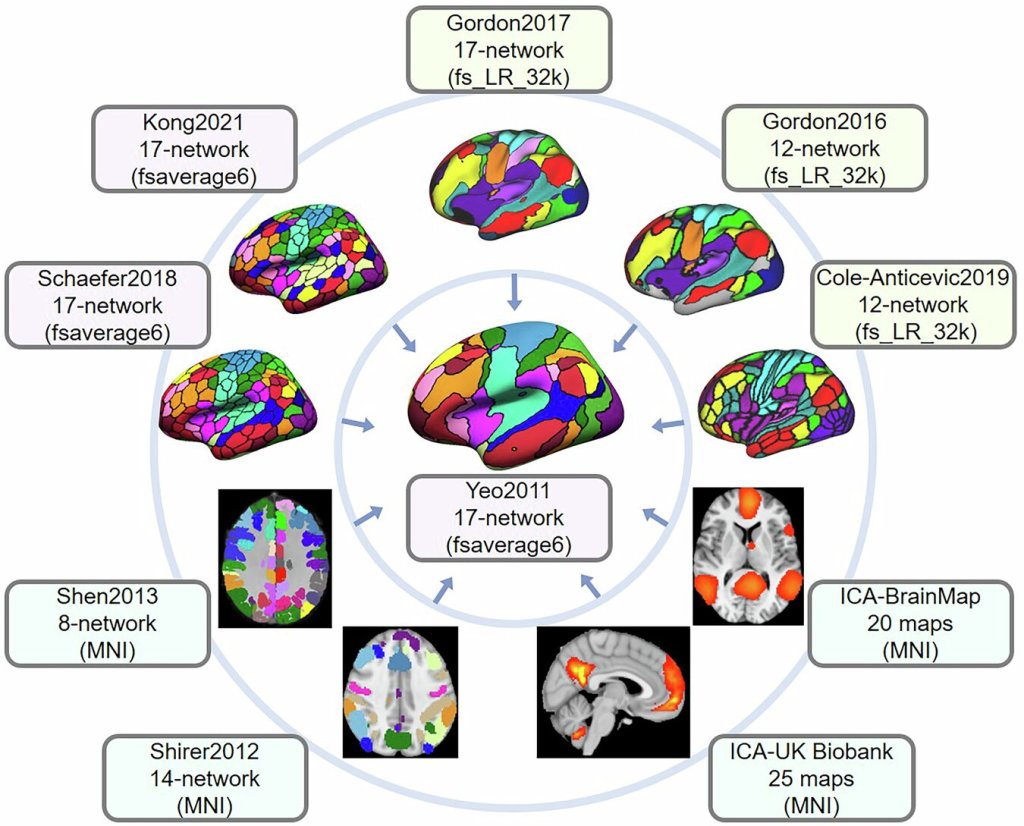
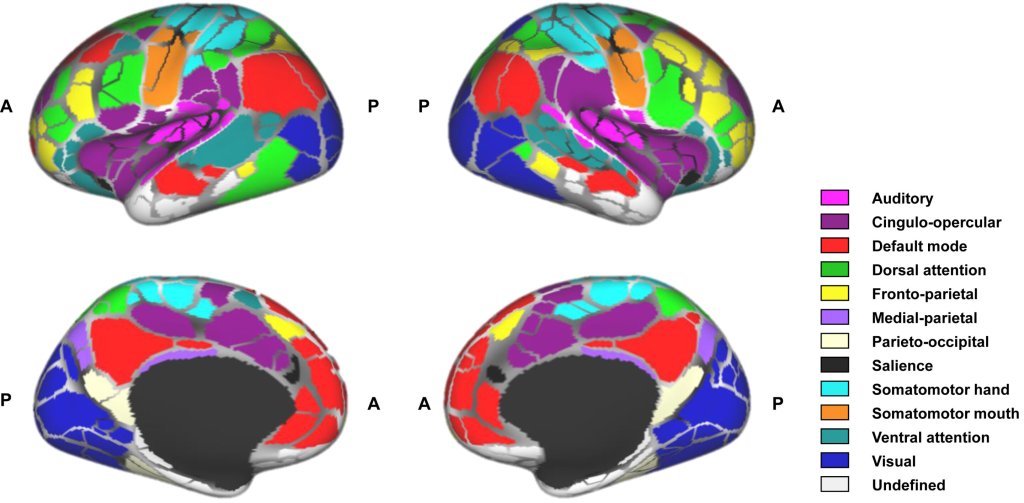
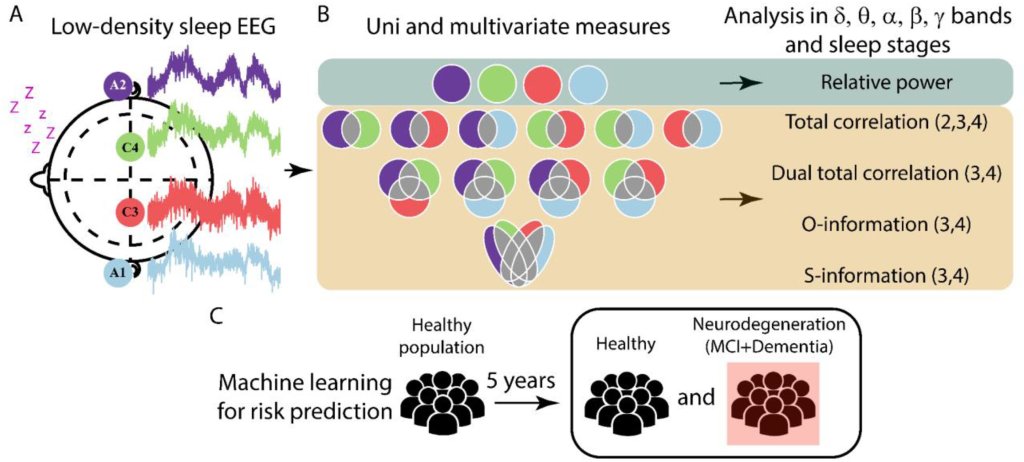
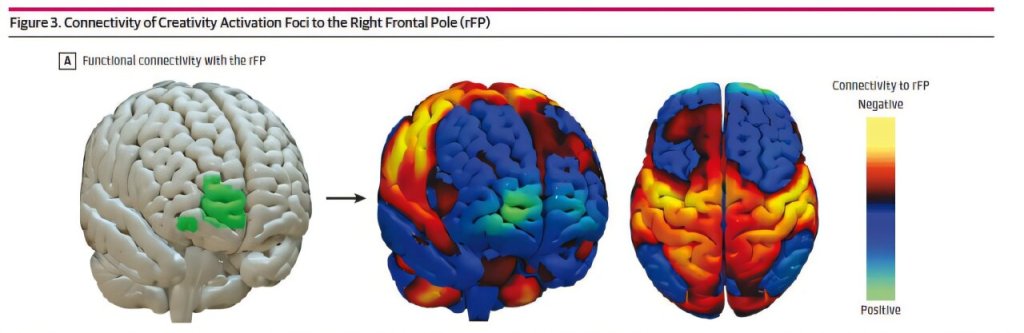
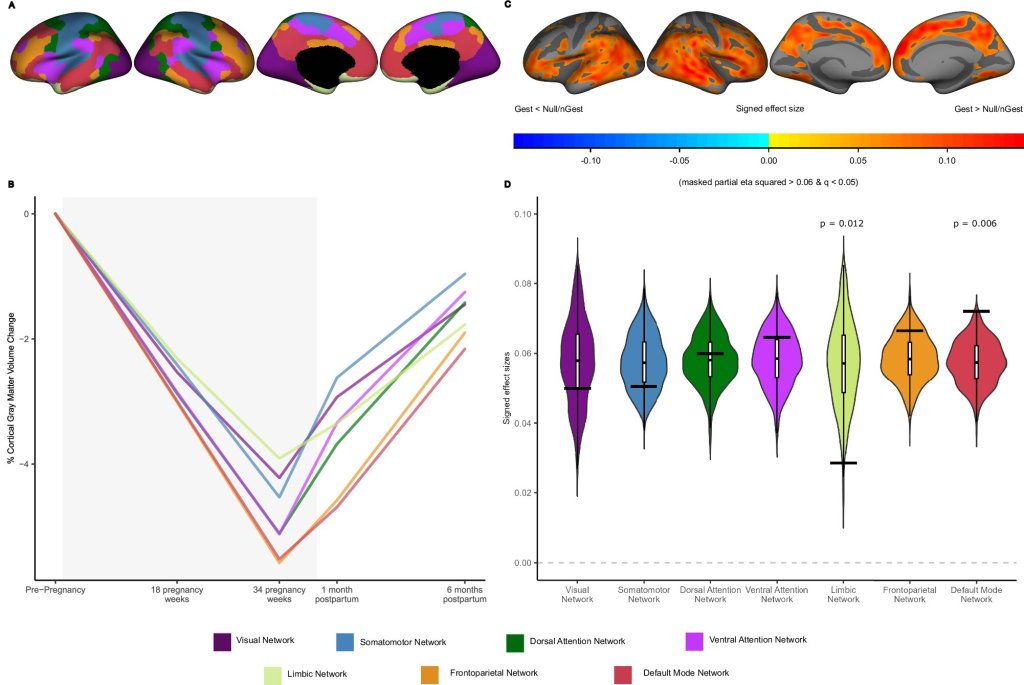
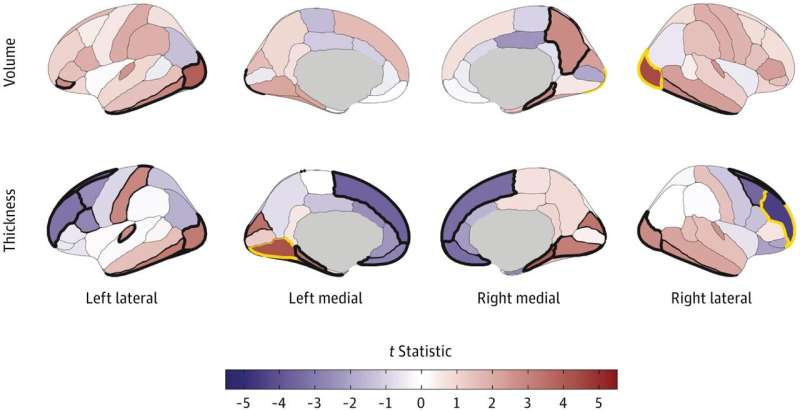
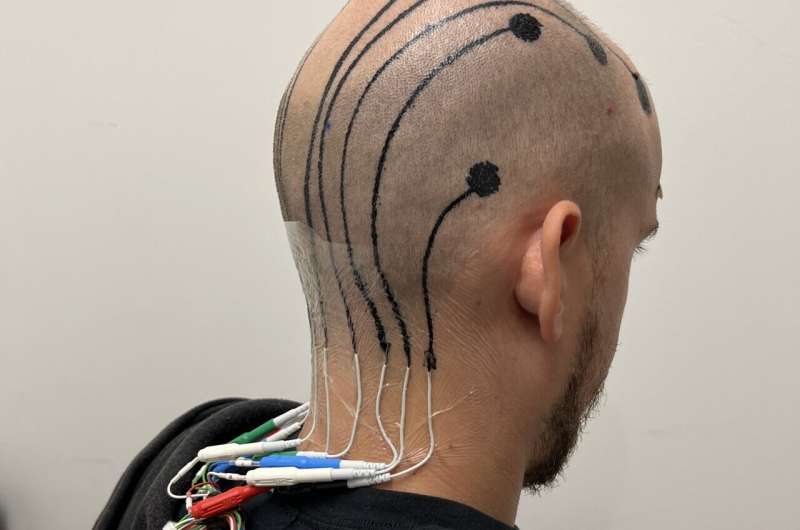
A new wearable brain stimulation device is being developed, aiming to make therapeutic brain stimulation portable and accessible. This technology could potentially allow for on-the-go treatment of various neurological and psychiatric conditions, moving brain stimulation therapy out of clinical settings and into everyday life.
A recent study provides the first detailed cellular insights into how psilocin, the active ingredient in magic mushrooms, promotes the growth and networking of human nerve cells.
Scientists have developed tiny, magnetically controlled robots designed for minimally invasive brain surgery. These robots can perform precise actions like gripping and cutting tissue, guided by external magnetic fields, potentially eliminating the need for large skull openings. The technology aims to significantly reduce patient recovery time and risks associated with traditional neurosurgery.
