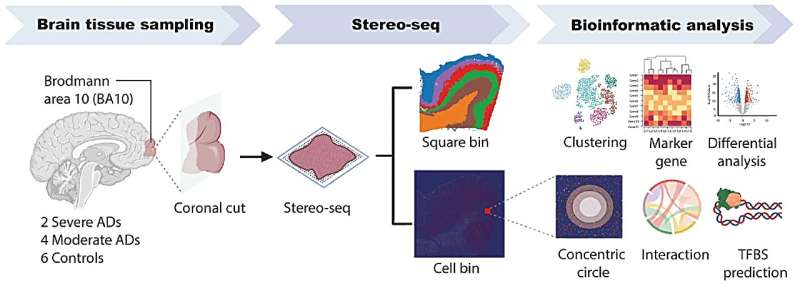
A study published in Nature Communications, has identified specific DNA-level changes in the brains of people with Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Using advanced biological analysis, the team mapped alterations in the brain’s regulatory landscape that may help explain why Alzheimer’s presents and progresses differently from person to person. The findings could also open new avenues for understanding other neurodegenerative diseases.
Researchers have demonstrated through Magnetoencephalography (MEG) that memories can be reactivated in the brain without reaching conscious awareness, indicating these memories persist even when believed forgotten.
Could the deepest parts of the brain hold some of the secrets of sleep that still remain elusive to science? An in-depth study that penetrates into the brain, finding that during the deepest sleep, breathing patterns and brain activity become more independent of one another—unlike in lighter sleep or quiet wakefulness.
New research objectively quantifies multisensory losses in patients with COVID-19. The study, published in BMC Medicine, follows long COVID patients reporting issues in smell, taste, balance, hearing, and brain fog.
Researchers may have found a reason why young adults with autism are about six times more likely to get Parkinson’s disease as they age. Some young adults with autism have issues with dopamine transporters—small molecules in the brain that recycle dopamine—on brain scans usually used to diagnose older adults with Parkinson’s disease.
Why do people with compulsive traits—seen in OCD, addiction, and eating disorders—rely on repetitive habits? A recent study reveals it’s not due to an inability to plan for the future, but rather a paralysis by uncertainty.
A meta-analysis of over 900 scientific papers has mapped the “immune signatures” that determine if our brains recover or decline post-infection. The study reveals that the immune response creates a chemical environment in the brain that can either protect or harm our memory, attention, and processing speed.
Finally, this week, a team of researchers has developed a technology capable of enabling early diagnosis of major neurological disorders, including epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, and schizophrenia, using only a small amount of saliva.