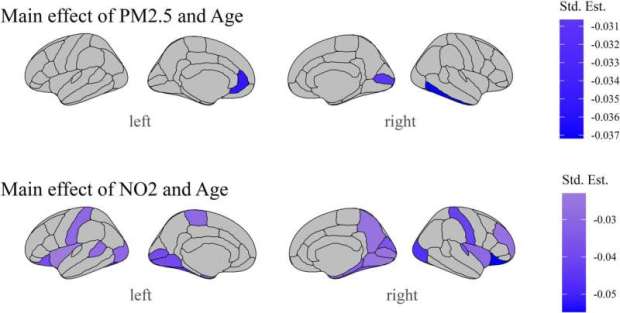
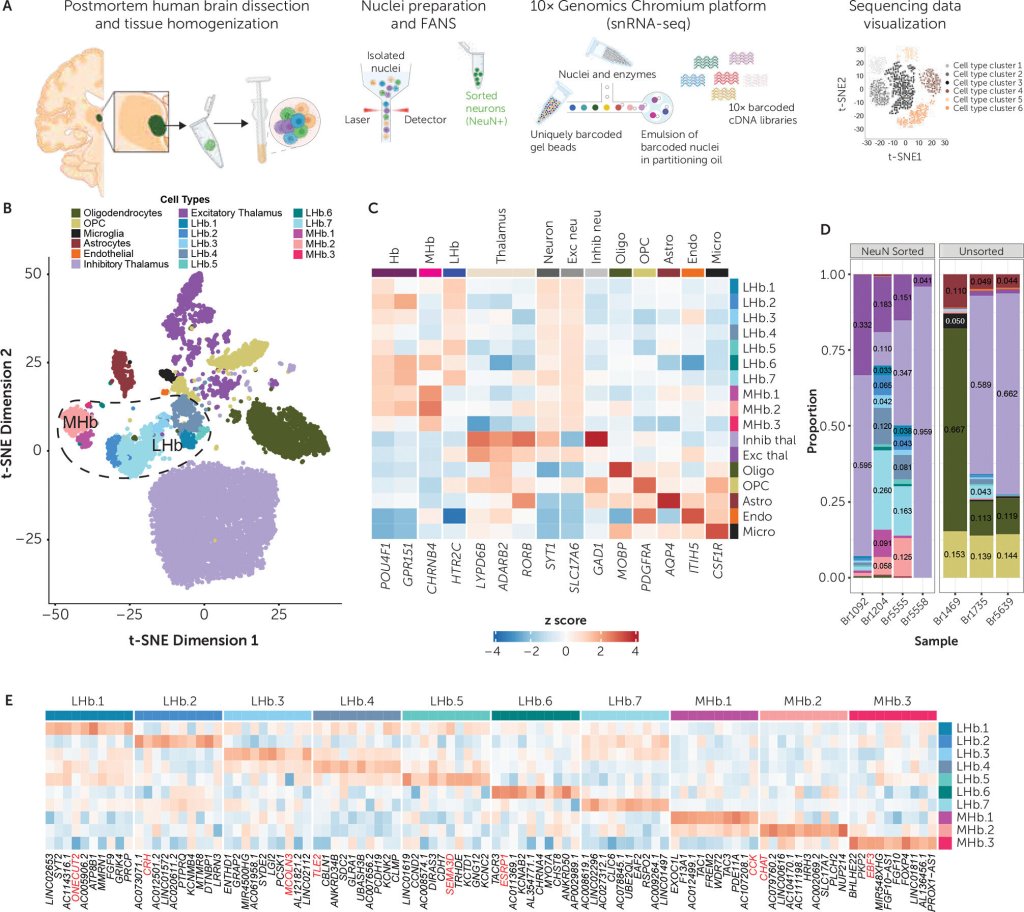
Autistic adults show reduced availability of a key glutamate receptor, mGlu5, across widespread brain regions. This difference supports the theory that an imbalance between excitatory and inhibitory signaling may contribute to autism-related traits.
Using marijuana just once or twice a month was associated with worse school performance and emotional distress for teens, according to a large study of adolescents.
