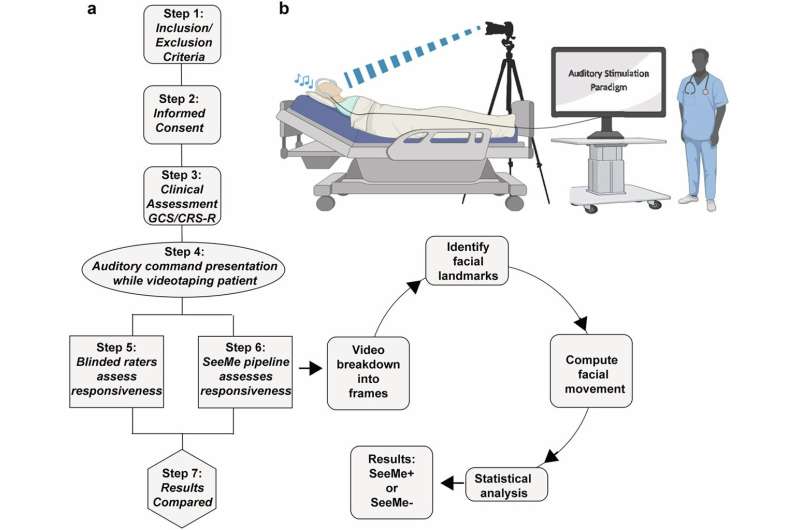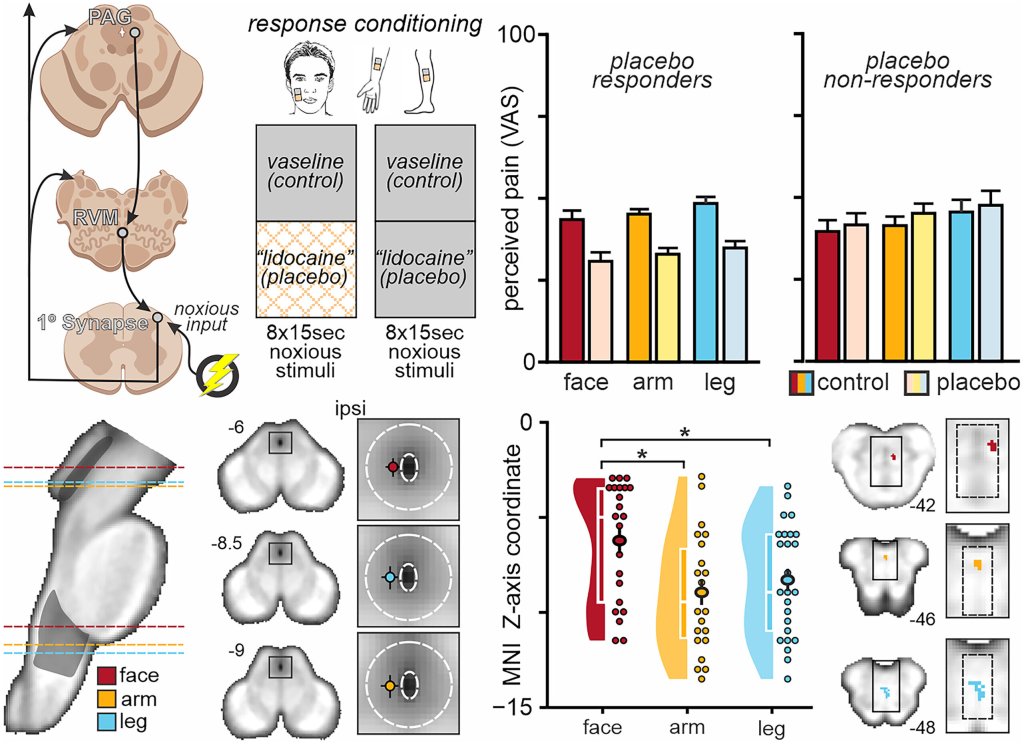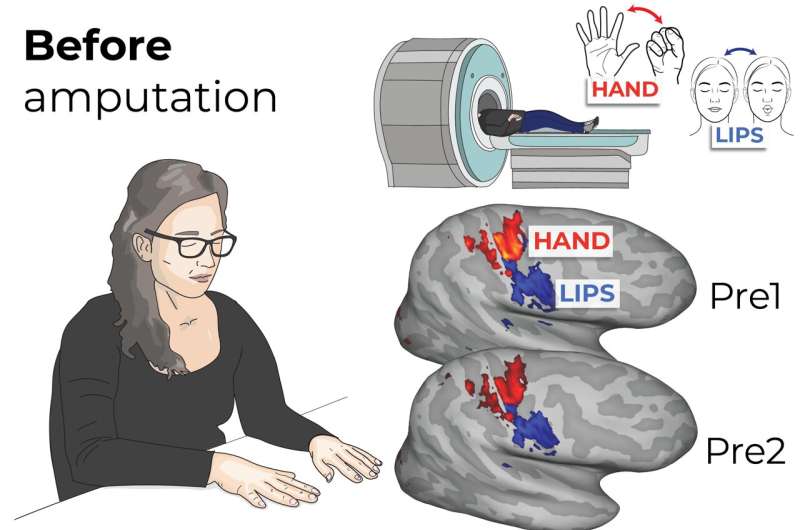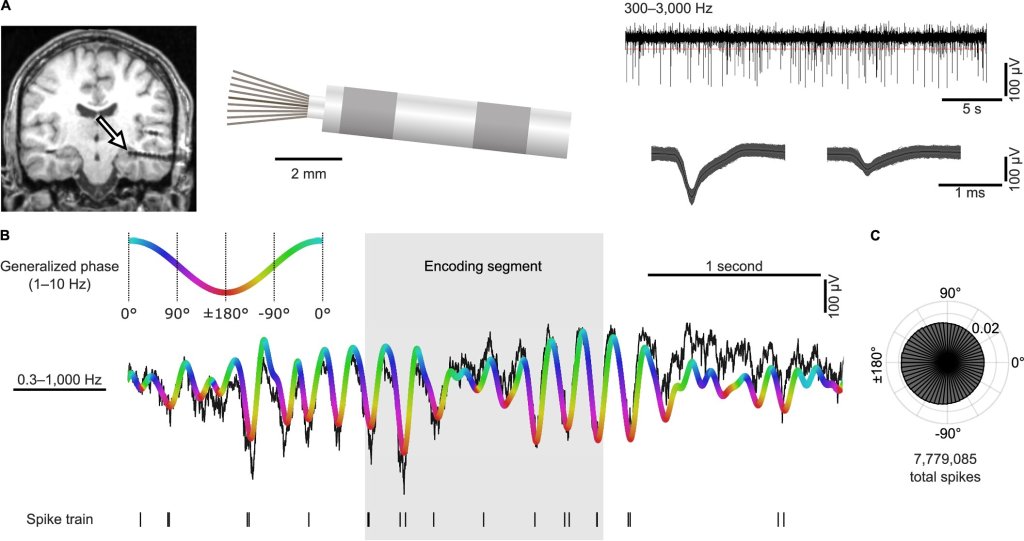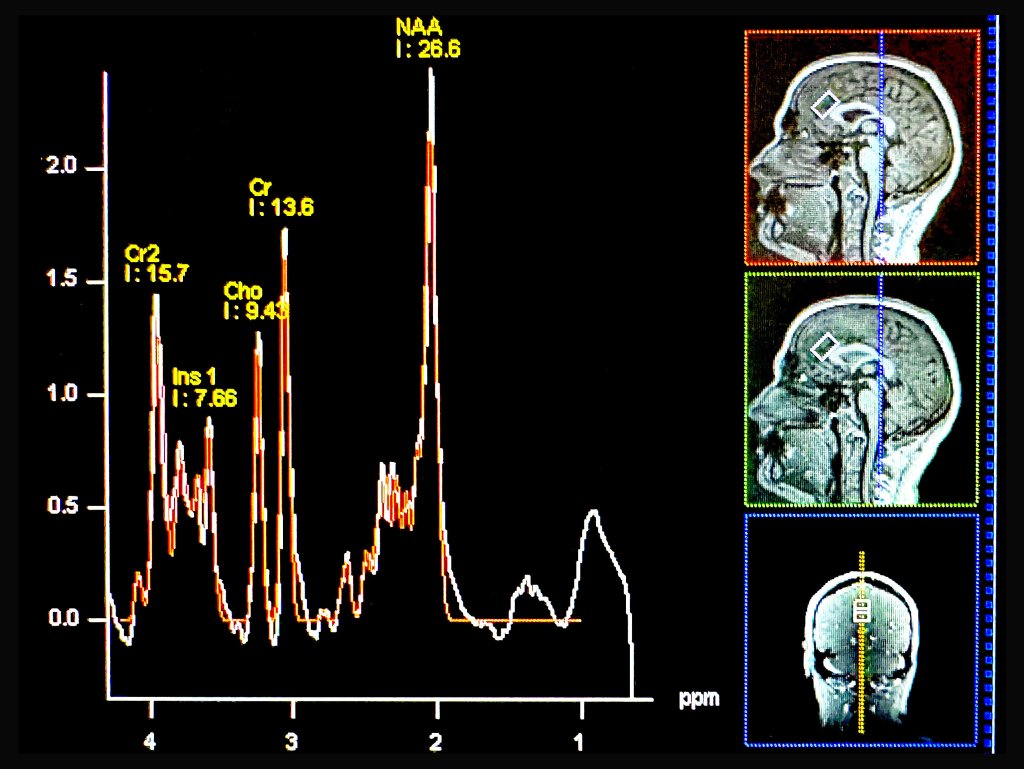
A new study shows that people with anxiety disorders tend to have lower levels of a chemical called choline in their brains compared to people without anxiety. Choline is a nutrient that plays an important role in brain function. It helps produce acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter involved in memory, mood regulation, and muscle control. It’s also a component of cell membranes, helping brain cells communicate efficiently.
Researchers have developed a highly sensitive diagnostic that predicts a person’s stage of dementia based on neurovascular and metabolic changes.
The way we speak in everyday conversation may hold important clues about brain health, according to a new study that found that subtle features of speech timing, such as pauses, fillers (‘uh,’ ‘um’) and word-finding difficulty, are strongly linked to executive function, the set of mental skills that support memory, planning and flexible thinking.
ADHD symptoms are influenced by socioeconomic factors in regions affected by conflict and resource limitations, a new study focusing on non-Western populations has found.