Marking a breakthrough in the field of brain-computer interfaces (BCIs), a team of researchers has unlocked a way to restore naturalistic speech for people with severe paralysis.
For the first time, scientists have confirmed a neurobiochemical link between dopamine and cognitive flexibility, according to new research published in The Journal of Nuclear Medicine. PET imaging shows that the brain increases dopamine production when completing cognitively demanding tasks, and that the more dopamine released, the more efficiently the tasks are completed. Armed with this information, physicians may soon be able to develop more precise treatment strategies for neurological and psychiatric disorders.
The risk of a full-blown stroke will remain high for at least a decade after a person has a slight brush with stroke, in the form of a transient ischemic attack or minor stroke, a new study says.
By analyzing DNA and proteins in the blood of people with and without acute spinal cord injuries (SCIs), researchers have developed a novel blood test that has the potential to rapidly predict the severity and likelihood of sensory and motor recovery within six months in a cost-effective manner.
A new study has demonstrated that the brains of people who experience migraines and other types of headaches cannot modulate visual stimulation in the same way a person without these conditions can.
Scientists have developed a way to map how individual connections between neurons change across the entire brain during learning, giving scientists a new view into how changes in behaviour show up in the brain. The new imaging method, DELTA, provides scientists with a brain-wide map of how individual synaptic proteins change over time. Proteins important for synaptic plasticity are known to be degraded or synthesized as synaptic connections change.
Research has found that metal particles from artificial joint implants can enter the central nervous system and accumulate in cerebrospinal fluid, raising concerns about potential neurological effects.
Though Alzheimer’s disease is often described as a buildup of proteins in the brain in the form of plaques and tangles, a new study has shown that blood vessels in the brain might hold another important clue to the disease.
Finally this week, virtual reality reveals that curiosity is key in shaping our spatial memory and mental map formation, according to new research.