A possible new treatment for impaired brain blood flow and related dementias is on the horizon. Recent research provides novel insights into the mechanisms that regulate brain blood flow and highlights a potential therapeutic strategy to correct vascular dysfunction.
A major review of prior research has found no evidence that menopause hormone therapy either increases or decreases dementia risk in postmenopausal women.
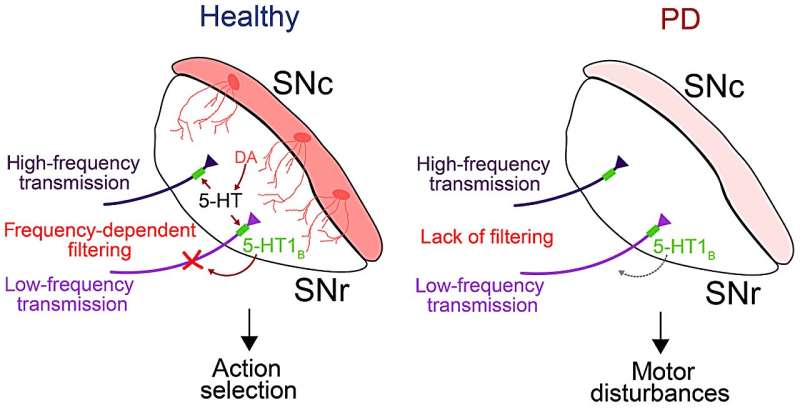
New research has provided the first direct evidence that schizophrenia is associated with a greater release of serotonin in the frontal cortex, and demonstrates its link to a greater severity of some of the most disabling symptoms of the disorder.
A new study has uncovered how children’s play styles differ depending on whether they are playing alone or with someone else, and how these differences relate to their social skills and brain activity.
The secret to a healthier and “younger” heart lies in the vagus nerve. A recent study has shown that preserving bilateral cardiac vagal innervation is an anti-aging factor. In particular, the right cardiac vagus nerve emerges as a true guardian of cardiomyocyte health, helping to preserve the longevity of the heart independently of heart rate.
AI, using a simple blood test combined with standard brain images has, for the first time, been able to identify two biologically distinct types of multiple sclerosis (MS).
A new study comparing stroke survivors with healthy adults reveals that post-stroke language disorders stem not from slower hearing but from weaker integration of speech sounds. While patients detected sounds as quickly as controls, their brains processed speech features with far less strength, especially when words were unclear.
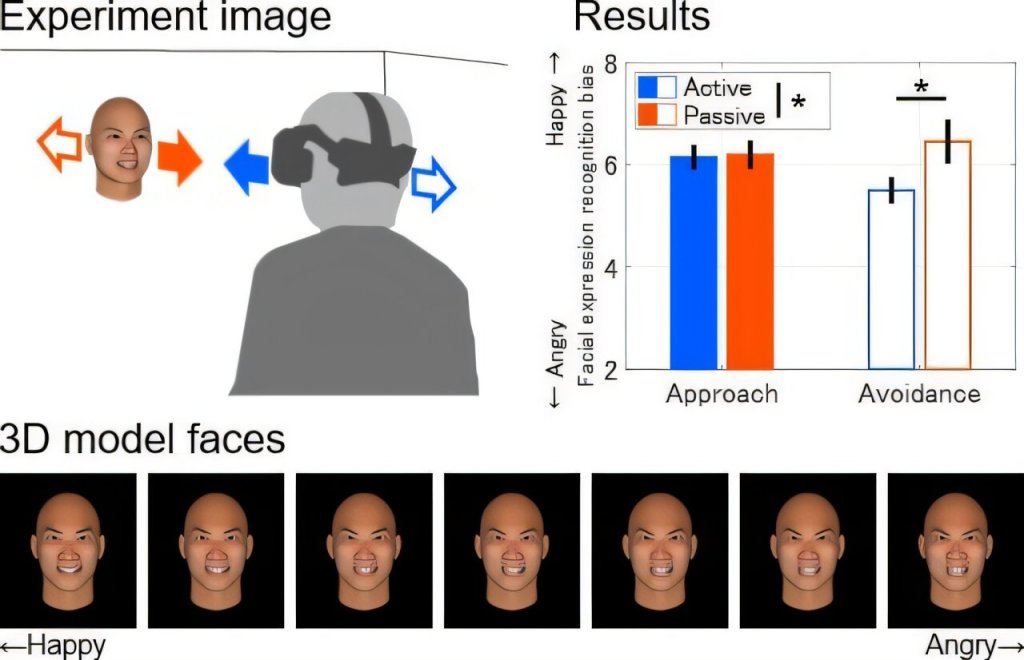
New research reveals that numbers in our visual field can subtly distort how we judge spatial positions, showing that perception is shaped by both numerical magnitude and object-based processing.