Infants born deaf or hard of hearing show adverse changes in how their brains organise and specialise, which can significantly affect their cognitive and linguistic development. However, recent studies indicate that timely exposure to sound and language, even in modified forms, can considerably help these children develop more normally and bridge the gap in their learning processes.
A research team has discovered extensive genetic links between neurological disorders like migraine, stroke and epilepsy, and psychiatric illnesses such as schizophrenia and depression.
New research reveals that trait shyness is linked to reduced spontaneous neural activity in the cerebellum, a brain region traditionally associated with motor control but increasingly recognised for its role in emotion and social cognition.
Scientists have developed the most detailed molecular map yet of how the brain develops and reacts to inflammation, revealing that disease processes can “reawaken” genes from early life.
A new brain decoding method called mind captioning can generate accurate text descriptions of what a person is seeing or recalling—without relying on the brain’s language system. Instead, it uses semantic features from vision-related brain activity and deep learning models to translate nonverbal thoughts into structured sentences.
Researchers have found that living in a socioeconomically deprived neighbourhood can harm brain health as early as midlife.
A new study reveals that autism symptom severity correlates with shared brain-connectivity patterns in children with autism or ADHD. Stronger autistic traits are linked to increased connectivity between frontoparietal and default-mode networks, which are vital for social cognition and executive functions.
Mayo Clinic researchers have developed a new tool that can estimate a person’s risk of developing memory and thinking problems associated with Alzheimer’s disease years before symptoms appear.
Using full-genome sequencing data from more than 347,000 individuals, researchers have quantified how much genetic variation explains human traits such as height, body mass index, fertility, and disease risk. The results show that genes account for roughly 30% of the variation between individuals, with higher estimates for traits like height and lower for fertility.
Finally this week, a large-scale study of more than 86,000 Europeans found that speaking multiple languages may help slow biological and cognitive aging.