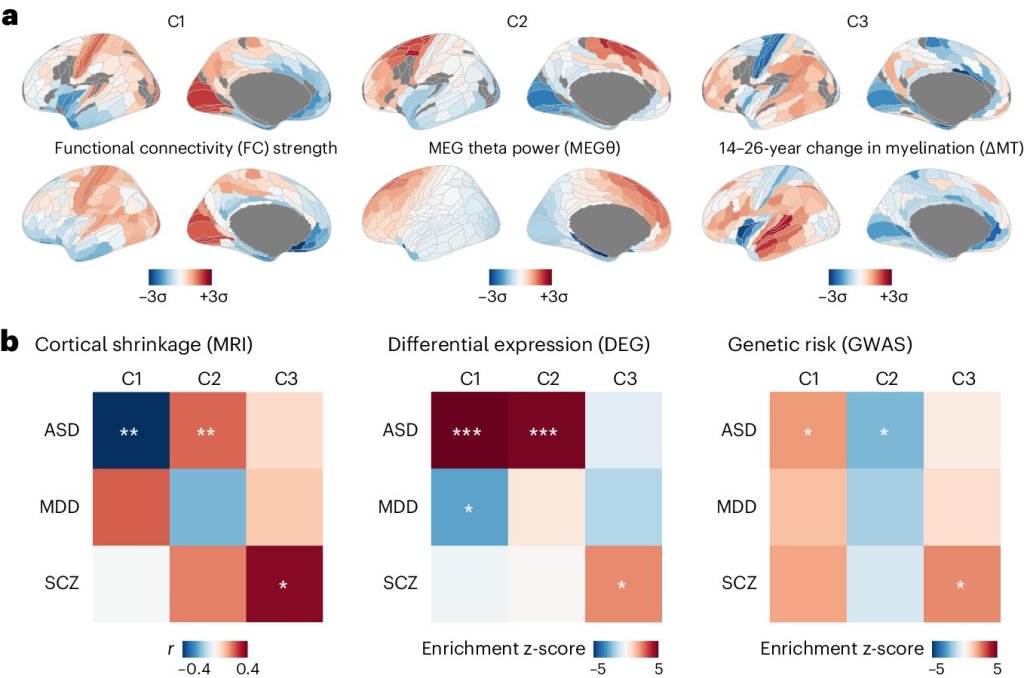

Functional brain networks that are connected to the affective intensity and valence information. Left: The affective valence information is connected to the limbic and default mode networks, and the affective intensity information is connected to the ventral attention network. Right: The probability that the affective intensity and valence is connected to each of seven functional brain networks. Credit: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (2024).
A team of researchers has revealed how the brain processes emotional information of sustained pain and pleasure.
Scientists have uncovered the inner relay of a molecular switch that protects the brain against the development of Parkinson’s disease. The research provides new potential strategies to develop drugs that may benefit patients with Parkinson’s.
Brain-to-brain technology boosts brain-computer interface performance, a new study demonstrates.
Researchers have identified, for the first time, disease-specific reduction in emotional expressivity in Lewy body dementia by quantifying vocal expression of emotions using deep neural network techniques. This reduction in vocal emotional expressions was associated with cognitive impairment and specific brain region atrophy and could serve as a distinguishing factor for individuals with Lewy body dementia.
A new study finds the timing of brain waves shapes the words we hear.
New research has given a precise picture of young children’s developing brains, using a wearable brain scanner to map electrical brain activity. The work opens up new possibilities for tracking how critical developmental milestones, like walking and talking, are underpinned by changing brain function, and how neurodevelopmental conditions like autism emerge.
A new AI technique can identify seizure types, including rare forms of epilepsy.
A new study reveals that a poor quality diet may lead to brain changes associated with depression and anxiety. Researchers found that unhealthy eating habits reduce grey matter and alter neurotransmitter levels in the brain.
Research sheds new light on the contribution of dopamine to reinforcement learning.
A new study uncovered neural mechanisms used in planning, revealing an interplay between the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus. The study shows how the brain imagines future outcomes to guide decisions.
Losing the ability to smell properly—a common sensory deficit as people age—may help predict or even contribute to the development of heart failure, new research suggests.
A new study reveals that the main psychoactive component in cannabis or marijuana disrupts the normal connections and activity of the brain’s prefrontal cortex, a region that is crucial for decision-making and self-control.
Finally this week, people tend to underutilize their visual working memory rather than maxing out its capabilities according to new research.