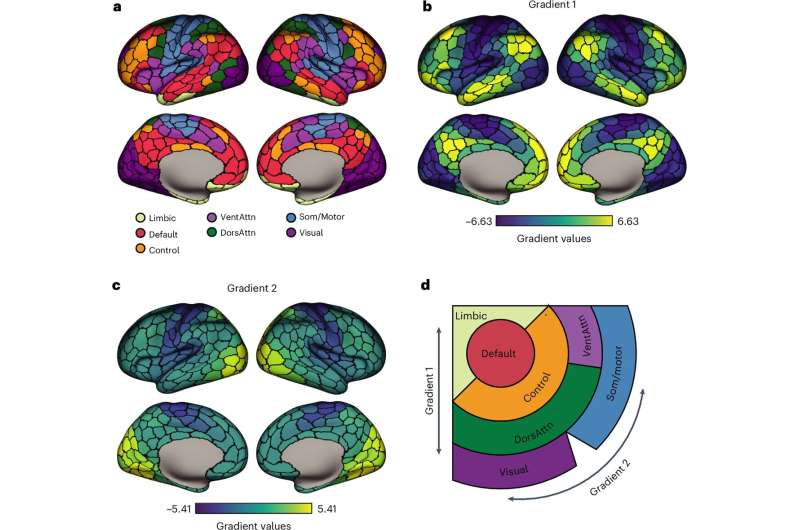
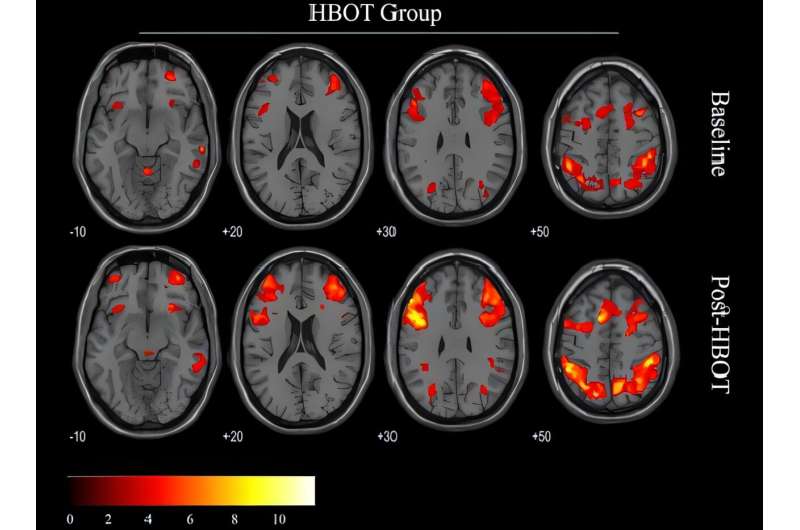
Your brain is the most complex organ in your body, responsible for everything you think, feel, and do. Keeping it healthy is essential for a fulfilling life. Here are 10 things you can do to boost your brainpower:
1. Engage in Regular Exercise
Physical activity isn’t just good for your body; it’s also a powerful brain booster. Exercise increases blood flow to the brain, delivering essential nutrients and oxygen. It also stimulates the growth of new brain cells and improves cognitive function.
Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
2. Prioritize Quality Sleep
Sleep is crucial for consolidating memories and clearing out brain waste products. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
Establish a regular sleep schedule, create a relaxing bedtime routine, and optimize your sleep environment.
3. Challenge Your Mind
Just like muscles, your brain needs to be challenged to stay strong. Engage in activities that require mental effort, such as:
- Learning a new language
- Playing brain games
- Reading challenging books
- Solving puzzles
4. Eat a Brain-Healthy Diet
Nutritious foods provide the fuel your brain needs to function optimally. Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein in your diet.
Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive alcohol.
5. Manage Stress
Chronic stress can damage brain cells and impair cognitive function. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as:
- Meditation
- Yoga
- Spending time in nature
- Listening to music
6. Stay Socially Connected
Social interaction is essential for brain health. Spending time with loved ones, friends, and community members provides mental stimulation and emotional support.
Join clubs, volunteer, or participate in social activities.
7. Learn a New Skill
Learning new things keeps your brain flexible and adaptable. Take a class, learn a musical instrument, or pick up a new hobby.
The challenge of learning something new helps to form new neural connections.
8. Protect Your Head
Head injuries can have serious consequences for brain health. Wear a helmet when engaging in activities that carry a risk of head injury, such as biking, skateboarding, or playing contact sports.
9. Limit Screen Time
Excessive screen time can be detrimental to brain health, especially for children.
*Set limits on screen time and encourage activities that don’t involve screens.
10. Consult a Healthcare Professional
If you have concerns about your brain health, talk to your doctor. They can assess your risk factors and recommend strategies for maintaining optimal brain function.
Early intervention can be crucial for managing conditions that affect brain health.
By incorporating these tips into your daily life, you can take steps to protect your brain and ensure a healthier, happier future.