Researchers recently carried out a study investigating the possible connection between gut microbiota and the depressive episodes experienced by people diagnosed with Bipolar Disorder. Their findings, published in Molecular Psychiatry, suggest that the microorganisms in the digestive system can directly influence connections between specific brain regions known to be affected by BD depression.
New research has found that high risk of obstructive sleep apnea is linked to poorer mental health in adults over 45.
New research following children for more than a decade links high screen exposure before age two to accelerated brain maturation, slower decision-making, and increased anxiety by adolescence. Infants with more screen time showed premature specialization in brain networks involved in visual processing and cognitive control, which later reduced flexibility during thinking tasks.
A research group has uncovered a key mechanism in the development of Alzheimer’s. The mechanism in question identifies toxic proteins and disposes of them.
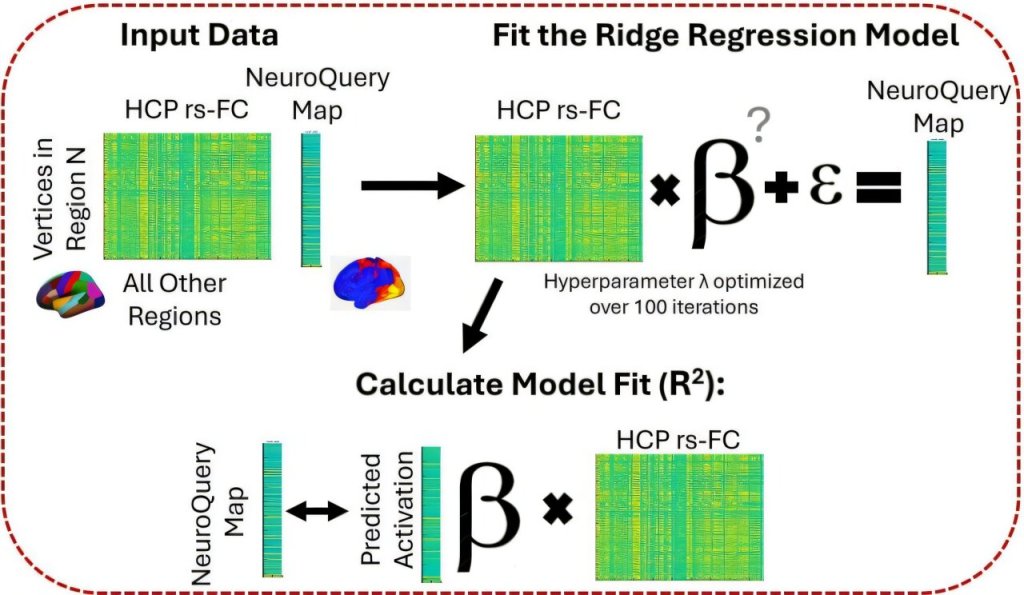
Researchers mapped the brain connectivity of 960 individuals to uncover how neural processes support complex behavior. They found that intrinsic neural timescales—each region’s processing window—are shaped by white-matter pathways that distribute signals. Individuals with a closer match between their wiring and regional timescale demands showed more efficient transitions between behavior-linked brain states.
