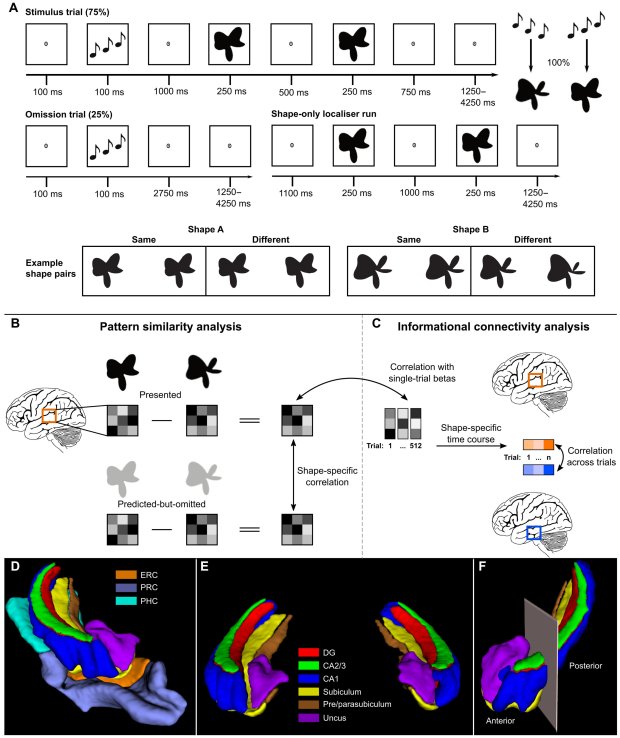
A research collaboration has identified the specific nerve pathways responsible for relaying pain signals from the bowel to the brain, paving the way for new irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) treatments.
Game-based training improves not only the cognitive abilities of people with initial signs of developing dementia, but also leads to positive changes in the brain, according to two new studies.
A next-generation neuroprosthetic hand that restores a sense of touch is moving into a pivotal home-use clinical trial. The “iSens” system uses implanted electrodes to read muscle intent and stimulate nerves, relaying fingertip sensations to the brain so the prosthesis feels embodied.
A new breakthrough demonstrates how robots can now integrate both sight and touch to handle objects with greater accuracy, much like humans.
Researchers have traced a neural mechanism that explains why humans explore more aggressively when avoiding losses than when pursuing gains. Their work reveals how neuronal firing and noise in the amygdala shape exploratory decision-making.
Scientists have found a way to stop brain cancer cells spreading by essentially ‘freezing’ a key molecule in the brain.
Researchers have developed an ultrasound device that can precisely stimulate areas deep in the brain without surgery, opening up new possibilities for neurological research and the treatment of disorders such as Parkinson’s disease.
Artificial intelligence can detect and interpret social features between people from images and videos almost as reliably as humans, according to a new study published in the journal Imaging Neuroscience.
A large study of nearly 13,000 adults found that consuming high levels of certain artificial sweeteners is associated with faster declines in memory and cognitive function over an eight-year period. The effect was particularly strong in people with diabetes and those under 60. While the study does not prove causation, it raises concerns about the long-term brain health risks associated with common sugar substitutes.
Experiments have shown that AI can develop in-context learning abilities after extensive incremental practice, much like humans do.
A new study suggests that autism may be linked to the rapid evolution of brain cell types unique to humans. Researchers have found that outer-layer neurons in the human brain evolved significantly faster than in other apes, with notable changes in autism-associated genes.
A new study shows that brain iron levels, measured using a specialized MRI technique, can predict cognitive decline years before symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease appear.
People with chronic insomnia may experience faster declines in memory and thinking skills as they age—along with brain changes that can be seen on imaging scans—than people who do not have chronic insomnia, according to a study published in Neurology.
Researchers have discovered how the brain develops reliable visual processing once the eyes open.
Scientists discovered how the brain uses objects to anchor our sense of direction, solving part of the mystery of spatial navigation. Experiments in mice showed that cells in the postsubiculum fired strongly when facing an object, while cells in other directions were suppressed, sharpening orientation.
In adults aged 60 years and older, tinnitus, especially severe and prolonged tinnitus, is significantly associated with cognitive impairment, according to a study published in Brain Sciences.
A more precise and personalized form of electric brain stimulation may be a more effective and faster treatment for people with moderate to major depression compared to other similar treatments, according to a UCLA Health study.
Finally this week, researchers may have found a way to limit the debilitating damage strokes can cause.