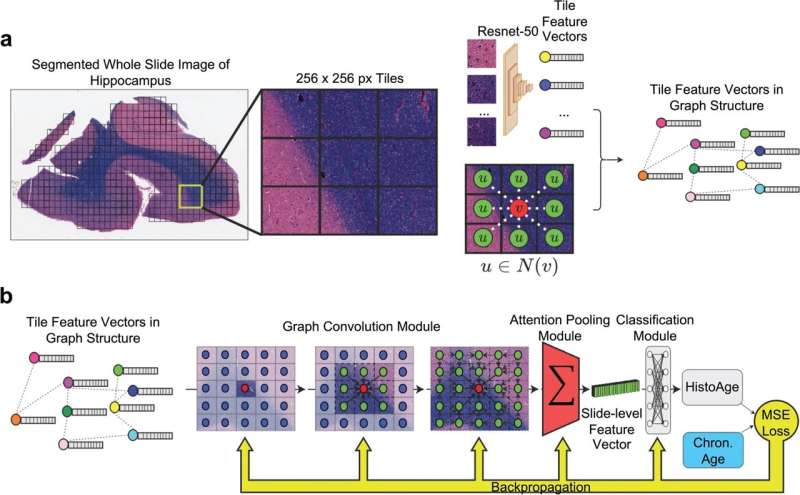
The way in which brains shrink in those who develop Alzheimer’s disease follows no specific or uniform pattern, finds a new study by researchers at UCL and Radboud University in the Netherlands.
A McGill University study has shown that hearing plays a crucial role in how people coordinate and control speech movements in real-time. Published in The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, the research shows that when people cannot hear their own speech, even briefly, their ability to move their jaw and tongue in a coordinated manner is impaired.
Recent research offers novel insights about the biological mechanisms behind major depressive disorder and especially on the role of the immune system.
A new analysis from Imperial’s human challenge study of COVID-19 has revealed subtle differences in the memory and cognition scores of healthy volunteers infected with SARS-CoV-2, which lasted up to a year after infection. The findings, published in the journal eClinicalMedicine, show a small but measurable difference following highly intensive cognitive testing of 18 healthy young people with infection compared to those who did not become infected, monitored under controlled clinical conditions
A simple scoring system may help doctors predict which patients will likely become seizure-free after minimally invasive epilepsy surgery.
The European Commission has released the 10-year assessment of the Human Brain Project (HBP), an EU-Flagship initiative that concluded in 2023. The report highlights that the HBP made major contributions and had a transformative impact on brain research. One of the main outcomes of the HBP is EBRAINS, the open research infrastructure that continues to push neuroscience research forward.
A new, large study from France underscores the link between adult hearing loss and dementia. In addition, hearing loss is linked to loss of volume in critical areas of the brain.
Scientists are investigating the extraordinary longevity of neurons, which can survive for over 90 years, in a new research project. The findings could not only improve understanding of neural aging but also lead to treatments for neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson’s and ALS. The research could potentially expand beyond neurons, offering insights into extending the health span of other cell types.
Bright light therapy is an effective adjunctive treatment for nonseasonal depressive disorder, according to a review published in JAMA Psychiatry.
A recent study has shown that conscious thought relies on synchronized brain rhythms to maintain communication between sensory and cognitive brain regions. Under general anesthesia, this rhythm-based communication breaks down, disrupting the brain’s ability to detect and process surprising stimuli.
A new trial reveals that weekly injections of the weight-loss drug Wegovy (semaglutide) lowered the risk of death from COVID-19 by about a third and reduced overall mortality by 19%.
In a breakthrough study, researchers have imaged a network of pathways in the human brain believed to clear waste proteins that can lead to Alzheimer’s and dementia. Using advanced MRI techniques, they revealed perivascular channels that guide cerebrospinal fluid through the brain, providing strong evidence of the glymphatic system’s role in waste removal.
New research has discovered that disruptions in the brain’s salience network, often tied to tau protein buildup, correlate strongly with behavioural changes in people with early-stage dementia.
A research team has published a comprehensive review on the application of brain network models (BNMs) in the medical field. This study summarizes recent advances and challenges in using BNMs to simulate brain activities, understand neuropathological mechanisms, evaluate therapeutic effects, and predict disease progression.
New research reveals that immune responses play a crucial role in the formation of Lewy bodies, protein aggregates that mark Parkinson’s disease and other neurological conditions.
A new study has found microplastics in human brains for the first time, raising concerns about the potential health impact. Researchers analyzed samples from autopsies and discovered an accumulation of plastic particles in brain tissue, likely due to exposure through food, water, and air. Although the study is still in its preliminary stages, it highlights the need for further investigation into the effects of microplastics on brain health. While microplastics have been shown to cause inflammation and damage in laboratory experiments, their long-term impact on human health remains unclear.
Finally this week, researchers are working on a novel gene therapy that holds potential in treating patients with epilepsy.