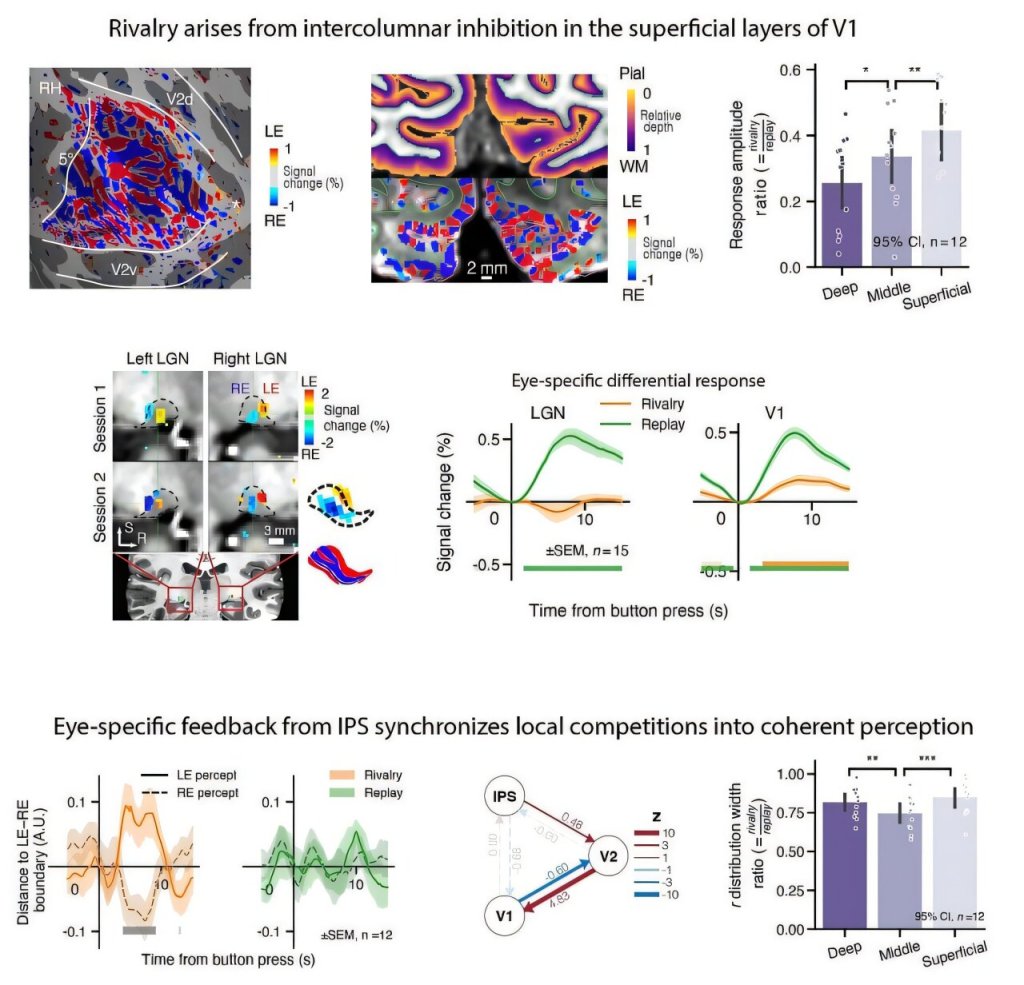
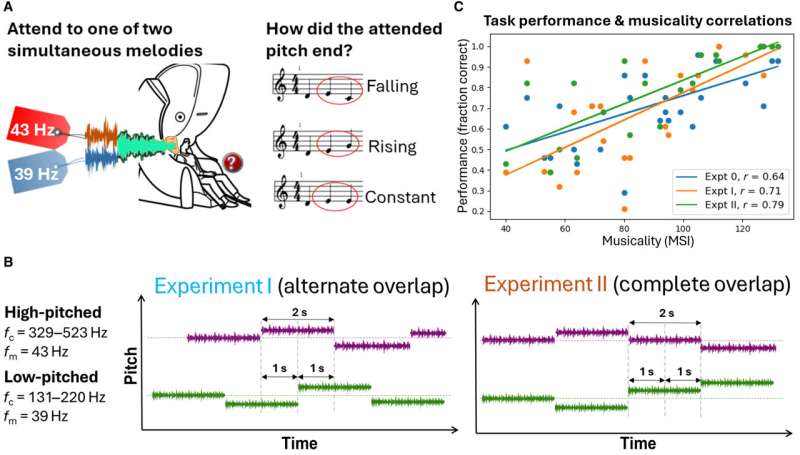
Finally this week, a new study revealed that visual awareness acts as a “conductor” refining the speed and precision of attentional rhythmic sampling.