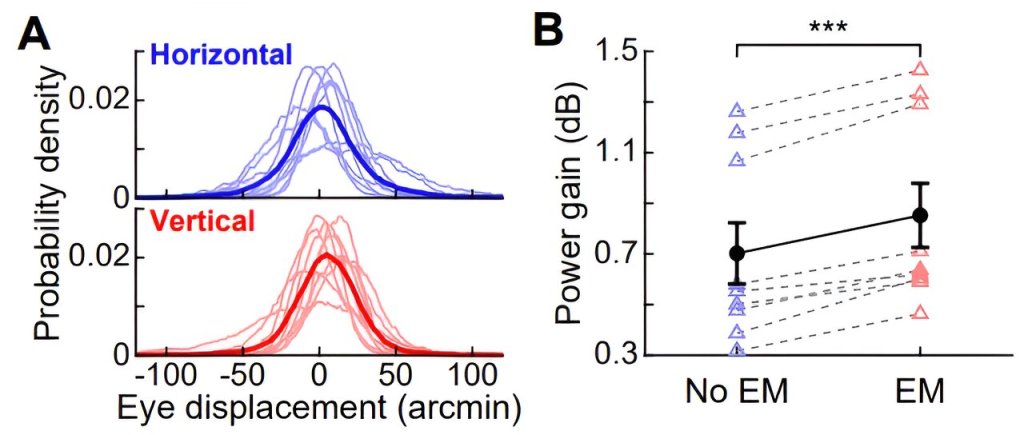
Scientists at the University of Rochester, in the U.S., have found that eye blinking does more than simply wet the eyes—it also helps to keep vision sharp by maintaining the strength of visual signals.
A new study investigates the brain’s mechanisms behind deep focus. The research employs fMRI to explore low-frequency fluctuations in brain networks during focused and less-focused states. The team discovered that certain brain networks synchronize and desynchronize, affecting an individual’s ability to maintain attention. This insight into the dynamic nature of brain activity could lead to better strategies for enhancing focus and attention in various cognitive tasks.
New research indicates that physical activity lowers cardiovascular disease risk in part by reducing stress-related signaling in the brain.
Researchers released new findings on how sex and gender influence cognitive abilities. The research found that while spatial cognition correlates more with biological factors such as sex at birth and hormones, verbal cognition is more influenced by sociocultural factors like gender identity.
Scientists have published a study in Neuron that identified two types of interneurons, the inhibitory neurons of the brain, as instructors of a key developmental process in the brain.
A new study involving jazz guitarists has explored the brain processes that enable creative flow. The research reveals that achieving flow requires a solid foundation of expertise, after which one must learn to relax conscious control to allow creativity to flourish.
Researchers have developed a groundbreaking approach using Diffusion MRI to explore the brain structures of individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD).
A new study emphasizes the importance of brain rhythms in understanding cognition. The research explores how rhythmic electrical fields, generated by neurons, influence and align neighboring neurons, enhancing cognitive function.
The harder your brain works at your job, the less likely you may be to have memory and thinking problems later in life, according to a new study published in Neurology.
Researchers have shed light on how individuals with treatment-resistant depression (TRD) process emotions differently due to abnormalities in the amygdala and prefrontal cortex. By using stereotactic electroencephalography (sEEG), they were able to observe how these brain regions react to positive and negative stimuli, revealing a significant imbalance in emotional processing.
A new study offers new insight into the development of the human forebrain.
Researchers have linked a region in the brain to how humans redirect thoughts and attention when distracted. The connection is important because it offers insights into the cognitive and behavioral side effects of a technique being used to treat patients with Parkinson’s disease.
Finally this week, some people with tough-to-treat epilepsy might benefit if doctors target a brain region newly linked to the disorder, a new study suggests.








